目 录
Pyrometry高温测量
1SCOPE 范围
2 REFERENCES参照
2.1 Applicable Documents适用文件
2.2 Definitions定义
3TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS技术要求
3.1 Temperature Sensors温度传感器
3.2 Instrumentation仪表化
3.3 Thermal Processing Equipment热处理设备
3.4 System Accuracy Test系统精度测试
3.5 Temperature Uniformity Surveys (TUS)温度均匀性测量
3.6 Laboratory Furnaces实验室炉
3.7 Records记录
3.8 Rounding修约
4QUALITY ASSURANCE PROVISIONS质量保证条款
5PREPARATION FOR DELIVERY交货准备
6 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT确认
7 REJECTIONS拒绝
8NOTES注释
AEROSPACE MATERIAL SPECIFICATION 航空航天工业材料规范
AMS2750™ REV. H Issued 1980-04 Revised 2024-07 Superseding AMS2750G
Pyrometry高温测量
AMS2750H results from a Two-Year Review and update of this specification with changes to Definitions (see 2.4.21, 2.4.25, 2.4.36, 2.4.47, and 2.4.84; General Sensor Requirements (see Table 3); Sensor Calibration (see 3.1.4.6 and Table 5); SAT and TUS Sensor Reuse (see 3.1.7.4 and 3.1.7.5); Base Metal Load Sensors (see 3.1.10.3); General instrumentation Requirements (see 3.2.1.4.1, 3.2.1.5, and Table 7); Control, Recording, and Over-Temperature instruments (see 3.2.3.4, 3.2.3.5, 3.2.3.16, and 3.2.3.18); instrumentation Calibration Results and Records (see 3.2.5.1); General instrument Correction and Modification Offset Requirements (see 3.2.6.1.2 and 3.2.6.1.8); Thermal Processing Equipment (see 3.3.7); General SAT Requirements (see Table 11, Table 12, and 3.4.1.2.1); Performing an SAT (see 3.4.2.2); Alternate SAT Frequency (see 3.4.8.3); SAT Waiver (see 3.4.9.6.3); SAT Difference Pass/Fail Requirements (see 3.4.10.4); Comparison SAT (see 3.4.11.1.e);Parts furnace class, instrument type, and TUS internal (see Table 15); Raw material furnace class, instrument type, and TUS internal (see Table 16); Initial TUS Temperatures (see 3.5.2.4); TUS Requirements for Batch Furnaces, Salt Baths, Controlled Temperature Liquid Baths and Fluidized Bed Furnaces (Excluding Controlled Temperature Quench Baths) (see Table 17); TUS Data Collection (see 3.5.10.1 and 3.5.10.2); Relocation of Hot or Cold Recording Sensors for Type A and C instrumentation (see 3.5.15.2): Radiation Survey (see 3.5.17, 3.5.17.1, and 3.5.17.2); TUS interval Deviations (see 3.5.18); Rounding (see 3.8); and Quality Assurance Provisions (see 4.2, 4.4, and Table 22). Deleted Zener Voltage Reference (was 3.5.87).
1、 Scope 范围
1.1 This specification covers pyrometric requirements for equipment used for the thermal processing of metallic materials. Specifically, it covers temperature sensors, instrumentation, thermal processing equipment, correction factors and instrument offsets, system accuracy tests, and temperature uniformity surveys. These are necessary to ensure that parts or raw materials are heat treated in accordance with the applicable specification(s).
本规范涵盖了用于金属材料热加工的设备的热测量要求。具体而言,它涵盖了温度传感器、仪表仪表、热处理设备、校正因子和仪表偏移、系统精度测试和温度均匀性测量。这些是必要的,以确保零件或原材料按照适用的规范进行热处理。
1.2 This specification may be used in other non-heat treating applications when specified.
如果有规定,本规范可用于其他非热处理应用。
1.3 This specification is not applicable to heating or to intermediate thermal processing unless otherwise specified.
除非另有规定,本规范不适用于加热或中间热处理。
1.4 This specification applies to laboratory furnaces to the extent specified in 3.6.
本规范在3.6规定的范围内适用于实验室熔炉。
2、 Applicable Documents 适用文件
The issue of the following documents in effect on the date of the purchase order form a part of this specification to the extent specified herein. The supplier may work to a subsequent revision of a document unless a specific document issue is specified. When the referenced document has been cancelled and no superseding document has been specified, the last published issue of that document shall apply.
在采购订单日期生效的下列文件在此规定的范围内构成本规范的一部分。供应商可以进行文件的后续修订,除非规定了具体的文件问题。当被引用的文件被取消且没有指定替代文件时,该文件的最后一次发布应适用。
2.1 SAE Publications出版物
Available from SAE International, 400 Commonwealth Drive, Warrendale, PA 15096-0001, Tel: 877-606-7323 (inside USA and Canada) or +1 724-776-4970 (outside USA), www.sae.org.
AS7766 Terms Used in Aerospace Metals Specifications航空航天金属规范条款
2.2 ASTM Publications出版物
Available from ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, P.O. Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959,Tel: 610-832-9585, www.astm.org.
ASTM E29 Using Significant Digits in Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications在测试数据中使用有效数字来确定与规范的一致性
ASTM E207 Standard Test Method for Thermal EMF Test of Single Thermoelement Materials by Comparison with a Reference Thermoelement of Similar EMF-Temperature Properties通过与具有相似电动势温度特性的参考热敏元件的比较对单个热敏元件进行热敏电动势试验的标准试验方法
ASTM E220 Calibration of Thermocouples by Comparison Techniques用比较技术校准热电偶
ASTM E230 Temperature-Electromotive Force (EMF) Tables for Standardized Thermocouples标准热电偶温度-电动势(EMF)表
ASTM E608 Mineral-Insulated, Metal-Sheathed Base Metal Thermocouples矿物绝缘,金属护套贱金属热电偶
ASTM E1137 Industrial Platinum Resistance Thermometers工业铂电阻温度计
ASTM E1751 Standard Guide for Temperature Electromotive Force (emf) Tables for Non-Letter Designated Thermocouple Combinations非字母指定热电偶组合的温度电动势(emf)表的标准指南
ASTM MNL7 Presentation of Data and Control Chart Analysis数据展示和控制图分析
ASTM MNL12 Use of Thermocouples in Temperature Measurement在温度测量中热电偶的使用
2.3 IEC Publications出版物
Available from IEC Central Office, 3, rue de Varembe, P.O. Box 131, CH-1211 Geneva 20, Switzerland,
Tel: +41 22 919 02 11, www.iec.ch.
IEC 60751 Industrial Platinum Resistance Thermometers and Platinum Temperature Sensors工业铂电阻温度计和铂温度传感器
ISO/IEC 17025 General Requirements for the Competence of Testing and Calibration Laboratories检测和校准实验室能力的一般要求
2.4 Definitions定义
Terms used in AMS2750 are defined in AS7766 and as follows:
AMS2750中使用的术语在AS7766中定义如下:
2.4.1 Accuracy精度/准确度
The maximum deviation of the instrument or sensor being tested from the values of a traceable standard. 被测仪表或传感器与可追溯标准值的最大偏差。
2.4.2 Adjustment调整
Any change to an instrument’s parameters仪表参数的任何改变。
2.4.3 Autoclave高压釜
An oven capable of operating at pressures higher than atmospheric pressure (nominally 760 mm Hg), commonly used in the processing of materials. It may be pressurized with steam, compressed air, or inert gas.
一种能在高于大气压的压力(名义上760毫米汞柱)下工作的烘箱,通常用于材料加工。它可以用蒸汽、压缩空气或惰性气体加压。
2.4.4 Base Metal Sensor廉金属传感器
Sensor whose thermoelements are composed primarily of base metals and their alloys. Examples of base metal sensors include Types E, J, K, N, M, and T.
热元件主要由廉金属及其合金组成的传感器。基本金属传感器的例子包括类型E, J, K, N, M和T。
2.4.5 Batch Furnace周期炉
A furnace where parts or raw materialare stationary during the soak.
在浸泡过程中零件或原材料静止的炉。
Note: Some batch furnaces may oscillate material within a stationary work zone.
注意:有些间歇炉可能会在固定的工作区域内使物料摆动。
2.4.6 Bias Or Input Shift偏倚或输入偏移
The act of making an adjustment to an instrument to add, remove, or alter an offset.
对仪表进行调整以增加、删除或改变偏移量的行为
2.4.7 Bimonthly两月一次
See Frequency看到频率
2.4.8 Biweekly两周一次
See Frequency看到频率
2.4.9 Calibration校准
An assessment of the accuracy of a sensor or an instrument to a traceable standard sensor and/or field test or standard instrument, based on one or more measurements, and potentially adjusting an instrument and/or compiling a deviation chart for a sensor or instrument in order to ensure compliance with requirements.
对传感器或仪表对可追踪的标准传感器和/或现场测试或标准仪表的精度的评估,基于一次或多次测量,并可能调整仪表和/或编制传感器或仪表的偏差图,以确保符合要求。
2.4.10 Continuous Furnace连续炉
A furnace where parts or raw material are conveyed continuously or semi-continuously from the charge area to the discharge area. Examples include: bump furnace, shaker furnace, belt furnace, roller furnace, and rotary hearth furnace.
一种连续或半连续地将零件或原料从上料区输送到下料区的炉子。包括鼓式炉、摇床炉、带式炉、辊式炉、转底炉。
2.4.11 Control Instrument控制仪表
An instrument connected to a control sensor used to control the temperature of thermal processing equipment. The instrument may or may not also record temperature data.
一种连接到控制传感器的仪表,用于控制热加工设备的温度。仪表可能也可能不记录温度数据
2.4.12 Control Sensor控制传感器
A sensor connected to a control instrument on thermal processing equipment, the temperature of which may or may not be recorded.
一种与热加工设备上的控制仪表相连的传感器,其温度可以记录也可以不记录。
2.4.13 Control Zone控制区
A portion of the working zone in thermal processing equipment having a separate sensor, instrument, and heating or cooling system to control its temperature. This portion of the thermal processing equipment is independently controlled.
热加工设备中工作区域的一部分,具有单独的传感器、仪表和加热或冷却系统来控制其温度。这部分热加工设备是独立控制的。
2.4.14 Controlled Temperature Liquid Bath控温液浴
A furnace containing a liquid that is heated to the desired heat treat temperature. Parts and raw material are normally immersed in the liquid.
一种包含液体的炉,该液体被加热到所需的热处理温度。零件和原料通常浸泡在液体中。
2.4.15 Controller控制器
A digital, or mechanical device that controls the temperature of thermal processing equipment (e.g., furnace control instruments, quench mechanical thermostat, freezer pressure controls, etc.).
一种控制热加工设备温度的数字或机械装置(如炉膛控制仪表、淬火机械恒温器、冷冻压力控制装置等)。
2.4.16 Correction Factor校正系数
The number of degrees, determined from the most recent calibration, that must be added to, or subtracted from, the temperature reading of a sensor, or an instrument, or a combination thereof (system) to obtain true temperature. The correction factors of sensors and instruments are usually kept separately and added together algebraically when a combination is used. Correction factor is the algebraic opposite of deviation (error)
在传感器、仪表或其组合(系统)的温度读数上加上或减去最近的校准值以获得真实温度的度数。传感器和仪表的校正系数通常分开保存,当使用组合时用代数法加在一起。修正因子是偏差(误差)的代数反义词。
2.4.17 Data Acquisition System数据采集系统
An instrument system used to automatically collect and store process data as an electronic record; for example, a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC).
一种用于自动收集和存储过程数据的电子记录的仪表系统,如可编程逻辑控制器(PLC)。
2.4.18 Deviation/Error偏离/误差
In the context of this specification, the difference between the uncorrected indicated temperature and the true temperature (Indicated temperature - True temperature = Deviation/error).
在本规范中,未校正的指示温度与真实温度之间的差值(指示温度-真实温度=偏差/误差)。
2.4.19 Digital Instrument数字式仪表
An instrument that records process measurements in a digital (numeric) display format or an instrument that prints both the scale (graph) and trend line simultaneously. Examples include recorders with pre-printed scales and printed tabular data meeting 3.2.1.4 data collection intervals and recorders that create scales and trend line or tabular data and also display indicated temperature.
一种以数字(数字)显示格式记录过程测量的仪表,或同时打印刻度(图形)和趋势线的仪表。例如:带有预打印刻度和打印表格数据的记录仪3.2.1.4数据收集间隔,以及创建刻度和趋势线或表格数据并显示指示温度的记录仪。
2.4.20 Electronic Record电子记录
Any combination of text, graphics, data, audio, pictorial, or other information representation in digital form that is created,modified, maintained, archived, retrieved, or distributed by a computer system.
由计算机系统以数字形式创建、修改、维护、归档、检索或分发的任何文本、图形、数据、音频、图形或其他信息表示形式的组合。
2.4.21 Expendable Sensors易耗型传感器
Sensors where any portion of the thermoelements are exposed to the thermal process equipment environment. Sensors with braided fiberglass insulation or plastic insulation are not designed to be inserted into a closed protection tube as the confined space causes drift when the additives (e.g., Teflon, color dies, and other chemicals) burn off. Therefore, these sensors are expendable even when installed into a closed protection tube.
热敏元件的任何部分暴露在热加工设备环境中的传感器。具有编织玻璃纤维绝缘或塑料绝缘的传感器不被设计为插入封闭的保护管,因为当添加剂(例如,特氟龙,色模和其他化学品)燃烧时,密闭空间会导致漂移。因此,即使安装在封闭的保护管中,这些传感器也是消耗性的。
2.4.22 Extension Wire延长导线
Wire used for transmitting an unmodified signal from the sensor to the instrumentation system. Wire is generally of the same sensor type, except for some sensor types that allow compensated extension wire.
用于从传感器向仪表系统传送未经修改的信号的导线。电线通常是相同的传感器类型,除了一些传感器类型允许补偿延长线。
2.4.23 Field Test Instrument现场测试仪表
An instrument meeting the requirements of Table 7 that has calibration traceable to a secondary standard instrument or better and is used to conduct on-site calibrations or tests of thermal processing equipment.
