您当前的位置:检测资讯 > 行业研究
嘉峪检测网 2022-02-24 23:07
前言导读
手术机器人是一种先进的医疗设备,借助微创伤手术及相关底层技术的发展而发明。手术机器人被用于在高于人类能力的微创伤手术领域中实现高于人类能力的对手术器械的精准操控。手术机器人通常由手术控制台、配备机械臂的手术车及视像系统组成。外科医生坐在手术控制台,观看由放置在患者体内腔镜传输的手术区域三维影像,并操控机械臂的移动,以及该机械臂附带的手术器械及腔镜。机械臂模拟人类的手臂,为外科医生提供一系列模拟人体手腕的动作,同时过滤人手本身的震颤。
机器人手术系统是集多项现代高科技手段于一体的综合体,其用途广泛,在临床上外科上有大量的应用。外科医生可以远离手术台操纵机器进行手术,完全不同于传统的手术概念,在世界微创外科领域是当之无愧的革命性外科手术工具。
市场分析
近年来,全球手术机器人进入迅猛发展阶段。数据显示,2015年的30亿美元增至2020年的83亿美元,复合年增长率为22.6%。预期全球手术机器人市场将继续快速增长,2026年达到336亿美元,自2020年起复合年增长率为26.2%。
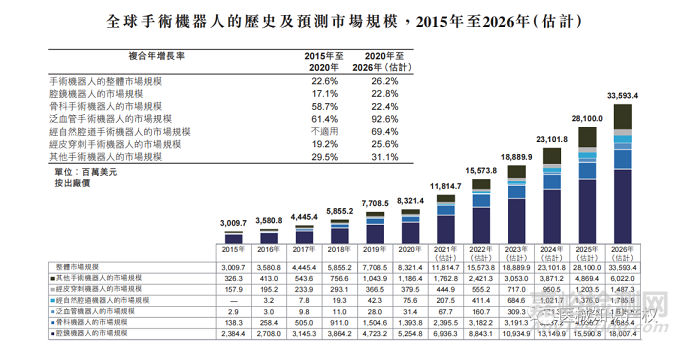
数据来源:弗若斯特沙利文
中国手术机器人市场仍处于早期发展阶段,但增长潜力巨大。2020年,中国手术机器人市场规模为425.3百万美元,预期市场将以44.3%的复合年增长率快速增长,2026年将达到3,840.2百万美元。
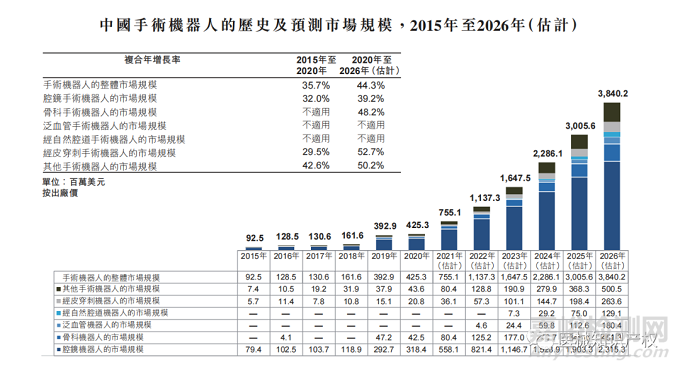
数据来源:弗若斯特沙利文
认识达芬奇
达芬奇(da Vinci)手术机器人由美国直观医疗公司制造生产。美国直观医疗公司创立于1995年,总部设在美国加州,是开发革命性微创手术仪器和技术的先驱。
1999年,第一台达芬奇手术机器人面世。2000年,达芬奇手术机器人正式成为第一个受FDA批准用于临床手术的机器人辅助腹腔镜手术系统。
20 多年来,达芬奇平台开创了手术室的新功能,改变了微创手术领域。通过超过 500 万次手术,Intuitive已成为手术机器人领域公认的领导者。
达芬奇手术机器人拥有三维高清视野,头发丝大小的血管在医生眼里也能清晰可见;达芬奇手术机器人的器械拥有可转腕的关节,比人手更加的小巧灵活;同时医生的手部动作可以准确无延时地重现在患者体内的器械上。
达芬奇机器人手术和开放手术或传统腹腔镜手术相比具有以下潜在优势:
更小创伤:极大减轻患者的疼痛。
更加精准:出血更少,并发症更少,感染风险降低。
更快恢复:住院时间更短,更快恢复正常生活,提高生活质量。减少误工费用和陪床费用。
专利分析
对于达芬奇机器人相关专利,其申请人主要聚集于Intuitive Surgical公司。笔者针对Intuitive Surgical所涉及的专利情况,进行了检索,其结果进行如下展示:
专利概览
下图给出Intuitive Surgical公司专利的申请和公开情况。可以清晰得知,可以清晰得知,其专利申请和授权情况主要集中于2005年后。出现这种情况的出现也和达芬奇机器人的更新换代有着密切关系,结合下文中所提及的技术脉络,也进一步预示其初始专利已陆陆续续到期或即将到期,这也给部分机器人赛道入场者提供了部分机会和技术借鉴。
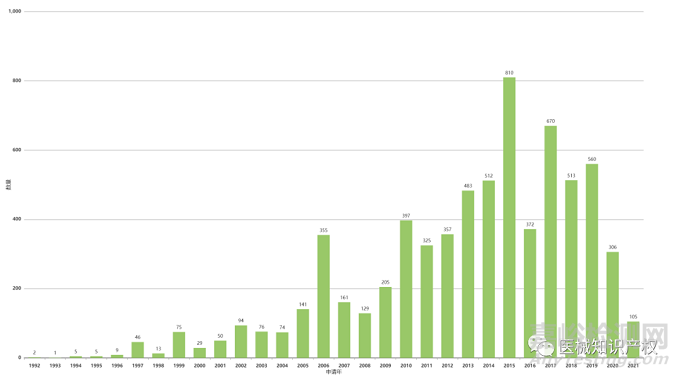
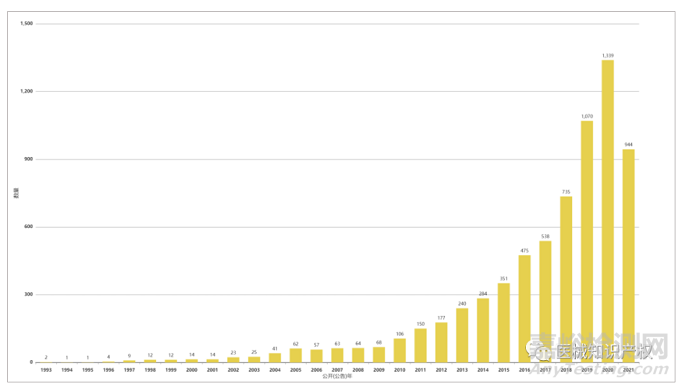
下面两幅图给出了达芬奇手术机器人专利布局情况,可以非常明确得到达芬奇手术机器人的专利地域布局情况,其专利申请目标国主要聚集于美国、欧洲、中国等区域性中心国家或地区,同样的,以2011年为界限,可以明确得知第一、二代达芬奇手术机器人和第三代达芬奇手术机器人的专利地域布局情况。
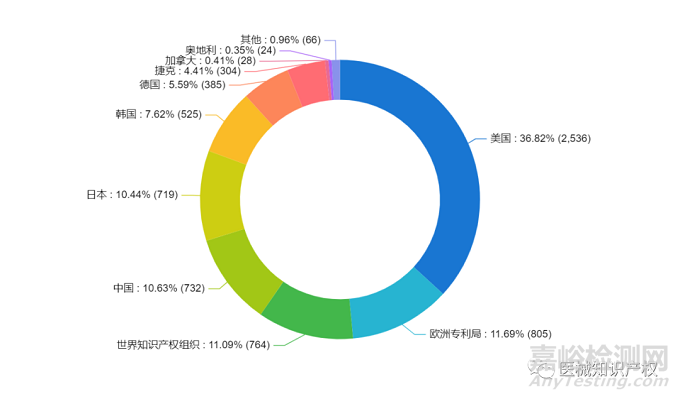
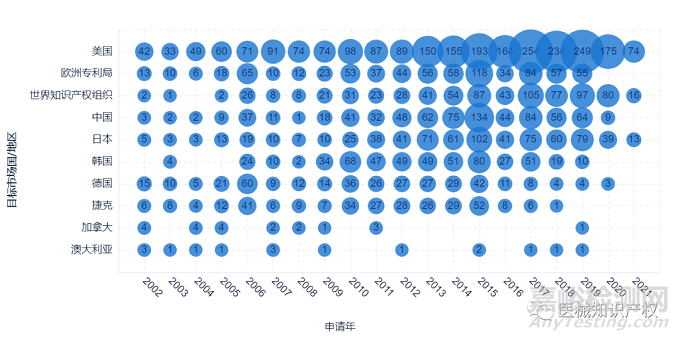
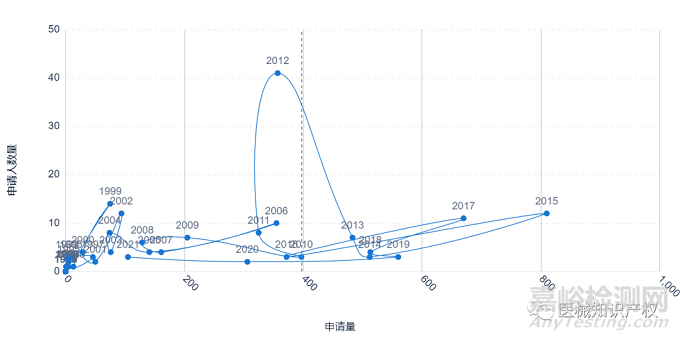
下图给出了Intuitive Surgical公司的技术生命周期情况。
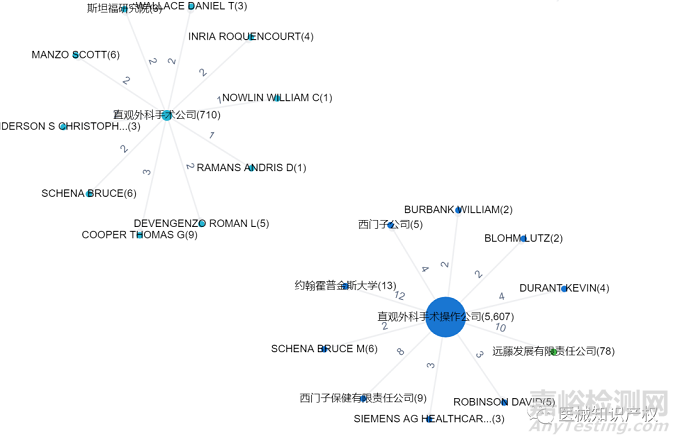
下图给出了Intuitive Surgical公司相关专利合作和布局的情况,可以非常清晰的看出,与各个医疗器械大厂一样,作为手术机器人龙头公司,Intuitive Surgical也与众多企业和科研院所展开的合作研究。
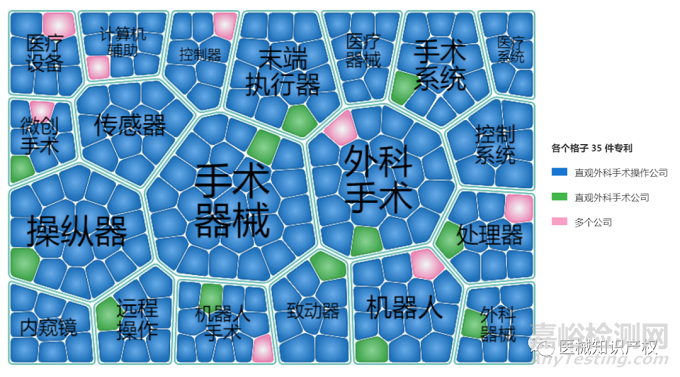
下图给出了Intuitive Surgical公司相关专利的专利地图情况,从该专利地图可以很明了的得到Intuitive Surgical公司相关专利的技术分支情况。
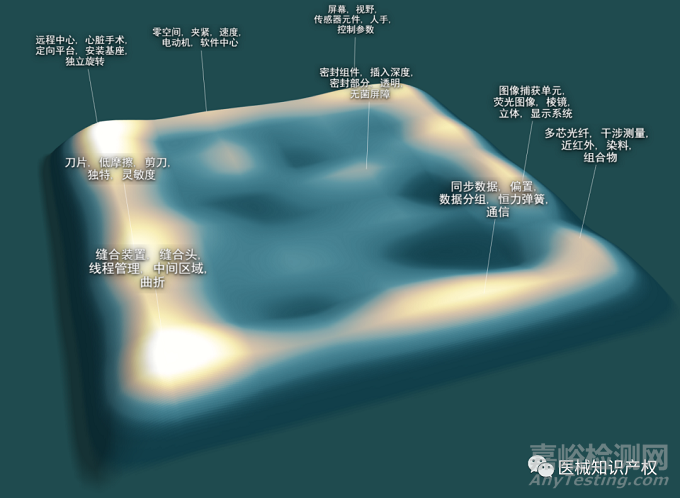
发展脉络
达芬奇系列手术机器人共经历的四代进化。
达芬奇机器人1996年推出了第一代,2006年推出的第二代机器人机械手臂活动范围更大了,允许医生在不离开控制台的情况下进行多图观察。
2009年在第二代机器人的基础上增加了双控制台、模拟控制器、术中荧光显影技术等功能,进而推出了第三代达芬奇Si系统。
第四代达芬奇Xi系统在2014年推出,灵活度、精准度、成像清晰度等方面有了质的提高,公司在2014年下半年还开发了远程观察和指导系统。

图片来源:Intuitive Surgical公司官网,Intuitive Surgical公司公告,中金公司研究部
机构组成
系统主要由三部分组成:医生操控台、床旁机械臂系统以及影像处理平台。主刀医生坐在控制台前控制器械和镜头;床旁机械臂系统是达芬奇手术机器人的操作部分,它放置在患者身旁为器械和镜头提供支撑,并实现医生的操作;影像处理系统,为患者身边的手术团队提供图像信息。
技术剖析
针对医生操控台、床旁机械臂系统以及影像处理平台三部分机构组成,笔者进行了详细的技术剖析,并且根据技术剖析结果,对达芬奇手术机器人和配套器械的相关专利根据类别分别进行了分类整理和分析,对于全部清单列表和分析内容,感兴趣的读者可以和笔者取得联系,这里笔者以第一代产品为例,对相关分析结果简单进行展示:
旁床机械臂系统
床旁机械臂系统分为直立部分及底座,连接摄影机及器械手臂,并与医师控制中心以电线连接,手术车台上的器械臂会随着医师操控主控制器而动作。每辆车台有一支摄影机臂,附有摄影机/内视镜组合,还有两支以上的器械臂, 支援ISI的全系列器械,并实现了多孔向单孔的改进,床旁机械臂系统的总结归纳由如下附图展示:

机械臂是达芬奇手术机器人非常重要的组成部分,对于机械臂相关的技术分解可以通过如下附图获悉:

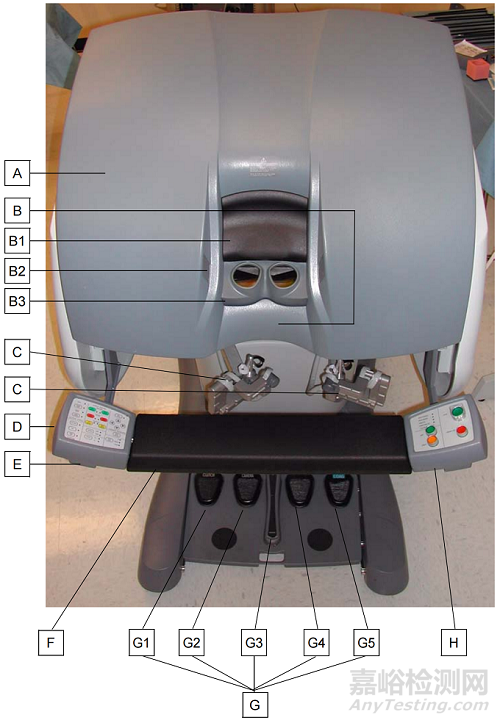
医生操作台
主刀医生坐在控制台中,位于手术室无菌区之外,使用双手(通过操作两个主控制器)及脚(通过脚踏板)来控制器械和一个三维高清内窥镜。正如在立体目镜中看到的那样,手术器械尖端与外科医生的双手同步运动。医生操作台的总结归纳由如下附图展示:
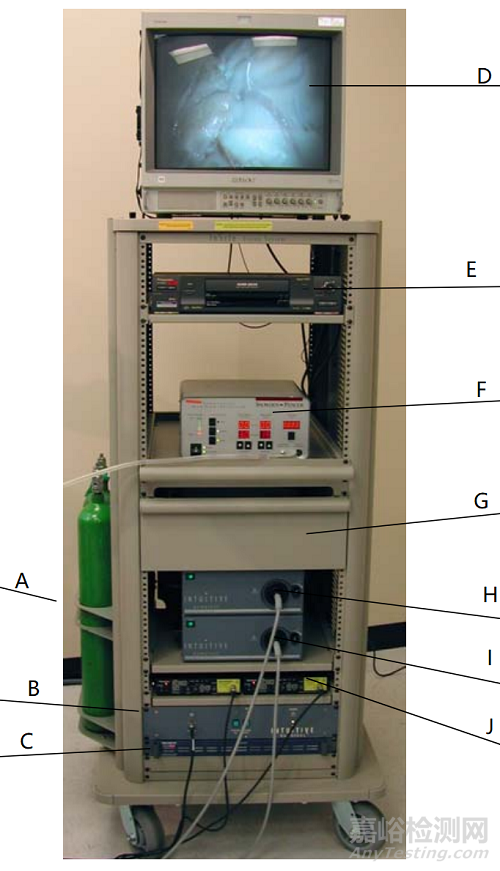
影像平台
影像平台内装有外科手术机器人的核心处理器以及图象处理设备,在手术过程中位于无菌区外,可由巡回护士操作,并可放置各类辅助手术设备。外科手术机器人的内窥镜为高分辨率三维(3D)镜头,对手术视野具有10倍以上的放大倍数,能为主刀医生带来患者体腔内三维立体高清影像,使主刀医生较普通腹腔镜手术更能把握操作距离,更能辨认解剖结构,提升了手术精确度。影像平台的总结归纳由如下附图展示:
专利解析
需要特别说明的是,对于达芬奇手术机器人,不论是从技术分解还是发展脉络,笔者均进行了详细研读和分析,形成了卓有成效的工作成果,基于篇幅原因,本篇文章择机进行展示,如若获取完整达芬奇手术机器人专利清单与分析报告可以与笔者取得联系,共同交流学习。
1
|
公开/公告号 |
US6905491B1 |
申请日 |
1997-05-16 |
|
|
发明名称 |
Apparatus for performing minimally invasive cardiac procedures with a robotic arm that has a passive joint and system which can decouple the robotic arm from the input device |