一种符合表7要求,校准可溯源至二级标准仪表或以上,用于对热加工设备进行现场校准或测试的仪表。
2.4.24 Fluidized Bed Furnace流态床炉
A furnace that contains a medium that becomes suspended or fluidized due to atmosphere gas or products of combustion passing upward through the medium. Parts and raw material are normally immersed in the fluidized medium.
由于大气气体或燃烧产物向上通过介质而使介质悬浮或流化的熔炉。零件和原料通常浸泡在流态化介质中。
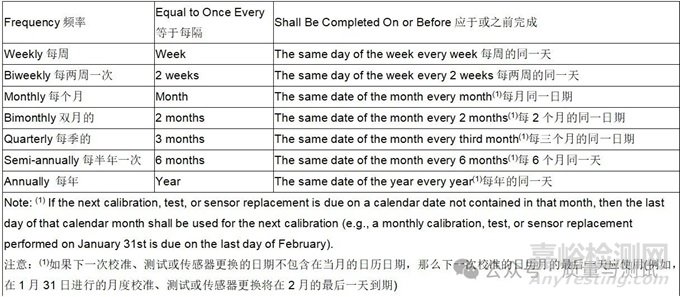
2.4.25 Frequency (Interval)频率(间隔)
The calendar days from the day/date a calibrations, tests, or sensor replacement was performed and the next day/date a calibration, test, or sensor replacement is due (inclusive). In the context of this specification, the following shall apply:
从执行校准、测试或传感器更换之日/日期起的日历天,到下一个校准、测试或传感器更换之日/日期(含)。在本规范的范围内,应适用以下规定:
2.4.26 Furnace炉子
Equipment used for the thermal processing of parts or raw material. The terms “furnace” and “oven” can be used interchangeably用于零件或原材料热加工的设备。炉子和烘箱这两个术语可以互换使用。
2.4.27 Heat Sink测温试块
A mass of material with an embedded sensor or sensors which supplies temperature data of that mass to recording instruments一块材料嵌入一个或多个传感器,可向记录仪提供温度数据。
2.4.28 Interval间隔
See Frequency见频率
2.4.29 Laboratory Thermal Processing Equipment实验室热加工设备
Equipment used exclusively for thermal processing of samples, specimens, or test parts as required by materials and processing specifications.
据材料和加工规范的要求,专用于试样、试样或试验件的热加工设备
2.4.30 Load Sensor载荷传感器
Sensor that is attached to, or in contact with, parts or raw material, a representation of parts or raw material, or is buried in the load of parts (e.g., fasteners) or raw material and which supplies temperature data of the parts or raw material to recording instruments that may be used to control the sequence of the production process, such as the start of soak.
附在工件或原材料上或与之接触的传感器,工件或原材料的表示,或埋藏在部件(如紧固件)或原材料的负载中,并向记录仪表提供工件或原材料的温度数据,记录仪表可能用于控制生产过程的顺序,如浸泡的开始。
2.4.31 Material Producer (Metallic)金属制品
The manufacturer of raw material as stated in 2.4.53原料制造商如2.4.53所述。
2.4.32 Maximum Permitted Error最大允许误差
A tolerance band for the thermal electric response expressed in degrees or percentages. Maximum permitted error provides a tolerance within which various types of sensors shall conform to standard sensor reference tables, or equivalent.
用度数或百分比表示的热电响应的容限。最大允许误差提供了一个公差,在此范围内各种类型的传感器应符合标准传感器参考表,或等效。
2.4.33 Measuring Junction测量接点
The location of a sensor where the wire elements are joined together to complete a measurement circuit, which is used to measure an unknown temperature. Also called the “hot junction”.
一个传感器的位置,在那里电线元件连接在一起,以完成一个测量电路,用来测量一个未知的温度。也叫热接点。
2.4.34 Multiple Zoned Furnaces多个分区炉
Furnaces with multiple separate temperature control zones. 具有多个独立温度控制区域的熔炉。
2.4.35 Noble Metal Sensor贵金属传感器
Sensor whose thermoelements are composed primarily of noble metals (e.g., platinum/platinum-rhodium) and their alloys. Examples of noble metal sensors include Types R, S, B, and RTDs.
热敏元件主要由贵金属(如铂/铂铑)及其合金组成的传感器。贵金属传感器的例子包括类型R, S, B和RTD。
2.4.36 Nonexpendable Sensors耐久型传感器
Sensors having no portion of the thermoelements exposed to the thermal process equipment environment. Sensors with ceramic insulators over bare wire inserted into a closed protection tube to prevent exposure to the thermal process equipment environment are considered nonexpendable sensors.
传感器的热敏元件部分不暴露在热处理设备环境中。
陶瓷绝缘体在裸线上插入封闭的保护管以防止暴露在热处理设备环境中的传感器被认为是非消耗性传感器。
2.4.37 Non-Metallic Materials非金属材料
In the context of this specification, this term refers to the curing of composite or adhesive bonded assemblies that are typically processed in autoclaves, air ovens, or heated presses.
在本规范中,这个术语指的是复合材料或粘合剂粘合组件的固化,这些组件通常在高压釜、烘箱或加热压力机中加工。
2.4.38 Offset补偿
Any manual or electronic adjustment to an instrument made to alter either the desired set point or the displayed value of the instrument’s calculated temperature. Manufacturer specific terminology may also include “bias”, “input shift”, etc.
对仪表进行的任何手动或电子调整,以改变所需的设定点或仪表计算温度的显示值。制造商专用术语还可能包括偏置、输入偏移等
2.4.38.1 Correction Offset修正补偿
Manual or electronic adjustment of an instrument to compensate for known errors of the measurement system (instrument, extension wire/connectors, sensor) to make the system more accurate.
手动或电子调整仪表,以补偿测量系统的已知误差(仪表,延长线/连接器,传感器),使系统更准确。
2.4.38.2 Modification Offset修改补偿
Manual or electronic adjustment of an instrument to compensate for known conditions such as, but not limited to, a skewed TUS result or control thermocouple placement in a retort or muffle.
手动或电子调节仪表,以补偿已知条件,如(但不限于)弯曲的TUS结果或控制热电偶在蒸馏器或消声器的位置。
2.4.39 Oven烘箱
Equipment used for the thermal processing of materials and parts. The terms “oven” and “furnace” can be used interchangeably.
用于材料和零件热加工的设备。术语oven和furnace可以互换使用。
2.4.40 Over-Temperature Instrumentation超温测温仪表
An independent sensor and instrument combination installed in the thermal processing equipment that is used to detect any over-temperature occurrence and generate an alarm and/or cut back or shut down heat input. The purpose for this control is to protect parts or raw material and/or the thermal processing equipment from overheating. Integrated control/recording/over-temperature instruments are permitted provided it can be demonstrated that the over-temperature instrument/module of an integrated system is separated from the furnace control/recording system.
一个独立的传感器和仪表组合安装在热加工设备中,用于检测任何超温事件并产生报警和/或削减或关闭热输入。这种控制的目的是防止零件或原材料和/或热处理设备过热。允许集成控制/记录/超温仪表,只要能证明集成系统的超温仪表/模块与炉膛控制/记录系统分离。
2.4.41 Parts工件
Usually identified by a part number, produced from raw material in accordance with the requirements of an engineering drawing and are usually tested by non-destructive techniques only. Parts are heat treated, by or for a fabricator, in accordance with a drawing, purchase order, fabrication order, or heat-treat specification.
通常由零件编号标识,由原材料按照工程图纸的要求生产,通常只采用无损检测技术。根据图纸、采购订单、制造订单或热处理规范,由制造商或为其进行热处理。
NOTE: The cognizant engineering organization has the authority to assign the terms “parts” or “raw material.” 注:认可的工程组织有权指定术语“部件”或“原材料”
2.4.42 Preventive Maintenance Program or PM Program预防性维护计划或PM计划
A program for evaluating, taking corrective action as required, and documenting the condition of items that have potential to adversely affect thermal processing equipment conformance to any requirement of this specification. Frequency of PM checks is established based on experience to ensure that no major problems occur between periodic PMs.
对可能对热加工设备符合本规范任何要求产生不利影响的项目进行评估、采取必要的纠正措施和记录的程序。根据经验建立PM检查的频率,以确保在定期PM之间不发生重大问题。
2.2.43 Primary Standard Instrument一级标准器
An instrument that is calibrated directly against a reference standard instrument and meeting the requirements of Table 7接对照参考标准仪表进行校正并符合表7要求的仪表。
2.4.44 Primary Standard Sensor一级标准传感器
Sensor calibrated directly against a reference standard and meeting the requirements of Table 1.
根据参考标准直接校准的传感器,并满足表1的要求。
2.4.45 Process Chart Recorder流程图表记录器
See Recording Instrument见记录仪表
2.4.46 Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)可编程控制器
A digital computer control system that continuously monitors the state of input devices and makes decisions based upon a programmed input (recipe) to control the state of output devices.
一种数字计算机控制系统,它不断地监视输入设备的状态,并根据程序输入(配方)作出决定来控制输出设备的状态。
2.4.47 Qualified Operating Temperature Range合格的工作温度范围
The nominal set point temperature range of thermal processing equipment where temperature uniformity has been tested within a qualified work zone and foundto be compliant with required tolerances (i.e., qualified operating temperature range = nominal range of TUS set points).
热加工设备的标称设定点温度范围,在合格的工作区域内测试温度均匀性,并找到符合要求的公差(即合格的工作温度范围= TUS设定点的标称范围)。
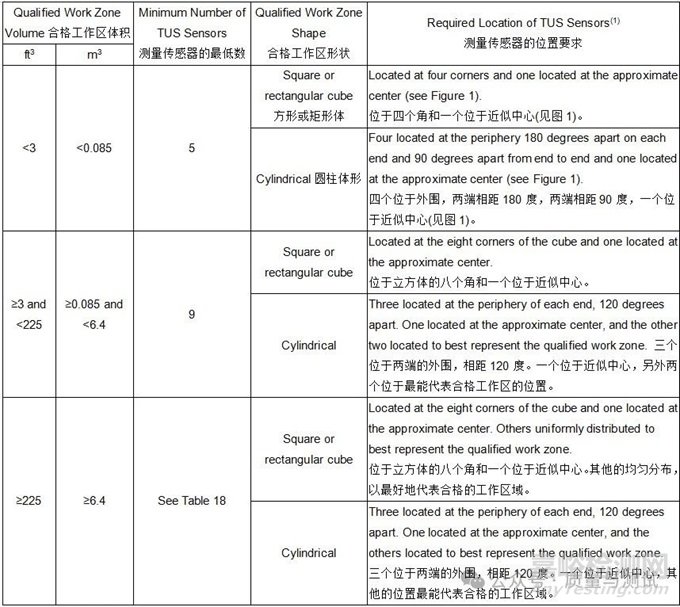
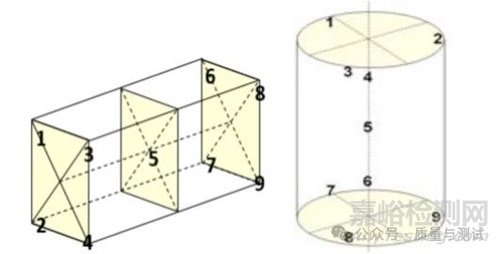
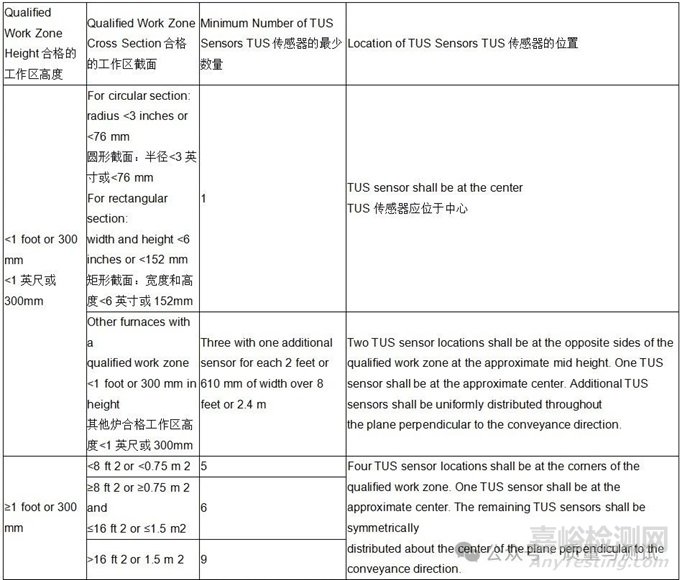
2.4.48 Qualified Work Zone合格的工作区域
The portion of a thermal processing equipment volume where temperature variation conforms to the required uniformity tolerance within the qualified operating temperature range as defined by the placement of sensors during the most recent temperature uniformity survey.
在最近的温度均匀性调查中,传感器的放置确定了合格的工作温度范围内,温度变化符合所需均匀性公差的热加工设备体积的一部分
2.4.49 Quality Organization Approval质量组织批准
Objective evidence of review and acceptance or rejection of a calibration or test as defined by a documented process within the user’s quality system which also defines any delegation of this approval.
用户质量体系文件化过程中定义的对校准或测试的评审、接受或拒绝的客观证据,也定义了该批准的任何授权
2.4.50 Quench System淬火系统
A system that provides rapid cooling, usually accomplished using oil, water, water/polymer mixtures, or gaseous mediums.
一种提供快速冷却的系统,通常使用油、水、水/聚合物混合物或气体介质。
2.4.51 Radiation Survey辐射测量
Initial survey of aluminum alloy thermal processing equipment used above 800 ℉ or 427 ℃ when the heat source (e.g., electrical elements or gas tubes) is exposed to the qualified work zone or only separated by a metal baffle.