|||
|
解决的技术问题 |
There have been attempts to perform CABG procedures without opening the chest cavity. Minimally invasive procedures are conducted by inserting surgical instruments and an endoscope through small incision in the skin of the patient. Manipulating such instruments can be awkward, particularly when suturing a graft to a artery. It has been found that a high level of dexterity is required to accurately control the instruments. Additionally, human hands typically have at least a minimal amount of tremor. The tremor further increases the difficulty of performing minimal invasive cardiac procedures. It would be desirable to provide a system for effectively performing minimally invasive coronary artery bypass graft procedures.. |
|||
|
技术方案 |
A system for performing minimally invasive cardiac procedures. The system includes a pair of surgical instruments that are coupled to a pair of robotic arms. The instruments have end effectors that can be manipulated to hold and suture tissue. The robotic arms are coupled to a pair of master handles by a controller. The handles can be moved by the surgeon to produce a corresponding movement of the end effectors. The movement of the handles is scaled so that the end effectors have a corresponding movement that is different, typically smaller, than the movement performed by the hands of the surgeon. The scale factor is adjustable so that the surgeon can control the resolution of the end effector movement. The movement of the end effector can be controlled by an input button, so that the end effector only moves when the button is depressed by the surgeon. The input button allows the surgeon to adjust the position of the handles without moving the end effector, so that the handles can be moved to a more comfortable position. The robotic arm may contain a passive joint that provides an additional degree of freedom. Additionally, the system may include a disconnect input device that decouples the arm from an input device such as the handles. |
|||
|
相关附图 |
|
|||
2
|
公开/公告号 |
US6783524B2 |
申请日 |
2002-04-18 |
|
发明名称 |
Robotic surgical tool with ultrasound cauterizing and cutting instrument |
||
|
解决的技术问题 |
Surgical ultrasound instruments are generally capable of treating tissue with use of frictional heat produced by ultrasonic vibrations. For example, the heat may be use to cut and/or cauterize tissue. With many currently available instruments, tissue may first be grasped by an ultrasound surgical device and then ultrasound energy may be delivered to the tissue to cut, cauterize or the like. Ultrasound instruments provide advantages over other cutting and cauterizing systems, such as reduced collateral tissue damage, reduced risk of unwanted burns, and the like. Currently, however, ultrasound instruments for use with a robotic surgical system are not available. |
||
|
技术方案 |
A surgical instrument for enhancing robotic surgery generally includes an elongate shaft with an ultrasound probe, an end effector at the distal end of the shaft, and a base at the proximal end of the shaft. The end effector includes an ultrasound probe tip and the surgical instrument is generally configured for convenient positioning of the probe tip within a surgical site by a robotic surgical system. Ultrasound energy delivered by the probe tip may be used to cut, cauterize, or achieve various other desired effects on tissue at a surgical site. In various embodiments, the end effector also includes a gripper, for gripping tissue in cooperation