当热源(如电气元件或气管)暴露在合格的工作区域或仅用金属挡板隔开时,对使用在800℉或427℃以上的铝合金热加工设备的初步测量。
2.4.52 Radiation Survey Sensor辐射测量传感器
A TUS sensor, typically base metal (Types E, J, K, N, M, and T) sensor, used in conjunction with a test panel for determining the heating characteristics of furnaces used for solution heat treating aluminum alloys.
TUS传感器,通常为贱金属(E、J、K、N、M和T型)传感器,与测试板一起用于确定铝合金固溶热处理炉的加热特性。
2.4.53 Raw Material原料
Usually includes, but is not limited to, such items as sheet, plate, wire, rod, bar, forgings, castings, and extrusions. Raw material is usually identified by a heat or lot number and is usually tested destructively for acceptance. Raw material is heat treated, by or for a material producer, in accordance with a process or material specification.
通常包括但不限于:薄板、板材、线材、棒材、棒材、锻件、铸件和挤压件。原材料通常通过熔炼号或批号来识别,通常在验收前进行破坏性测试。原料由原料生产商按照工艺或材料规范进行热处理。
NOTE: The cognizant engineering organization has the authority to assign the terms “parts” or “raw material.”
注:认可的工程组织有权指定术语“部件”或“原材料”
2.4.54 Raw Material Furnaces原材料炉
Equipment used in accordance with a process or material specification to process raw material.
按照工艺或材料规范加工原材料的设备。
2.2.55 Recording Instrument记录仪表
An instrument connected to a controlling, load and/or recording sensor that documents process equipment temperature data and generates a permanent process record. Examples are a chart recorder, electronic data recorder, or a data acquisition system.
一种连接到控制、负载和/或记录传感器的仪表,它记录工艺设备的温度数据,并产生永久的工艺记录。例如海图记录器、电子数据记录器或数据采集系统。
2.4.56 Recording Sensor记录传感器
A sensor that is connected to a recording instrument or connected to a control instrument of an integrated control/recording system.
连接到记录仪表或连接到综合控制/记录系统的控制仪表的传感器
2.4.57 Recurrent Temperature Pattern周期性的温度模式
Cycling of furnace temperature due to operation of the temperature control instrument.
由于温度控制仪表的操作,炉温的循环。
2.4.58 Reference Standard Instrument参考标准仪表
A standard test instrument that has been calibrated by NIST or other internationally recognized standards organization meeting Table 7 requirements.
由NIST或其他国际认可的标准组织校准的符合表7要求的标准测试仪表。
2.4.59 Reference Standard Sensor (Noble Metal)参考标准传感器(贵金属)
A noble metal standard sensor that has been calibrated by NIST or other internationally recognized standards organization meeting Table 1 requirements.
一种贵金属标准传感器,已由NIST或其他国际公认的标准组织校准,符合表1的要求。
2.4.60 Refractory Sensor耐火材料的传感器
A sensor whose thermoelements are composed primarily of refractory metals (e.g., Tungsten, Rhenium, Tantalum, Niobium,and Molybdenum) and their alloys. Example: Type C sensors.
一种热敏元件主要由难熔金属(如钨、铼、钽、铌和钼)及其合金组成的传感器。例如C型传感器。
2.4.61 Refrigeration Equipment冷处理设备
A compartment, cabinet, or room that may be held below room temperature and >32 ℉ or 0 ℃ (refrigerator), or ≤32 ℉ or 0 ℃ (freezer) depending on the temperature range of use. This equipment may be used for retarding or advancing metallurgical transformation or for storage of metallic materials. 一种隔间、柜子或房间,根据使用的温度范围,它可以保持在室温以下,温度为32℉或0℃(冰箱),或≤32℉或0℃(冷冻柜)。该设备可用于延缓或推进冶金转化,或用于金属材料的储存。
2.4.62 Resident SAT Sensor常驻SAT传感器
A test sensor that remains resident in the test location between system accuracy tests.
在系统精度测试之间保持在测试位置的测试传感器
2.2.63 Resistance Temperature Device (RTD)电阻温度装置
A device (for example, PT100, PRT, etc.) that produces a change in resistance across an element in response to the temperature at the element (usually in the tip).
一种器件(如PT100、PRT等),它能根据元件(通常在尖端)的温度在整个元件上产生电阻变化。
2.4.64 Retort Furnace马弗炉
A furnace that contains a retort or muffle which isolates the parts or raw material being heat treated from the heating elements. The furnace normally surrounds the retort.
一种含有蒸馏器或马弗的熔炉,它将被热处理的部件或原料与加热元件隔离开来。熔炉通常包围着蒸馏器。
2.4.65 Salt Bath盐浴
A furnace containing molten salt that is heated to the desired heat-treat temperature. Parts or raw material are normally immersed in the molten salt.
一种含有熔盐的熔炉,被加热到所需的热处理温度。零件或原料通常浸泡在熔盐中。
2.4.66 Secondary Standard Test Instrument二级标准测试仪表
An instrument calibrated directly against a primary standard or reference standard meeting Table 7 requirements and which is operated in a controlled test environment.
一种在受控的测试环境中操作的,直接根据主要标准或参考标准进行校准的仪表,符合表7的要求。
2.4.67 Secondary Standard Test Sensor二级标准测试传感器
A sensor calibrated directly against a primary standard test sensor, meeting the requirements of Table 1.
传感器直接校准的主要标准测试传感器,满足表1的要求。
2.4.68 Semi-Continuous Furnace半连续的炉子
See continuous furnace见连续炉
2.4.69 Sensor Or Temperature Sensor传感器或温度传感器
In the context of this specification, a device designed to detect or measure temperature (e.g., thermocouple, RTD, etc.).
在本规范中,用于检测或测量温度的设备(如热电偶、RTD等)。
2.4.70 Special Limits Of Error Sensor Wire特殊误差传感器线限
Sensors and extension wires whose initial calibration accuracy meets or exceeds the requirements of ASTM E230, Tables 2 and 3 for special tolerances.
初始校准精度满足或超过ASTM E230表2和表3特殊公差要求的传感器和延长线。
2.4.71 Stabilization稳定化(Also Referred To As Equalization, Equilibrium, Steady State, Or Soaked Condition也指均衡、平衡、稳态或浸泡状态)
Equipment stabilization occurs when all control and recording sensors are within the allowable temperature uniformity survey tolerance span and controllers are cycling and/or maintaining the desired temperature in each zone. Temperature uniformity survey stabilization occurs when all temperature uniformity survey sensors have reached the desired uniformity range and are not exhibiting a continual upward or downward trend away from the set point during and after the stabilized period of the temperature uniformity survey.
当所有控制和记录传感器都在允许的温度均匀性测量公差范围内,并且控制器在每个区域循环和/或保持所需的温度时,设备就会稳定。当所有温度均匀性测量传感器达到所需的均匀性范围,并且在温度均匀性测量的稳定期内和之后没有表现出从设定点持续上升或下降的趋势时,温度均匀性测量稳定发生。
2.4.72 System Accuracy Test (SAT)系统精度校验
An assessment of the sum of the combined errors or correction factors of the sensor, extension wire (and connectors), and instrument to ensure compliance with Table 11 or 12 requirements.
对传感器、延长线(和连接器)和仪表的综合误差或校正系数进行总和评估,以确保符合表11或12的要求。
2.4.72.1 Comparison SAT比对SAT
An assessment by comparison of the difference between the readings of the thermal process equipment sensor system being tested (sensor, extension wire, and instrument) and the corrected reading of the test sensor system (test sensor, extension wire, and field test instrument) after test sensor and field test instrument correction factors are applied (see 3.4.7). Also referred to as a “probe check.”
应用测试传感器和现场测试仪表校正因子后,通过比较被测试的热工艺设备传感器系统(传感器、延长线和仪表)的读数与测试传感器系统(测试传感器、延长线和现场测试仪表)的校正读数之间的差异来评估(见3.4.7)。也称为“探查检查”。
2.4.72.2 Alternate SAT替代SAT
A mathematical assessment of the sum of the errors or correction factors of the thermal processing equipment sensor and the calibration error or correction factor of the connector, extension wire, and instrument channel (see 3.4.8).
对热加工设备传感器的误差或修正系数和连接器、延长线和仪表通道的校准误差或修正系数之和的数学评估(见3.4.8)。
2.4.72.3 SAT Waiver豁免SAT
Additional requirements and comparisons to be made when the comparison or alternate SAT methods are not performed (see 3.4.9).
当不进行比较或备用SAT方法时,需要进行额外的要求和比较(见3.4.9)。
2.4.73 System Accuracy Test Sensor系统精度测试传感器
A calibrated and traceable sensor meeting the requirements of Table 1 used for an SAT
用于SAT的校准和可追踪传感器,满足表1的要求
2.4.74 Temperature Overshoot温度超调
When any temperature sensor exceeds the upper temperature tolerance as defined by the applicable thermal processing equipment class as stated in Table 8.
当任何温度传感器超过表8中所述的适用热加工设备类别所定义的最高温度公差时。
2.4.75 Temperature Sensor Pass-Through温度传感器直通
Installed wiring connecting sensors (typically thermocouples) inside the thermal processing equipment to the instrumentation outside, usually with sockets, jacks, or terminals at each end.
在热加工设备内部安装连接传感器(通常是热电偶)到外部仪表的接线,每一端通常有插座、插孔或端子。
2.4.76 Temperature Uniformity温度均匀性
The temperature variation (usually expressed as ± degrees) within the qualified work zone with respect to set point temperature. For retort furnaces where a sensor in the retort is used to control temperature, the temperature variation is with respect to the sensor in the retort and not to the furnace set point temperature. The requirement is established by the required thermal processing equipment class in accordance with Table 8.
合格工作区域内相对于设定值温度的温度变化(通常用±度表示)。对于蒸馏炉,在蒸馏炉中使用传感器来控制温度,温度变化是相对于蒸馏炉中的传感器而不是炉设定点温度。该要求根据表8所要求的热处理设备类别确定。
2.4.77 Temperature Uniformity Recorder温度均匀性记录器
Independent digital recording instrument meeting the requirements of Table 7 for a field test Instrument and used to perform temperature uniformity surveys.
独立数字记录仪表,满足表7对现场测试仪表的要求,用于进行温度均匀性测量。
2.4.78 Temperature Uniformity Sensor温度均匀性传感器
A calibrated and traceable sensor meeting the requirements of Table 1.
校准可追溯的传感器满足表1的要求。
2.4.79 Temperature Uniformity Survey (TUS)温度均匀性测量
An assessment of the temperature variation within the qualified work zone of thermal processing equipment prior to and after stabilization using a field test instrument (TUS recorder) meeting Table 7 requirements and sensors meeting the requirements of Tables 1, 17, and 18, as applicable.
使用满足表7要求的现场测试仪表(TUS记录仪)和满足表1、17和18要求的传感器(视情况而定),对热处理设备的合格工作区域稳定前后的温度变化进行评估。
2.4.80 Thermal Processing热处理
Any process in which parts or raw material are exposed to controlled heating, soaking, or cooling to achieve the specified properties or condition of the parts or raw material for which there is no exception in accordance with 1.3.
对零件或原材料进行受控加热、浸泡或冷却,以达到零件或原材料的特定性能或条件的任何工艺过程,无一例外地符合1.3的要求。
2.4.81 Thermal Processing Equipment热处理设备
A term used to refer to any vessel (such as autoclave, furnace, oven, quench and refrigeration equipment, liquid bath, heated press, etc.) used to process parts or raw material at controlled temperatures.
用于在控制温度下加工零件或原料的任何容器(如高压釜、熔炉、烘箱、淬火和制冷设备、液浴、加热压力机等)。
2.4.82 Thermocouple热电偶
A temperature sensor consisting of two wires (thermoelements) of dissimilar thermoelectric characteristics connected at a measuring junction. An EMF is developed between the two junctions in proportion to the temperature gradient.
由两根热电特性不同的导线(热电元件)组成的温度传感器连接在一个测量节点上,在两个节点之间根据温度梯度的比例形成电动势。
2.4.83 Traceable Or Traceability可追踪的或可追溯性
The ability to relate measurement results through an unbroken chain traceable to the International System of Units (SI) through internationally recognized standards organizations such as, but not limited to:
通过可溯源到国际单位制(SI)的不间断链,通过国际公认的标准组织,如但不限于:
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) 国家标准与技术研究所(NIST)
National Physical Laboratory (NPL) 国家物理实验室
Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB)
Swedish National Authority for Testing, Inspection, and Metrology瑞典国家测试、检验和计量管理局
China National Calibration Technology Specification (CNAS)中国国家校准技术规范
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST)国立先进工业科学技术研究所
Instituto Nacional de Metrologia, Normalização e Qualidade Industrial (INMETRO)国立计量学会
Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (BIPM)国际测量局
2.4.84 Use (Of A Sensor) (传感器的)使用
One cycle of heating or cooling upon the sensor being placed into service (see Table 5 note 5, 3.1.4.2, 3.1.7.2, 3.1.7.5, and 3.1.11.1).
传感器投入使用后的一个加热或冷却周期(见表5注5、3.1.4.2、3.1.7.2、3.1.7.5和3.1.11.1)。
2.4.85 Vacuum Furnace真空炉
A furnace that processes parts or raw material at any pressure lower than atmospheric pressure (nominally 760 mm Hg) during soak.
在浸泡过程中,在低于大气压力(名义上760毫米汞柱)的任何压力下加工零件或原材料的炉
2.4.86 Wireless Transmitter无线传输器
A device for sending electromagnetic waves; the part of a broadcasting apparatus that generates and modulates the radio frequency current and conveys it to a receiver.
发射电磁波的装置;广播设备中产生和调制射频电流并将其传送给接收器的部分
3 Technical Requirements技术要求
3.1 Temperature Sensors温度传感器
3.1.1 General Sensor Requirements传感器的一般要求
3.1.1.1 Unless specifically noted, the requirements defined in this specification shall apply to all sensors.
除非特别注明,本规范中定义的要求应适用于所有传感器。
3.1.1.2 All sensors shall comply with the requirements of Table 1. Other sensors that possess equal or better calibration accuracy may be used. Thermocouple composition shall comply with the requirements of ASTM E230 or ASTM E1751, and Table 2.