with the ultrasound probe tip. The base is generally configured to removably couple the surgical instrument to a robotic surgical system and to transmit forces from the surgical system to the end effector, through the elongate shaft. A method for enhancing robotic surgery generally includes coupling the surgical instrument to a robotic surgical system, positioning the probe tip in contact with tissue at a surgical site, and delivering ultrasound energy to the tissue. |
||
|
相关附图 |
|
||
3
|
公开/公告号 |
US8100133B2 |
申请日 |
2006-06-28 |
|
发明名称 |
Indicator for tool state and communication in multi-arm robotic telesurgery and method of use |
||
|
解决的技术问题 |
While the new telesurgical systems, devices and methods have proven highly effective and advantageous, still further improvements would be desirable. In general, it would be desirable to provide improved robotic and/or surgical devices, systems and methods, particularly for performing telesurgical procedures. It may also be desirable to provide improved techniques for communication among the members of a telesurgical team, and for interfacing with the telesurgical apparatus so as to more fully take advantage of the capabilities of telesurgery to provide enhanced patient outcomes with improved efficiencies. It may be particularly beneficial to avoid unnecessary interruptions and distractions of a surgeon or other system operator, and to avoid delays and/or mistakes in the coordinated activities of a telesurgical team. |
||
|
技术方案 |
Medical and/or robotic devices, systems and methods can provide an indicator associated with each manipulator assembly of a multi-arm telerobotic or telesurgical system. The exemplary indicator comprises a multi-color light emitting diode (LED) mounted to a manipulator moving an associated surgical instrument, allowing the indicator to display any of a wide variety of signals. The invention may provide an additional user interface to facilitate communications between the telesurgical system and/or members of a telesurgical team. |
||
|
相关附图 |
|
||
4
|
公开/公告号 |
US8545515B2 |
申请日 |
2009-11-13 |
|
发明名称 |
Curved cannula surgical system |
||
|
解决的技术问题 |
To further reduce patient trauma and to retain the benefits of robotic surgical systems, surgeons have begun to carry out a surgical procedure to investigate or treat a patient's condition through a single incision through the skin. In some instances, such “single port access” surgeries have been performed with manual instruments or with existing surgical robotic systems. What is desired, therefore, are improved equipment and methods that enable surgeons to more effectively perform single port access surgeries, as compared with the use of existing equipment and methods. It is also desired to be able to easily modify existing robotic surgical systems that are typically used for multiple incision (multi-port) surgeries to perform such single port access surgeries. |
||
|
技术方案 |
A robotic surgical system is configured with rigid, curved cannulas that extend through the same opening into a patient's body. Surgical instruments with passively flexible shafts extend through the curved cannulas. The cannulas are oriented to direct the instruments towards a surgical site. Various port features that support the curved cannulas within the single opening are disclosed. Cannula support fixtures that support the cannulas during insertion into the single opening and mounting to robotic manipulators are disclosed. A teleoperation control system that moves the curved cannulas and their associated instruments in a manner that allows a surgeon to experience intuitive control is disclosed. |