所有传感器应符合表1的要求。可以使用具有相同或更高精度的其他温度传感器。热电偶成分应符合ASTM E230或ASTM E1751和表2的要求。
3.1.1.3 Resistance temperature devices (RTDs) shall be noble metal, shall comply with the requirements of Table 1, and shall be considered non-expendable.
电阻温度器件(RTD)应为贵金属,应符合表1的要求,并应视为非易耗品。
3.1.1.4 Sensors may be made either from bare or coated wire, or mineral insulated/metal sheathed (MIMS) cable as described in Tables 2 and 3.
传感器可以由裸线或包覆线,或矿物绝缘/金属护套(MIMS)电缆制成,如表2和3所示。
3.1.1.5 Measuring junctions shall be made by either of the following methods:
测量连接应采用下列任一方法:
• Any combination of twisting and/or welding the thermoelements provided there is no addition of filler metal (including ungrounded and grounded MIMS).
在不添加填充金属的情况下,对热敏元件进行任何扭转和/或焊接的组合(包括未接地和已接地的MIMS)。
• Spot welding the thermoelements directly to a part, simulated part, or heat sink is permitted for temperatures ≤2000 ℉ or 1100 ℃
在温度≤2000℉或1100℃时,允许将热元件直接点焊到零件、模拟零件或散热器上.
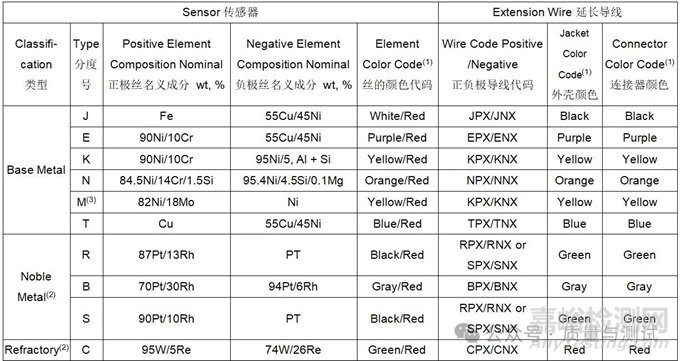
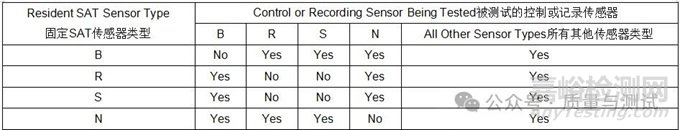
Table 1 - Sensors and sensor calibration传感器和传感器校准(12)
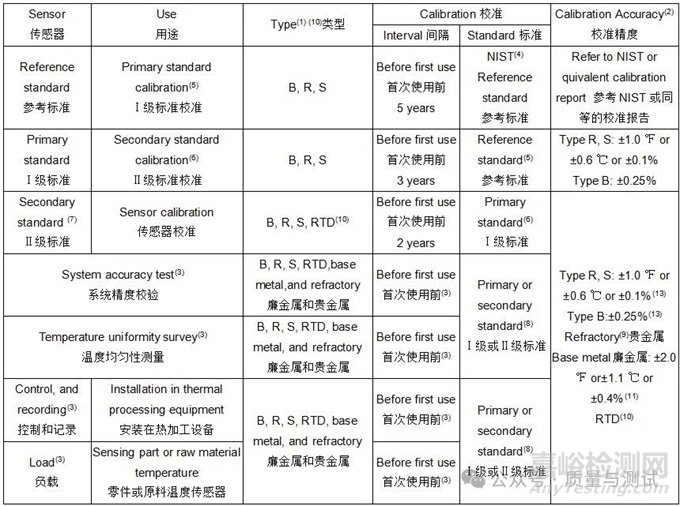
(1)Sensors of equal or better calibration accuracy are acceptable可接受同等或更高校准精度的传感器。
(2) Percent of reading or correction factor in ℉ or ℃, whichever is greater读数的百分数或修正值(以℃表示),取较大者。
(3) Sensor recalibration and reuse requirements are provided in Table 5 传感器再校准和复用要求见表5。
(4) NIST or other internationally recognized standards organization NIST或其他国际公认的标准组织。
(5) A reference standard sensor together with a primary standard instrument shall be used to calibrate primary standard sensors 一个参考标准传感器和一个Ⅰ级标准仪表应用于校准Ⅰ级标准传感器。
(6) A primary standard sensor together with a primary standard instrument shall be used to calibrate secondary standard sensors一个Ⅰ级标准传感器和一个Ⅰ级标准仪表应用于校准Ⅱ级标准传感器。
(7) Use shall be limited to the calibration of control, recording and load sensors, SAT, and TUS sensors.
用于控制、记录和负载传感器、SAT和TUS传感器的校准。
(8) A primary or secondary standard sensor together with a primary or secondary standard instrument shall be used to calibrate these sensors 一个Ⅰ级或Ⅱ级标准传感器和一个Ⅰ级或Ⅱ级标准仪表用于校准控制、记录和负载传感器。
(9) For refractory sensors Type C: ±8.0 ℉ or ±4.4 ℃ or ±1%, the sensor correction factor shall be used for all applications C型耐久传感器:±4.4℃或±1%t,所有传感器修正值应使用。
(10) RTDs, when used, shall be platinum type and meet Class/grade A tolerances given in ASTM E1137 or IEC 60751. This does not apply to RTDs used in conjunction with a refrigeration equipment controller当使用RTD时,应是铂型,并满足ASTM E1137或IEC 60751中给出的A级公差。这不适用于与制冷设备控制器连接使用的RTD。
(11) For temperatures <32 ℉ or <0 ℃ for Types K, E, and T only, calibration accuracy shall meet the following:
仅对温度<0℃的K、E和T类型,校准精度应满足以下要求:
Type K: -328 to 32 ℉, ±4.0 ℉ or -200 to 0 ℃, ±2.2 ℃, or ±2.0 % for either, whichever is greater.
K型:-200~0℃,±2.2℃或±2.0%t,取较大者。
Type E (MIMS): -328 to 32 ℉, ±4.0 ℉ or -200 to 0 ℃, ±2.2 ℃, or ±2.0 % for either, whichever is greater.
E型(MIMS):-200~0℃,±2.2℃或±2.0%t,取较大者。
Type E (all other): -328 to 32 ℉, ±3.0 ℉ or -200 to 0 ℃, ±1.7 ℃, or ±1.0 % for either, whichever is greater.
E型(其他所有):-200~0℃,±1.7℃或±1.0%t,取较大者。
Type T: -328 to 32 ℉, ±1.8 ℉ or -200 to 0 ℃, ±1.0 ℃, or ±1.5 % for either, whichever is greater
T型:-200~0℃,±1.0℃或±1.5%t,取较大者。
(12) Sensors and sensor materials are normally supplied to meet the tolerances specified in the table for temperatures above 32 ℉ or 0 ℃. The same materials, however, may not fall within the tolerances for temperatures below 32 ℉ or 0 ℃. Two separate sensors may be required, one for each range.
传感器和传感器材料的供应通常满足表中规定的温度大于0℃的公差。然而,相同的材料可能不符合0℃以下的温度公差。可能需要2个单独的传感器,每个范围1个。
(13) When correction factors are used during production在生产中使用修正值时:
Type B sensors shall meet a calibration accuracy of ±0.5% B型传感器应满足±0.5%t的校准精度
Types R and S sensors shall meet calibration accuracy of ±2.7 ℉ or ±1.5 ℃ or ±0.25%, whichever is greater
R型和S型传感器应满足±1.5℃或±0.25%t的校准精度,取较大者。
Table 2 - Sensor and extension wire/connector传感器和延长导线/接头
(1) All color codes stated are in accordance with ASTM E230. Color codes in accordance with other internationally recognized standards organizations are acceptable.
所有颜色代码都符合ASTM E230。颜色编码按照其他国际公认的标准组织是可以接受的
(2) Most base metal extension wires have the same nominal composition as the sensor wires with which they are intended to be used, whereas the compensating extension wires for noble metal (Types S, R, and B) or refractory metal sensors (Type C) are usually of a different, more economical composition whose relative thermoelectric properties as a pair nonetheless closely approximate those of the noble metal or refractory metal sensors with which they are to be used over a limited temperature range.
多数有相同的名义成分的廉金属延长导线被连接传感器使用,而贵金属补偿导线(类型S, R, B)或难熔金属传感器(C型)通常是不同的,更为经济成分的相对热电性能仍然是一对密切近似的贵金属或难熔金属传感器,这是他们在有限的温度范围内使用。
(3) The designation “Type M” may not be recognized by all international standards. Type K extension wire and connectors shall be used for Type M sensors. “M型”并非所有国际标准都认可。K型补偿导线和连接器可用于M型传感器。
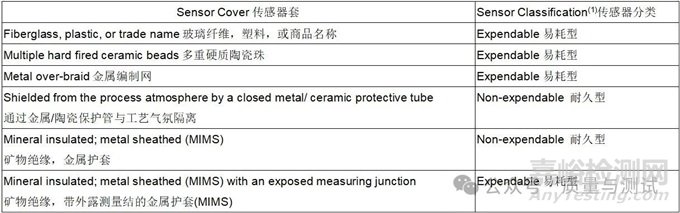
Table 3 - Sensor classification传感器分类
(1) See definitions for expendable and nonexpendable sensors见易耗型/耐久型传感器的定义。
3.1.2 Sensor Temperature Range of Use使用的传感器温度范围
Guidelines for sensor temperature range usage can be found in ASTM MNL12, ASTM E230, ASTM E608, ASTM E1137, ASTM E1751, IEC 60751, or other internationally recognized standard, and the sensor supplier.
传感器温度范围的使用指南可以在ASTM MNL12, ASTM E230, ASTM E608, ASTM E1137,ASTM E1751, IEC 60751或其他国际公认的标准和传感器供应商中找到。
3.1.3 Extension Wire and Connectors补偿导线及接头
3.1.3.1 Extension wire shall be of the same nominal composition as the sensor and instrumentation used, except when compatible compensating extension wire is allowed (e.g., noble metals). Extension wire shall meet the requirements of Table 2.
补偿导线的名义成分应与所使用的传感器和仪表匹配,除非允许兼容的补偿导线(例如,贵金属)。补偿导线应满足表2的要求。
3.1.3.2 Extension wire shall not be spliced other than using a compatible connector.
除使用兼容连接器外,补偿导线不得拼接。
3.1.3.3 Connectors, plugs, jacks, and terminal strips are permitted if they are the compatible type, i.e., they have thermoelectric properties conforming to the characteristics of the corresponding sensor type.
如果连接器、插头、插座和端子片是兼容类型,即它们的热电性能符合相应传感器类型的特性,则是允许的。
3.1.3.4 Wireless transmitters may be used as an alternative to extension wire.
无线传送器可代替补偿导线。
3.1.4 Sensor Calibration传感器校准
3.1.4.1 The sensor calibration technique shall comply with ASTM E207 or ASTM E220, or other internationally recognized standards.
传感器校准技术应符合ASTM E207或ASTM E220或其他国际公认标准。
3.1.4.2 Sensors shall be calibrated before their first use.
传感器在首次使用前应进行校准。
3.1.4.3 Sensor calibration intervals whether based on time, number of uses, or temperatures, are the maximums permitted.
传感器校准周期,无论是基于时间,使用次数,或温度,允许最大。
3.1.4.4 Users shall have procedures that control the replacement of thermal process equipment sensors including limits on maximum life and/or number of uses based on supporting data such as, but not limited to, SAT, TUS, and re-calibration data, and/or trend analysis.
用户应有控制热加工设备传感器更换的程序,包括基于支持数据(如但不限于SAT、TUS和重新校准数据和/或趋势分析)的最大寿命和/或使用数量限制。
3.1.4.5 Sensors shall be calibrated or re-calibrated at or lower than the lowest temperature of use and at or higher than the highest temperature of use. Sensors used at a single temperature may be calibrated at the single temperature of use.
传感器应在低于最低使用温度和高于最高使用温度进行校准或重新校准。在单一温度下使用的传感器可以在使用的单一温度下校准。
3.1.4.6 Intervals between calibration or recalibration temperatures provided by the calibration agency shall not exceed 250 ℉ or 140 ℃ for all sensors. The fixed point calibration method in ASTM MNL12 or other internationally recognized standards may be used. No matter what standard is used, the calibration agency shall provide additional calibration points that do not exceed 250 ℉ or 140 ℃ for all sensors.
对所有传感器,校准机构提供的校准或重新校准温度间隔不应超过140℃。可采用ASTM MNL12或其他国际公认标准中的定点校准方法。无论使用何种标准,校准机构都应为所有传感器提供不超过250℉或140℃的额外校准点。
3.1.4.7 Extrapolation of calibration correction factors above the highest calibration temperature and below the lowest calibration temperature is prohibited by any calibration source except NIST or other internationally recognized standards organization.
除NIST或其他国际公认的标准组织外,任何校准禁止采用高于最高校准温度和低于最低校准温度校准修正值外推法。
3.1.4.8 Interpolation of correction factors between two known calibration points is permitted using the linear method.
允许使用线性方法在两个已知校准点之间插入修正值。
3.1.4.9 Alternatively, the correction factor of the nearest calibration point shall be used.
或者,使用最近的校准点的修正值。
3.1.4.10 Whichever method is used shall be defined and applied consistently.
论使用哪种方法,都应一致地定义和应用。
3.1.4.11 For recalibration of sensors when permitted in Table 5, it is acceptable to use either the date of recalibration, or the date of first use following recalibration as the beginning of the calibration period. Procedures shall identify how the practice is applied and documented to ensure compliance.
对于表5中允许的传感器重新校准,可以使用重新校准日期或重新校准后首次使用的日期作为校准期的开始。程序应确定实际如何应用并形成文件,以确保符合性。
3.1.5 Wire/Cable Rolls导线/电缆卷
3.1.5.1 Calibrated expendable or non-expendable sensors made from rolls may be used in lieu of individually calibrated sensors.