||
|
相关附图 |
|
||
5
|
公开/公告号 |
US9358074B2 |
申请日 |
2013-05-31 |
|
发明名称 |
Multi-port surgical robotic system architecture |
||
|
解决的技术问题 |
A robotic surgery system includes an orienting platform, a support linkage movably supporting the orienting platform, a plurality of surgical instrument manipulators, and a plurality of set-up linkages. Each of the manipulators includes an instrument holder and is operable to rotate the instrument holder around a remote center of manipulation (RC). At least one of the manipulators includes a reorientation mechanism that when actuated moves the attached manipulator through a motion that maintains the associated RC in a fixed position. |
||
|
技术方案 |
While the new telesurgical systems and devices have proven highly effective and advantageous, still further improvements are desirable. In general, improved minimally invasive robotic surgery systems are desirable. It would be particularly beneficial if these improved technologies enhanced the efficiency and ease of use of robotic surgical systems. For example, it would be particularly beneficial to increase maneuverability, improve space utilization in an operating room, provide a faster and easier set-up, inhibit collisions between robotic devices during use, and/or reduce the mechanical complexity and size of these new surgical systems. |
||
|
相关附图 |
|
||
结 语
作为最成功的手术机器人,达芬奇医生只需要通过操作机械臂来完成手术,还能过滤掉手术者操作过程中手部的颤动,再加上高倍数的3D高清视野,令正常组织和肿瘤间的界限更清晰,能最大程度避免手术过程中对周围正常组织的损伤,确实在医疗器械领域开辟了一个崭新的时代。
诚如领域内人士共同认识的那样,手术机器人逐渐赢得市场追捧,站上了智能精细化发展、医保政策利好的快车道,随着达芬奇手术机器人核心专利的逐步过期,全球以及国内各大手术机器人厂商也必会将达芬奇机器人作为重要的标杆和对照,联动产学研医生多方力量,不断创新,推动中国手术机器人行业更智能化、精准化、微创化的发展,相关知识产权问题也必将会成为各大手术机器人厂商的研究重点课题,后续相关产品的的研发和专利事务值得持续关注。

来源:医械知识产权