由成卷的经过校准的易耗型或耐久型传感器可用来代替单独校准的传感器。
3.1.5.2 The maximum length of wire/cable in a roll at the time of calibration shall comply with Table 4.
校准时每卷电线/电缆的最大长度应符合表4。
Table 4 - Maximum permitted length of wire/cable in a roll电线/电缆卷的最大允许长度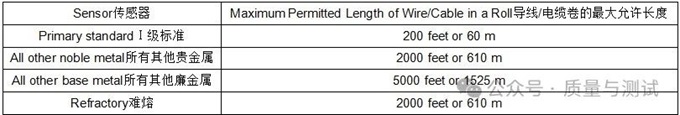
3.1.5.3 Rolls shall be sampled and calibrated at both ends. The individual correction factors from each end shall be within the requirements of Table 1 and the average correction factor shall be calculated from both ends of the roll at each calibration temperature and used for the entire length of the roll.
丝卷在两端取样校准。每端的单个修正值应在表1的要求内,平均修正值应在每个校准温度下从丝卷的两端计算,并用于整个丝卷。
3.1.5.4 The roll shall not be used if the difference between the correction factors from each end of the sample sensors at any individual calibration temperature exceeds:
如果样品传感器在任何单个校准温度下两端的修正值之差优于:
a. 1.0 ℉ or 0.6 ℃ for primary and secondary standard sensors.
Ⅰ级和Ⅱ级标准传感器0.6℃。
b. 2.0 ℉ or 1.1 ℃ for control, recording, and load sensors, SAT, and TUS sensors.
控制、记录、负载传感器、SAT和TUS传感器1.1℃。
3.1.5.5 The following shall apply to rolls not meeting the requirements of 3.1.5.4:
对于不符合3.1.5.4要求的丝卷,应采取下列措施:
a. It is permitted to divide the roll into shorter lengths provided the shorter lengths meet the requirements of 3.1.5.4.
只要丝卷的长度满足3.1.5.4的要求,就可以将丝卷分成较短长度的。
b. It is permitted to use individual sensors from the roll provided they are calibrated to the requirements of Table 1.
允许使用自丝卷的校准达到表1要求的单个传感器。
3.1.6 General Sensor Reuse Requirements一般传感器重复使用要求
Reuse of any sensor is not permitted unless the insulation remains intact and the wire/cable including the measuring junction are not damaged (see Table 5).
不允许重复使用任何传感器,除非绝缘保持完好,电线/电缆包括测量接点没有损坏(见表5)。
Table 5 - Sensor reuse and recalibration传感器重复使用和重新校准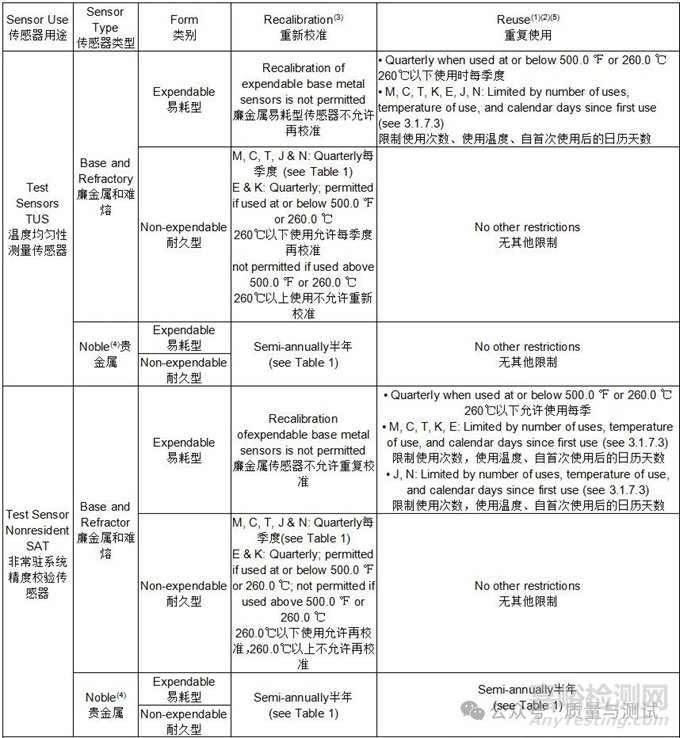
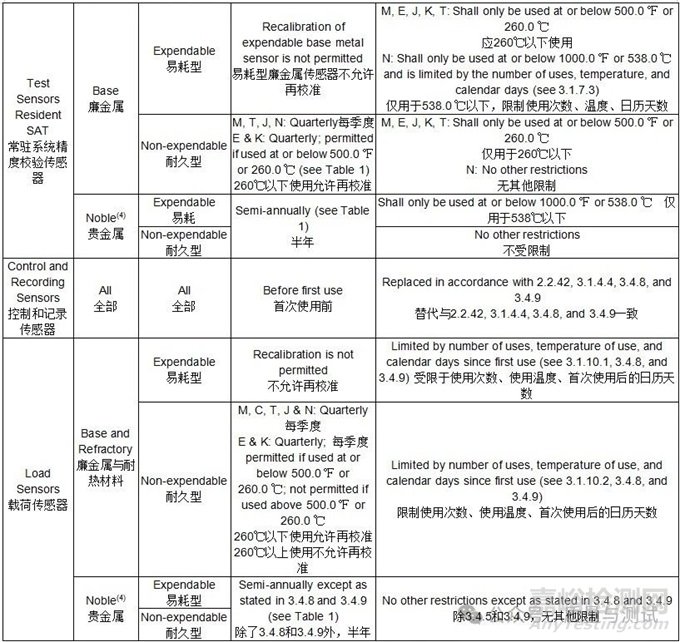
Notes:
(1) For reuse of any Type E or K sensor used above 500.0 ℉ or 260.0 ℃, the depth of insertion shall be equal to or greater than any previous use (see 3.1.7.1).
对于在260.0℃以上重复使用的任何E型或K型传感器,插入深度应等于或大于任何以前的插入深度(见3.1.7.1)。
(2) See 3.1.6 and 3.1.7 for general reuse restrictions.
参见3.1.6和3.1.7一般重复使用限制条件。
(3) Recalibration of any Type E or K sensor used above 500.0 ℉ or 260.0 ℃ is prohibited.
禁止在260.0℃以上使用任何E型或K型传感器进行重新校准。
(4) Includes RTDs 包括RTD
(5) Reuses: Example 1: Begin at room temperature, ramp to 900 ℉ or 480 ℃ for first TUS temperature, then ramp to 1200 ℉ or 650 ℃ for TUS max temperature, then cool back to room temperature. This is a single use.
重复使用:示例1:从室温开始,第一个TUS温度上升到900 ℉或480℃,然后上升到1200 ℉或650 ℃的TUS最高温度,然后冷却回室温。这是一次使用。
Example 2: Begin at room temperature, ramp to 1325 ℉ or 718 ℃ for first production temperature, then cool to 1150 ℉ or 621 ℃ for the second production temperature, then cool back to room temperature. This is a single use.
例2:从室温开始,第一次生产温度上升到1325 ℉或718℃,然后冷却到1150 ℉或621 ℃,第二次生产温度,然后冷却回室温。这是一次使用。
Example 3: Begin at room temperature, ramp to 1900 ℉ or 1038 ℃ for first production temperature, then cool to 300 ℉ or 150 ℃, then ramp up to 1100 ℉ or 593 ℃ for second production temperature, then cool back to room temperature. This is two uses even if the load remained closed inside the equipment.
例3:从室温开始,第一次生产温度上升到1900℉或1038℃,然后冷却到300℉或150℃,然后上升到1100℉或593℃进行第二次生产温度,然后冷却回室温。这是两个用途,即使负载保持关闭在设备内。
3.1.7 SAT and TUS Sensor Reuse系统精度校验和温度均匀性测量传感器的重复使用
3.1.7.1 During the reuse of Type E or K sensors when used above 500.0 ℉ or 260.0 ℃, the depth of insertion shall be equal to or greater than any previous use.
对E型或K型传感器在260.0℃以上重复使用,其插入深度应等于或大于任何以前的插入深度。
3.1.7.2 Expendable base metal, noble metal, and refractory SAT and TUS sensors may be reused:
易耗型廉金属、贵金属和难熔SAT和TUS传感器可重复使用:
a. Base metal and refractory sensors may be used for up to 3 months from first use, without limit to number of uses, when used exclusively at or below 500.0 ℉ or 260.0 ℃.
当仅在260.0℃以下使用时,廉金属和难熔传感器可从首次使用起使用3个月,使用次数不限。
b. Noble metal sensors may be used for up to 6 months from first use, without limit to number of uses or temperature of use.
贵金属传感器从首次使用起可使用长达6个月,不限制使用次数或使用温度。
3.1.7.3 Expendable Base Metal and Refractory SAT and TUS Sensors:
易耗型廉金属和难熔系统精度校验和温度均匀性测量传感器:
a. Types M, C, T, K, and E shall be limited to 3 months or five uses, whichever occurs first, between 500.0 ℉ and 1200.0 ℉ or between 260.0 ℃ and 650.0 ℃, and limited to a single use above 1200.0 ℉ or 650.0 ℃.
M、C、T、K和E型应限制在260.0℃~650.0℃间使用3个月或5次,以先到为准,并限制在650.0℃以上的一次使用。
b. Types J and N shall be limited to 3 months or ten uses, whichever occurs first, between 500.0 ℉ and 1200.0 ℉ or between 260.0 ℃ and 650.0 ℃, and limited to a single use above 1200.0 ℉ or 650.0 ℃.
J型和N型应限制在260.0℃~650.0℃之间使用3个月或10次,以先到为准,且限制650.0℃以上的单次使用。
3.1.7.4 Records shall be maintained of the accumulated sensor reuse including sensor batch number, temperature, and use count.
应保持传感器累计重复使用的记录,包括传感器批号、温度和使用计数。
Example 1: Sensors are replaced after a single use. Sensor batch number shall be recorded for the SAT and/or TUS.
例1:传感器使用一次后更换。应记录SAT和/或TUS的传感器批号。
Example 2: Sensors are reused. Sensor batch number, temperature, and use count shall be recorded for each use.
例2:传感器被重用。每次使用时应记录传感器批号、温度和使用次数。
3.1.7.5 Base metal or refractory TUS sensors shall be limited to no more than the maximum number of uses defined in 3.1.7.3 for expendable sensors, 270 uses for nonexpendable sensors, or 6 months from first use, whichever occurs first, and may be reused subject to the limitations of 3.1.6 and 3.1.8 that are:
廉金属或难熔温度均匀性测量传感器的使用次数不得超过3.1.7.3中定义的易耗型传感器的最大使用次数,耐久型传感器的最大使用次数270,或首次使用后6个月(以先到为准),并可在符合3.1.6和3.1.8的限制条件下重复使用:
a. Used exclusively ≤1200 ℉ or ≤650 ℃, 仅用于≤650℃。
b. Identified by the date of installation and by the number and temperatures of accumulated uses, and根据安装日期和累计使用的次数和温度确定。
c. Preserved/protected from damage (i.e., crimping, excessive moisture contact, corrosion, etc.) between each TUS or remain installed on a rack that is protected between each TUS.
保存/保护每次温度均匀性测量间的损坏(例如,卷曲、接头过度潮湿、腐蚀等)或保持安装在一个支架上,每个温度均匀性测量间的保护。
3.1.8 Sensor Salvage传感器修复
3.1.8.1 Salvage of damaged expendable sensors is permitted if the discrepant portion including any portion previously exposed inside of the furnace is removed and the hot junction remade.
如果有差异的部分(包括以前暴露在炉内的任何部分)被移除并重新制作热接点,则允许修复损坏的易耗性传感器。
3.1.8.2 The salvaged sensor’s original calibration data shall be used.
修复传感器应使用原校准数据。
3.1.9 Control and Recording Sensors控制和记录传感器
3.1.9.1 Control sensors shall be positioned in thermal processing equipment to ensure control and maintain temperature uniformity of the equipment within the qualified work zone. Recording sensors shall be located in accordance with the applicable instrumentation type (see Table 9).
控制传感器应置于热加工设备中,以保证控制和保持设备在合格工作区的温度均匀性。记录传感器的位置应与适用的仪表类型匹配(见表9)。
3.1.10 Base Metal Load Sensors廉金属载荷传感器
3.1.10.1 Expendable base metal and refractory load sensors may be used:
易耗型廉金属和难熔载荷传感器可用于:
a. Up to 3 months after first use without limit to number of uses when used at or below 500.0 ℉ or 260.0 ℃.
当在260.0℃以下使用时,首次使用后3个月不受使用次数限制。
b. Types M, C, T, K, and E shall be limited to 3 months or five uses, whichever occurs first, between 500.0 ℉ and 1200.0 ℉ or between 260.0 ℃ and 650.0 ℃, and limited to a single use above 1200.0 ℉ or 650.0 ℃.
M、C、T、K和E型应限制在260.0℃~650.0℃间使用3个月或5次,以最先使用的为准,并限制在650.0℃以上使用一次。
c. Types J and N shall be limited to 3 months or ten uses, whichever occurs first, between 500.0 ℉ and 1200.0 ℉ or between 260.0 ℃ and 650.0 ℃, and limited to a single use above 1200.0 ℉ or 650.0 ℃.
J型和N型应限制在260.0℃~650.0℃间使用3个月或10次,以最先使用的为准,并限制在650.0℃以上使用一次。
3.1.10.2 The life of non-expendable base metal load sensors shall be limited by the maximum operating temperature and the number of calendar days since the first use.
非易耗型廉金属载荷传感器的寿命应受自首次使用以来的最高工作温度和日历天数的限制。
3.1.10.3 Records shall be maintained of the accumulated load sensor use above 500 ℉ or 260 ℃ including sensor batch number, load cycle, temperature, and use count. The use count shall include uses during SAT and TUS. When sensors are replaced after a single use, the sensor batch number shall be recorded and traceable to the load.
应保存载荷传感器在260℃以上的累计使用记录,包括传感器批号、载荷周期、温度和使用次数。使用次数应包括系统精度校验和温度均匀性测量期间的使用。当传感器单次使用后更换时,应记录传感器批号并可追溯到负载。
3.1.10.4 The maximum replacement interval or number of uses, whichever occurs first since first use of non-expendable base metal load sensors, shall comply with Table 6.
耐久型廉金属载荷传感器首次使用后的最大更换间隔或使用次数,以第1次使用为准,应符合表6。
Table 6 - Non-expendable base metal load sensor use temperature, interval or uses
耐久型廉金属载荷传感器的使用温度、间隔或用途
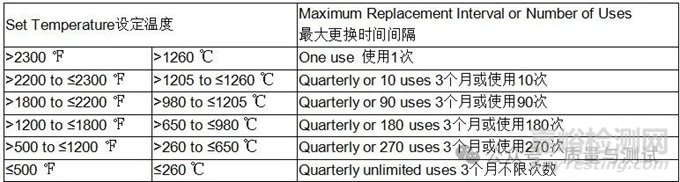
3.1.10.5 When load sensors are used in multiple qualified temperature ranges, the shortest interval or use shall apply.
当载荷传感器在多个合格的温度范围内使用时,应用最短的间隔。
Example 1: A sensor with nine uses at 2250.0 ℉ or 1232.0 ℃ has only one more use allowed in the 2200.0 to 2299.9 ℉ or 1204.5 to 1259.9 ℃ range, or any lower operating range. No uses remain at 2300.0 ℉ or 1260.0 ℃ or above.
例1:一个在1232.0℃使用有9次传感器,只允许在1204.5℃~1259.9℃范围内,或任何更低的工作范围内使用。在1260.0℃或更高的温度下不得使用。
Example 2: A sensor with 50 uses between 1400.0 ℉ and 1600.0 ℉ or 760.0 ℃ and 871.0 ℃ is then used at 1820.0 ℉ or 993.0 ℃.
例2:在760.0℃~871.0℃间使用50次传感器,然后在993.0℃使用。
The sensor has already exceeded the use limits for all ranges above 2199.9 ℉ or 1204.4 ℃.
The sensor is now subject to the 90 use limit as it has been used in a higher temperature range.
该传感器已经超过了2199.9℉或1204.4℃以上的所有范围的使用限制。该传感器现在受到90的使用限制,因为它已经在更高的温度范围内使用。
Example 3: A sensor with 50 uses between 1400.0 ℉ and 1600.0 ℉ or 760.0 ℃ and 871.0 ℃ is then used at 1015.0 ℉ or 546.0 ℃.
The sensor has already exceeded the use limits for all ranges above 2199.9 ℉ or 1204.4 ℃.
The sensor is subject to a 180 use limit as it has been used in the 1200.0 to 1799.9 ℉ or 648.9 to 982.2 ℃ temperature range.
例3:在1400.0℉和1600.0℉或760.0℃和871.0℃之间使用50个传感器,然后在1015.0℉或546.0℃使用。该传感器已经超过了2199.9℉或1204.4℃以上的所有范围的使用限制。该传感器受180的使用限制,因为它已经在1200.0至1799.9℉或648.9至982.2℃的温度范围内使用。
3.1.11 Sensor Calibration Results and Records传感器校准结果和记录
3.1.11.1 The results of sensor calibration or re-calibration shall be documented. The documentation shall include 传感器校准或重新校准的结果应记录下来。文件应包括:
a. Identification of the sensor, batch of sensors or wire/cable rolls.
传感器的识别,传感器的批次或电线/电缆卷。
b. Sensor type, e.g., K, N, E, RTD, etc.
传感器类型,如K, N, E, RTD等。
c. Date of calibration or recalibration.
校准或重新校准日期。
d. Quantity or length of wire/cable rolls represented in calibration report
在校准报告中显示电线/电缆卷的数量或长度。.
e. Identification if the calibration was initial or a recalibration.
识别是初始校准还是重新校准
f. The required calibration accuracy.
所需的校准精度。
g. Identification of the standard test sensor and standard test instrument used.
所使用的标准测试传感器和标准测试仪表的识别。
h. Nominal calibration temperatures.
名义校准温度。
i. Actual temperature readings of the sensor(s) being calibrated
正在校正的传感器的实际温度读数
j. Calibration technique referencing ASTM E220 or other internationally recognized standards.
参考ASTM E220或其他国际公认标准的校准技术
k. Correction factors or deviations/errors for each calibration temperature, including the average correction factor representing both ends for wire/cable rolls.
每个校准温度的修正系数或偏差/误差,包括代表电线/电缆卷两端的平均修正系数。
l. Documentation shall clearly state deviation (error) or correction factor.
文件应明确说明偏差(错误)或修正系数
m. A statement of traceability to NIST or other internationally recognized standards organization.
对NIST或其他国际公认标准组织的可追溯性声明
n. Identification of the calibration agency.
标定机构的识别。
o. Identification of technician performing calibration.
进行校准的技术人员的识别。
p. Approval of an authorized agent for the calibration agency.
对校准机构的授权代理人的批准。
q. User quality organization approval.
用户质量组织批准。
3.2 Instrumentation仪表化
3.2.1 General Instrumentation Requirements一般仪表要求
3.2.1.1 Conversion from millivolts to degrees or degrees to millivolts shall be in accordance with ASTM E230 or other internationally recognized standards.
从毫伏到度或度到毫伏的转换应符合ASTM E230或其他国际公认标准。
3.2.1.2 Output of sensors shall be converted to temperature readings by instruments specified herein or instruments of equal or greater accuracy.
应使用本标准规定的精度相同或更高精度的仪表,将温度传感器的输出转换为温度读数。
3.2.1.3 Instruments shall be calibrated in accordance with Table 7 and shall be traceable to NIST or other internationally recognized standards organization.
仪表应按照表7进行校准,并可溯源到NIST或其他国际公认的标准。
3.2.1.4 Process recording data collection shall be a minimum of six data points for each recorded sensor during each time at temperature processing cycle not to exceed 10-minute intervals.
过程记录的数据收集应为每个记录的传感器在每个温度处理周期不超过10分钟间隔的时间最少6个数据点。 在每次温度处理周期不超过10分钟的间隔,每个记录传感器应至少收集6个数据点。
3.2.1.4.1 For cycles where the time at temperature is <6 minutes, the data collection shall be ≤ once per minute.
对于温度持续时间<6分钟的周期,数据采集应≤每分钟一次。
3.2.1.5 Data collection intervals shall be sufficient to demonstrate conformance to sack time, heat-up, and cooling rate requirements数据收集间隔应符合保温时间、加热速率和冷却速率的要求。
3.2.1.5.1 The recording instrument shall actively record/collect data during the entire time that parts or raw material are in the thermal processing equipment. In cases where load sensors must be disconnected to transfer the load, users shall have other objective evidence of process compliance (e.g., data showing temperature drop from the temperature of other furnace recording sensor(s) compliant with the soak.
在工件或原材料进入热加工设备的整个过程中,记录仪表应主动记录/收集数据。在载荷传感器必须断开以转移载荷的情况下,用户应有其他符合工艺要求的客观证据(例如,数据显示温度降低与符合浸泡条件的其他炉子记录传感器)
Table 7 - Instruments and instrument calibration仪表及仪表校准
Notes:
(1) Instruments of equivalent or greater accuracy are acceptable可接受精度相当或更高的仪表。
(2) Applicable to quench or refrigeration equipment only仅适用于淬火或冷处理设备。
(3) Instrument calibration intervals shall be仪表校准间隔时间为:
(4) When the refrigeration and/or quench equipment sensor is connected to a channel in a furnace recording instrument the interval for calibration of that channel in the recording instrument shall be the same calibration interval as the other channels in the instrument.
当冷处理和/或淬火设备传感器连接到炉记录仪表的通道时,记录仪表中该通道的校准间隔应与仪表中其他通道的校准间隔相同。
(5)Field test instruments meeting the accuracy requirements of secondary standards may be used to calibrate SAT and TUS instruments in the field. These instruments shall be calibrated quarterly using a primary standard.
满足Ⅱ级标准精度要求的现场测试仪表可用于现场校准SAT和TUS仪表。这些仪表应每季度使用Ⅰ级标准进行校准。
(6) NIST or other internationally recognized standards organization. Per Manufacturer’s Specifications for Reference Standard Instruments (e.g., stability of 2 μV/V per year) and NIST or equivalent Calibration for Reference Standard Instruments.
NIST或其他国际公认的标准组织。根据参考标准仪表制造商的规范(例如,稳定性为每年2 μV/V)和NIST或等效的参考标准仪表校准。
(7) Includes wireless transmission systems包括无线传输系统。
(8) Instruments shall be stored and used in the environment specified by the instrument manufacturer.
仪表应在仪表制造商规定的环境中储存和使用。
(9) Calibration periods for instruments shall begin on the date of calibration.
仪表的校准周期从校准日期开始。
(10) Digital control instruments that only read in whole numbers shall have maximum calibration accuracy of ±2 ℉ or ±1 ℃ or ±0.2% of the temperature reading rounded inward towards the smaller whole number.
仅读取整数的数字控制仪表的最大校准精度应为±2℉或±1℃或温度读数的±0.2%向内修约到较小的整数。
(11)For thermal processing equipment that has documented “out of use/service” periods beyond the due date and extension days in Table 22, calibration of process instrumentation shall be performed before being returned to service.
对于热加工设备,其“停止使用/服务”期限超过了表22中规定的截止日期和延期日期,应在重新投入使用前对过程仪表进行校准。
3.2.2 Test Instruments (Primary Standard, Secondary Standard, and Field Test)
测试仪表(Ⅰ级标准,Ⅱ级标准和现场测试)
3.2.2.1 Primary and secondary standard instruments shall be digital and meet the calibration accuracy requirements of Table 7 in degrees of temperature or in millivolts that can be converted to demonstrate equivalent accuracy.
Ⅰ级和Ⅱ级标准仪表应是数字化的,并满足表7的校准精度要求,其温度或毫伏可以转换为显示等效精度。
3.2.2.2 Field test instruments shall be digital and have a minimum readability of 0.1 ℉ or 0.1 ℃ for any input and output used.
现场测试仪表应是数字化的,任何输入和输出的最小可读性为0.1℉或0.1℃。
3.2.2.3 Test instrument calibration shall be performed at a minimum of six simulated sensor input and/or output signals. These shall include the minimum and maximum of the operating range used for test or calibration and a minimum of four points in between either representing areas of normal operation or spaced at approximately equal intervals across the range in which the instrument is used for test or calibration.
测试仪表应在至少6个模拟传感器输入和/或输出信号下进行校准。其中应包括用于测试或校准的工作范围的最小值和最大值,以及其中表示正常工作区域或在仪表用于测试或校准的范围内以近似相等的间隔间隔的至少4个点。
3.2.2.3.1 For test instruments used only at a single temperature, the calibration shall be performed at that single temperature.
对于仅在单一温度下使用的测试仪表,校准应在该单一温度下进行。
3.2.2.4 Calibration shall be performed for each type of input and output used, e.g., each sensor type in use and for mV, mA, etc., if the instrument is used for these scales.
应对所用的每类输入和输出进行校准,例如,所用的每一种传感器,如果仪表用于这些刻度,则应校准毫伏、毫安等。
3.2.2.5 Calibration shall be performed on each channel in use that can be altered or adjusted individually, or on each group of channels that can be altered or adjusted as a group. Channels not in use shall be blocked or tagged to prevent unintentional use.
应对使用中的每个单独修改或调整的通道进行校准,或对每组可作为一组更改或调整的通道进行校准。不使用的通道应被封锁或贴上标签,以防止无意使用。
3.2.2.6 A test instrument meeting the accuracy of a secondary standard may be used in a production environment as a field test instrument. The calibration frequency shall be the same as a field test instrument and the instrument shall be operated within the environmental conditions specified by the instrument manufacturer.
满足Ⅱ级标准精度的测试仪表可以作为现场测试仪表在生产环境中使用。校准频率应与现场测试仪表相同,仪表应在仪表制造商规定的环境条件下操作。
3.2.3 Control, Recording, and Over-Temperature Instruments控制,记录和超温仪表
3.2.3.1 All control, recording, and over-temperature instruments shall be digital.
所有控制、记录和超温仪表都应是数字式的。
3.2.3.2 Digital recording instruments shall produce permanent records with a minimum readability of 0.1 ℉ or 0.1 ℃.
数字记录仪表应具有最低0.1℉或0.1℃的分辨率。
3.2.3.2.1 Digital recording instruments that only read in whole numbers may be used for 1 year after the release of AMS2750 Rev G and shall have maximum calibration accuracy of ±2 ℉ or ±1 ℃ or ±0.2% of the temperature reading rounded inward towards the smaller whole number.
仅读取整数的数字记录仪表可在AMS2750 Rev G发布1年后使用,校准精度最低为±2℉或±1℃或温度读数的±0.2%修约至较小的整数。
3.2.3.3 Instruments shall receive an unmodified signal from sensors except for analog to digital and digital to analog conversions, or a digitally processed, error-checked equivalent representation of a direct measured value.
除模拟量到数字量和数字量到模拟量的转换,或直接测量数值的数位处理、误差检查的等效表示以外, 仪表应从温度传感器接收未修正的信号。
3.2.3.4 Calibration shall be performed in the as-found condition taking into account any applied and documented offsets at a minimum of three simulated sensor inputs at the minimum, maximum and at least one point in the middle third of the entire qualified operating temperature range to document the as-found condition.
应在发现的条件下进行校准,考虑到至少三个模拟传感器输入的最小、最大和至少中间三分之一点的任何应用和记录的偏移,以记录发现的条件。
Example 1: A Class 2 ±10 ℉ furnace with a qualified operating temperature range of 300 to 1200 ℉ requires calibration at the Minimum = 300 ℉, at the Maximum = 1200 ℉, and at least 1 point in the middle third = 600 to 900 ℉.
例1:一个2±10°F的炉子,合格的工作温度范围为300°F至1200°F,需要在最低= 300°F,最高= 1200°F,中间三分之一处至少有一个点= 600至900°F进行校准。
Example 2: A Class 2 ±6 ℃ furnace with a qualified operating temperature range of 200 to 1100 ℃ requires calibration at the Minimum = 200 ℃, at the Maximum = 1100 ℃, and at least 1 point in the middle third = 500 to 800 ℃.
例2:一个2±6℃的炉,合格的工作温度范围为200℃至1100℃,需要在最低= 200℃,最高= 1100℃,中间三分之一处至少有一个点= 500℃至800℃进行校准。
3.2.3.5 For equipment that does not have a defined qualified operating temperature range (e.g., quench tanks and refrigeration equipment), calibration shall be performed at a minimum of three simulated sensor inputs at the minimum, maximum and at least one point in the middle third of the operating range used. Users shall have the ability to identify the operating range used for each piece of quench and/or refrigeration equipment.
对于没有确定的合格工作温度范围的设备(例如,急冷罐和制冷设备),应在使用的工作范围的最小、最大和中间三分之一的至少三个模拟传感器输入进行校准。用户应能够识别每件淬火和/或制冷设备的操作范围。
3.2.3.5.1 Instrument calibration points for equipment with a qualified operating temperature range and an unqualified operating range of use, such as a cryogenic-temper unit, shall be in accordance with 3.2.3.4 for the qualified operating range and in accordance with 3.2.3.5 for the unqualified range of use.
对工作温度范围合格、不合格使用温度范围的设备,如低温回火装置,其工作温度范围合格的按3.2.3.4,使用温度范围不合格的按3.2.3.5。
3.2.3.6 For control, recording, and over-temperature instruments used only at a single temperature, the instrument calibration shall either be performed at that single temperature of use, or in accordance with 3.2.3.4 or 3.2.3.5 as applicable.
对于仅在单一温度下使用的控制、记录和超温仪表,仪表校准应在该单一使用温度下进行,或按照适用的3.2.3.4或3.2.3.5进行。
3.2.3.7 The instrument error is the difference between the readings of the instrument being calibrated and the field test instrument. When any documented modification offsets are used in production, the reading of the instrument being calibrated shall be corrected algebraically.
仪表误差是指被校准仪表读数与现场测试仪表读数之间的差值。当任何记录在案的修正偏移量用于生产时,被校准仪表的读数应进行代数校正。
3.2.3.8 Following any calibration adjustments, the instrument shall be verified in accordance with 3.2.3.4, 3.2.3.5, or 3.2.3.6 as applicable to document the as-left condition.
在任何校准调整后,仪表应按照3.2.3.4、3.2.3.5或3.2.3.6(适用于记录保留状态)进行验证
3.2.3.9 Calibration shall be performed on each channel in use that can be altered or adjusted individually, or on each group of channels that can be altered or adjusted as a group.
应对使用中的每个可单独更改或调整的通道进行校准,或对每组可作为一组更改或调整的通道进行校准。
3.2.3.10 All active channels of multi-channel digital recording instruments shall be calibrated. Channels not in use shall be identified to prevent unintentional use.
多通道数字记录仪表的所有有源通道都应进行校准。未使用的通道应加以识别,以防止意外使用。
3.2.3.11 When the control and recording system is integrated such that the digitally displayed control value and the digitally recorded value are generated from the same measurement circuit and cannot be different, it is only necessary to document a single displayed/recorded value for the control reading.
当控制和记录系统集成在一起,使数字显示的控制值和数字记录的值从相同的测量电路产生且不能不同时,只需要记录一个显示/记录的值作为控制读数。
3.2.3.12 For retort furnaces, the temperature of the furnace shall be controlled such that the specified temperature is maintained within the retort. As a minimum, the control instrument shall be calibrated across the temperature range of use within the retort.
对于蒸馏炉,应控制其温度,使蒸馏炉内的温度保持在规定的温度范围内。作为最低限度,控制仪表应在蒸馏器内使用的温度范围内进行校准。
3.2.3.13 Refrigeration and quench equipment control instruments that display temperature shall be calibrated. All recording instruments shall be calibrated (see Table 7).
显示温度的制冷和淬火设备控制仪表应进行校准。所有记录仪表都应进行校准(见表7)。
3.2.3.14 The timing function for all digital recording instruments and data acquisition systems shall be calibrated at least annually and shall be accurate to ±1 min/h. The calibration may be performed for a time ≤1 hour and the results converted to meet ±1 min/h.
所有数字记录仪表和数据采集系统的定时功能应至少每年校准一次,并应精确到±1分钟/小时。校准时间≤1小时,结果转换为±1分钟/小时。
3.2.3.15 External timing devices such as timers, clocks, stopwatches, etc., shall be calibrated at least every 2 years and shall be accurate to ±1 s/min.
外部定时装置,如计时器、时钟、秒表等,应至少每两年校准一次,并应精确到±1秒/分钟。
3.2.3.16 As an alternative to 3.2.3.14 or 3.2.3.15, a defined digital synchronization of digital recording instruments and data acquisition systems or external timing devices to NIST or other international equivalent via satellite, internet, or telephonic systems at least monthly to support a ±1 min/h accuracy for digital recording instruments and/or ±1 sec/min for external timing devices is acceptable.
作为3.2.3.14或3.2.3.15的替代方案,数字记录仪表和数据采集系统或外部定时设备通过卫星、互联网或电话系统与NIST或其他国际等效设备进行定义的数字同步,至少每月一次,以支持±1分钟/小时的精度的数字记录仪或±1秒/分钟外部计时装置是可以接受的。
3.2.3.17 Wireless equipment which performs the analog to digital conversion at the furnace and transmits a digital signal to the recording instrument is permitted. However, calibration of the complete wireless system (wireless transmitter, wireless receiver and associated control and recording instruments) is required.
允许在电炉处执行模拟到数字转换并将数字信号传输到记录仪表的无线设备。但是,需要对整个无线系统(无线发射器、无线接收器和相关的控制和记录仪表)进行校准。
3.2.3.18 Correction Factors for Instruments仪器校正系数
3.2.3.18.1 Extrapolation of calibration correction factors above the highest calibration temperature and below the lowest calibration temperature is prohibited by any calibration source except NIST or other internationally recognized standards organization.
除NIST或其他国际公认的标准组织外,任何校准源都禁止在最高校准温度以上和最低校准温度以下外推校准校正因子。
3.2.3.18.2 Interpolation of correction factors between two known calibration points is permitted using the linear method. Alternatively, the correction factor of the nearest calibration point shall be used. Whichever method is used shall be defined and applied consistently.
允许使用线性方法在两个已知的校准点之间插值校正因子。或者,应使用最近的校准点的校正系数。无论采用哪一种方法,都应得到一致的定义和应用。
3.2.4 Electronic Records电子记录
3.2.4.1 An electronic record is any combination of text, graphics, data, audio, pictorial, or other information represented in digital form that is created, modified, maintained, archived, retrieved, or distributed by a computer system.
电子记录是指由计算机系统创建、修改、维护、存档、检索或分发的以数字形式表示的文本、图形、数据、音频、图像或其他信息的任何组合。
3.2.4.2 When using a system (control, recording or data acquisition) that creates electronic records the system shall:
当使用创建电子记录的系统(控制、记录或数据采集)时,该系统应:
a. Create records that cannot be altered without detection.
创建无法在不被检测的情况下更改的记录。
b. Provide software and playback utilities as a means of examining and/or compiling the data but shall not allow the user any means for altering the source data.
提供软件和回放工具作为检查和/或汇编数据的手段,但不允许用户使用任何方法更改源数据
c. Provide the ability to generate accurate and complete copies of records in both human readable and electronic form suitable for inspection, review, and duplication.
提供生成准确而完整的记录副本的能力,该副本可以是人类可读的,也可以是适合检查、审查和复制的电子形式。
d. Be capable of providing evidence the record was reviewed by recording an electronic review, or a method of printing the record for a physical marking verifying review.
能够通过记录电子评审或打印记录以进行物理标记验证评审的方法,提供对记录进行评审的证据。
e. Support protection, retention, and retrieval of accurate records throughout the record retention period.
在记录保存期间,支持对准确记录的保护、保留和检索。
f. Ensure that the hardware and/or software shall operate throughout the retention period as specified in 3.7.
确保硬件和/或软件在3.7规定的保留期内正常运行。
g. Provide methods of protection, such as a password, to limit system access to only individuals whose authorization is documented.
提供保护方法,例如密码,以限制系统的访问权限,只有获得文件授权的个人才能访问
3.2.4.3 Evidence shall be provided that software revisions are verified to ensure continued compliance with the material or process specification requirements and once installed have not altered programs, recipes, or other means used to control thermal processing parameters.
应提供证据证明软件修订版经过验证,以确保持续符合材料或工艺规范的要求,并且一旦安装,软件修订版没有改变用于控制热加工参数的程序、配方或其他手段。
3.2.5 Instrumentation Calibration Results and Records仪表仪表校准结果和记录
3.2.5.1 The most recent successful calibration status shall be readily accessible at or in close proximity to the thermal processing equipment. As a minimum, the information shall include:
最近一次成功的校准状态应在热加工设备附近或附近易于获取。至少,信息应包括:
a. Instrument number or furnace number.
仪表编号或炉号。
b. Date the calibration was performed.
标定完成日期。
c. Due date of the next calibration.
下一次校准的截止日期
d. Identification of the technician who performed the calibration.
进行校准的技术人员的识别
e. Indication if any limitations or restrictions of the calibration. A notation such as “see report” is acceptable指示是否有任何限制或校准的限制。像“见报告”这样的符号是可以接受的。
3.2.5.2 The results of instrument calibration shall be documented. As a minimum, the documentation shall include仪表校准结果应形成文件。文件至少应包括:
a. Unique identification of the instrument仪表的唯一标识。
b. Make and model of the instrument calibrated校准仪表的品牌和型号。
c. Unique Identification of the test instrument used during calibration在校准过程中使用的测试仪表的唯一标识。
d. Identification of each sensor type in use (e.g., Type K, N, etc.) and form (e.g., V, mA, etc.) if the instrument is used for these scales如果该仪表用于这些量表,则要识别所使用的每个传感器类型(如K型、N型等)和形式(如V、mA等)。
e. Identification of location where signal was input (only required for measurement systems employing the alternate SAT)信号输入位置的识别(仅用于使用备用SAT的测量系统)。
f. Required calibration accuracy需要的校准精度。
g. As-found data at each calibration point and as-left data if any adjustments are made, to include每一个校准点的发现数据和剩余数据(如进行任何调整),包括:
1. Nominal test temperature名义测试温度。
2. Reading of the instrument being calibrated被校准仪表的读数
3. Error or correction factor of test instrument (optional or when specified by the customer)测试仪表的误差或校正系数(可选或由客户指定)。
4. Error or correction factor of instrument under test (corrected or uncorrected for test instrument error when specified)被测仪表的误差或校正系数(按规定对测试仪表的误差进行校正或未校正)。
h. Correction and modification offsets as-found and as-left in accordance with 3.2.6.
根据3.2.6对发现和剩余的偏移量进行修正和修改。
i Instrument calibration pass or fail statement仪表校准通过或失败的声明。
j. Any limitations or restrictions of the calibration任何限制或校准的限制。
k. Date the calibration was performed标定完成日期。
l. Due date of the next calibration下一次校准的截止日期。
m. Statement of traceability to NIST or other internationally recognized standards organization.
对NIST或其他国际公认标准组织的可追溯性声明。
n. Identification of the technician who performed the calibration进行校准的技术人员的识别。
o. Identification of the calibration agency if calibration is not performed internally如果内部没有进行校准,则标识校准机构。
p. Approval of an authorized agent for the calibration agency if not performed internally对校准机构的授权代理的批准(如果不是内部执行)。
q. User quality organization approval用户质量组织批准。
注:AMS 2750D后有要求
3.2.6 Thermal Process Equipment Instrument Correction and Modification Offsets (see 2.2.38.1 and 2.2.38.2)
热加工设备仪表校正和修正偏移(见2.2.38.1和2.2.38.2)
3.2.6.1 General Instrument Correction and Modification Offset Requirements一般仪表校正和修正偏移量要求
3.2.6.1.1 If instrument correction and/or modification offsets are used, a documented procedure shall exist describing when and how to make instrument correction and/or modification offsets.
如果使用了仪表校正和/或修正偏移量,应制定文件程序,说明何时以及如何进行仪表校正和/或修正偏移量。
3.2.6.1.2 The maximum cumulative correction offset shall not exceed the uniformity tolerance for the thermal processing equipment or ±10.0 ℉ or ± 6.0 ℃ for refrigeration and quench instruments. (e.g., a Class 2 furnace instrument is limited to a maximum correction offset of ±10.0 ℉ or ±6.0 ℃).
最大累积校正偏移量不得超过热加工设备的均匀度公差或制冷和淬火仪表的±10.0℉或±6.0℃。(例如,2类炉仪表的最大校正偏移量限制在±10.0℉或±6.0℃)。
3.2.6.1.3 Instrument correction and/or modification offsets may be either internal (electronic) or external (manual), and shall be included in the calibration, SAT, and TUS documentation.
仪表校正和/或修正偏 移量可以是内部(电子)或外部(手动),并应包括在校准、SAT和TUS文件中。
3.2.6.1.4 Controlling instrument modification offsets for TUS shall not exceed the allowances in Table 15 or 16为TUS控制的仪表修正补偿不得超过表15或表16中的余量。
3.2.6.1.5 TUS modification offsets are not permitted on recorder channels other than for the channel recording the control sensor temperature.
除了记录控制传感器温度的通道外,在记录通道上不允许TUS修改偏移。
3.2.6.1.6 SAT modification offsets are not allowed. Control and recording instrument correction offsets for SAT shall not exceed the allowance in Table 15 or 16.
SAT修改偏移是不允许的。SAT的控制和记录仪表校正误差不应超过表15或表16中的允许值。
3.2.6.1.7 For load sensor systems used in production, correction offsets are allowed, but not modification offsets.
对于生产中使用的负载传感器系统,允许校正偏移,但不允许修改偏移。
3.2.6.1.8 When correction and/or modification offsets are implemented or changed, the effect of the new offset value over the entire qualified operating temperature range shall be evaluated. Objective evidence that the new offset value would not cause a failure of any other calibration, SAT, or TUS shall be documented.
当实施或改变校正和/或修改偏移量时,应评价新的偏移值在整个合格工作温度范围内的影响。新的偏移值不会导致任何其他校准、SAT或TUS失败的客观证据应记录在案。
3.3 Thermal Processing Equipment热处理设备
3.3.1 Furnace classes are defined in Table 8 and are based on the furnace class specified. When not specified, the furnace class shall meet the TUS requirements established in the governing specification for the parts or raw material being processed. Instrumentation types are defined by the level of instrumentation used to control, record, or indicate the desired temperature. Intervals for controlling and recording instrument calibration, SATs, TUSs, are based on the combined furnace class and instrumentation type stated in Table 7, 11, 12, 15, or 16.
表8中定义了加热炉的类别,并以指定的加热炉类别为基础。如果没有规定,炉级应满足TUS对正在加工的部件或原材料的控制规范中建立的要求。仪表类型由用于控制、记录或指示所需温度的仪表级别来定义。控制和记录仪表校准的时间间隔,SAT, TUSs,是基于综合熔炉等级和仪表类型,表7,11,12,15,或16所述。
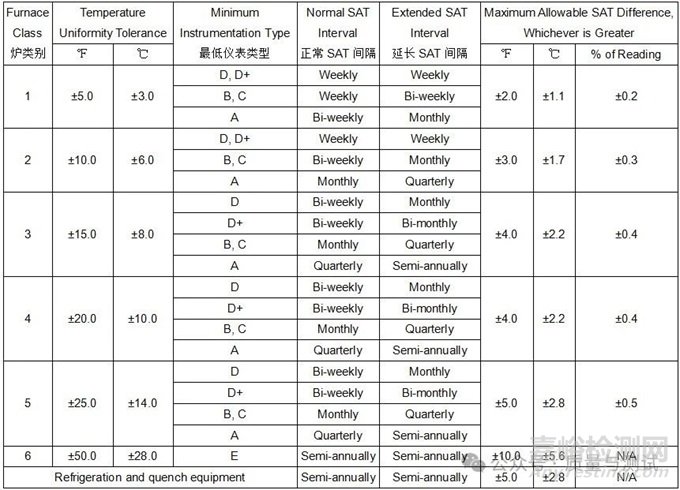
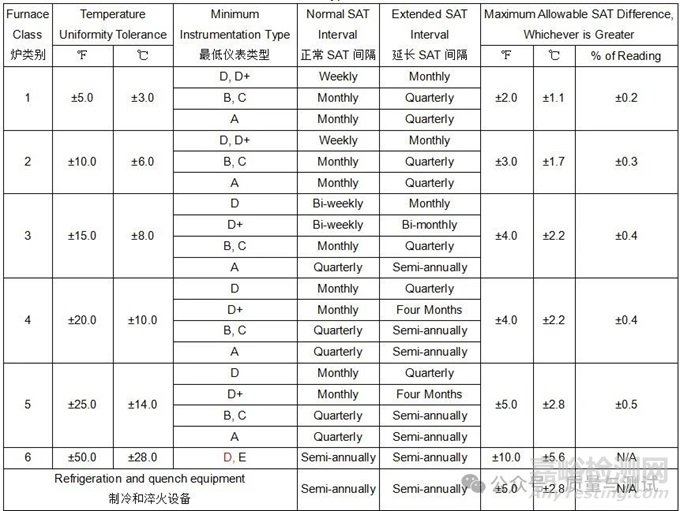
Table 8 - Furnace class uniformity tolerances炉类均匀性公差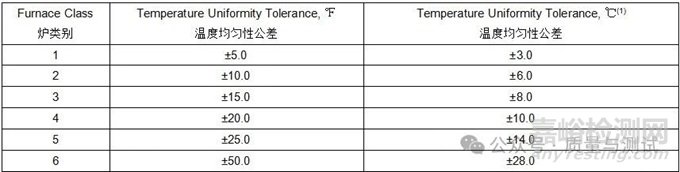
Notes:
(1) Some design authorities require TUS tolerances of ±5.0 ℃ and ±7.0 ℃ for Class 2 and Class 3, thermal processing equipment 一些设计机构要求2类和3类热处理设备的TUS公差为±5.0℃和±7.0℃。
3.3.2 Requirements for furnace instrumentation type classification are shown in Table 9.
炉子仪表类型分类要求如表9所示。
Table 9 - Instrumentation type requirements仪表类型需求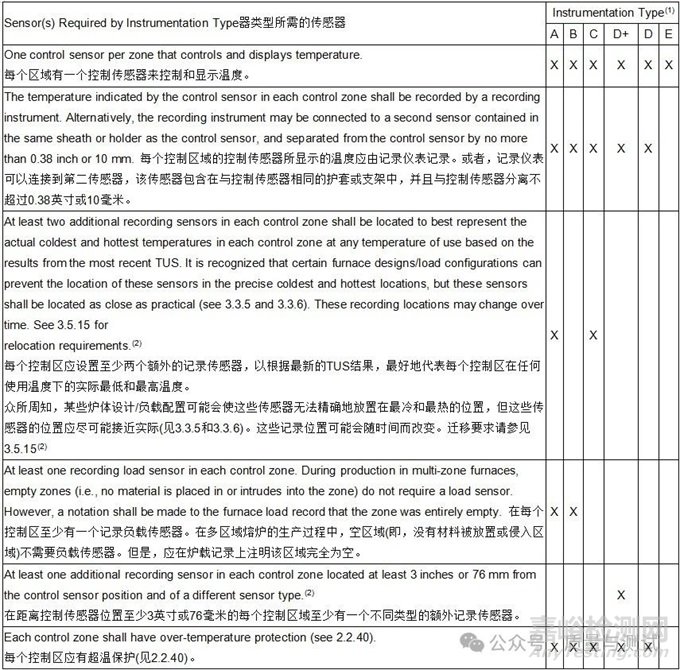
Notes:
(1) Instrumentation types are listed in descending order of quality from left to right; i.e., A is better than B, etc.
从左到右按照质量降序列出了工具类型;例如,A比B好,等等。
(2) The over-temperature protection sensor may also be utilized as the recording sensor representing the hottest location for instrumentation Type A or C or as the additional recording sensor for Type D+ if in the proper location.
过温保护传感器也可用作记录传感器,表示A或C类仪表的最热位置,如果位于适当位置,也可用作D+类仪表的附加记录传感器
3.3.3 Instrumentation Requirements for Refrigeration Equipment and Quench Systems
冷处理设备和淬火系统的仪表要求
3.3.3.1 All refrigeration equipment shall have a temperature controller. This temperature controller requirement is not applicable to liquid nitrogen, dry ice, or dry ice/liquid-cooled containers.
所有的冷处理设备都应该有一个温度控制器。此温度控制器要求不适用于液氮、干冰或干冰/液冷容器。
3.3.3.2 All refrigeration equipment shall be equipped with a temperature recording instrument where time-at-temperature (minimum, maximum, or both) is required.
所有的冷处理设备都应配备温度记录仪表,时间-温度(最低,最高,或两者)要求。
3.3.3.3 Unless otherwise specified, the requirements of 3.3.3.1 and 3.3.3.2 are not applicable during transportation of materials at sub-ambient temperatures
除另有规定外,在亚环境温度下的物料运输中,不适用3.3.3.1和3.3.3.2的要求。.
3.3.3.4 Quench systems (immersion or spray) shall be equipped with a sensor that is recorded by recording instrument where temperature (minimum, maximum, or both) is required.
淬火系统(浸入式或喷雾式)应配备传感器,当要求温度(最低、最高或两者同时)时,该传感器的温度可由记录仪表记录。
3.3.4 Additional Sensors附加传感器
There is no limit to the number of additional recording or load sensors in any control zone, but their use shall be defined in controlled operating instructions, or procedures.
在任何控制区附加记录或载荷传感器的数量没有限制,但它们的使用应在受控操作说明书或程序中定义。
3.3.5 Hot and cold temperature sensors, when required for instrument Types A and C, as stated in Table 10, may be inserted in heat sinks (see 2.2.27), and positioned at the hottest and coldest temperature locations of the control zone based on the most recent TUS when heat sinks of similar configuration are used during the TUS.
如表10所示,当A、C类仪表需要时,可将热、冷温度传感器插入散热器(见2.2.27),并在TUS期间使用类似配置的散热器时,根据最近的TUS将其放置在控制区最热和最冷的温度位置。
Table 10 - Minimum sensors required per control zone每个控制区所需的最少传感器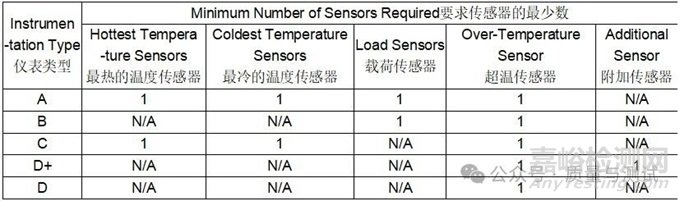
3.3.6 The minimum sensors required are shown in Table 10所需的最少传感器如表10所示。
3.3.7 For multiple control zone furnaces with <225 ft3 or 6.4 m3 in total qualified work zone volume, it is acceptable to treat the furnace qualified work zone volume as a single control zone (see Table 10) for locating hot and cold temperature recording sensors (Type A or C instrumentation) and determining the number of over -temperature and load sensors required, regardless of the number of control sensors (Type A or B instrumentation), when the longest dimension of width, length, diameter, or height is no more than three times any of the other dimensions.
对于多个控制区域炉,总合格工作区体积<225 ft3或6.4 m3,可以将炉子合格的工作区域体积作为一个单独的控制区域(见表10),用于定位冷热端温度记录传感器(a型或C型仪表)和确定所需的超温和负载传感器的数量,而不管控制传感器的数量(a型或B型仪表),当最大的宽度、长度、直径、或者说高度不超过其他任何维度的三倍。
3.3.7.1 For multiple zone furnaces with ≥225 ft3 or 6.4 m3 in total qualified work zone volume may be divided into control zones that shall not exceed 225 ft3 or 6.4 m3. Each control zone shall contain all the required sensors as defined in Table 10 for a single control zone. For furnaces that have individual control zones 225 ft3 or 6.4 m3 or greater in volume, each control zone shall contain all the required sensors as defined in Table 10.
对于总容积≥225立方英尺或6.4立方米的多区加热炉,合格工作区容积可划分为不超过225立方英尺或6.4立方米的控制区域。每个控制区应包含表10中定义的单个控制区所需的所有传感器。对于单个控制区容积为225立方英尺或6.4立方米或更大的熔炉,每个控制区应包含表10中定义的所有所需传感器。
3.4 System Accuracy Test系统精度校验
3.4.1 General SAT Requirements 一般需求
3.4.1.1 The SAT is an assessment of the sum of the combined errors or corrections of the sensor, extension wire (and connectors), and instrument to ensure compliance with the requirements of Table 11 or 12.
SAT是对传感器、延长导线(和连接器)和仪表的综合误差或修正量的评估,以确保符合表11或表12的要求。
Table 11 - Parts furnace class, instrument type and SAT interval工件炉类、仪表类型及SAT间隔
Table 12 - Raw material furnace class, instrument type and SAT interval原料炉类、仪表类型及SAT间隔
3.4.1.2 The SAT shall be performed on all control and recording systems required by the applicable instrumentation type, as well as any additional recording systems used for parts and raw material acceptance in each control zone of each piece of thermal processing equipment used for production heat treatments.
SAT应适用于适用仪表类型所要求的所有控制和记录系统,以及用于生产热处理的每件热处理设备的每个控制区中用于零部件和原材料验收的任何附加记录系统
3.4.1.2.1 Load sensors are not required to be in contact with parts, raw material, or any representation of parts or raw material during the SAT.
在测试过程中,负载传感器不需要与部件、原材料或任何部件或原材料的代表接触。
3.4.1.3 When the control and recording system is integrated such that the digitally displayed control value and the digitally recorded value are generated from the same measurement circuit and cannot be different, it is only necessary to document a single displayed/recorded value for the SAT.
当控制和记录系统集成在一起,使数字显示的控制值和数字记录的值从相同的测量电路产生且不能不同时,只需要为SAT记录一个显示/记录的值。
3.4.1.4 The SAT shall be performed on additional systems used to justify SAT interval extension (see 3.4.3.2) SAT应在用于证明SAT间隔延长的额外系统上进行(见3.4.3.2)。
3.4.1.5 The SAT is not required for systems whose only function is over-temperature protection.
对于只有过温保护功能的系统,不需要SAT
3.4.1.6 The SAT shall be performed using calibrated and independent SAT sensors meeting the requirements of Table 1 and calibrated and independent field test instruments meeting the requirements of Table 7.
应使用符合表1要求的校准独立的SAT传感器和符合表7要求的校准独立的现场测试仪表进行SAT测试。
3.4.1.7 Recording instruments used on thermal processing equipment shall not be used as a field test instrument unless it can be demonstrated that the SAT sensor recording channels of an integrated system are separated from the furnace recording system and also meet field test instrument requirements.
热处理设备上使用的记录仪表不得用作现场测试仪表,除非能证明集成系统的SAT传感器记录通道与炉膛记录系统是分离的,并且满足现场测试仪表的要求。
3.4.2 Performing an SAT 实施SAT
3.4.2.1 The SAT shall be performed initially and periodically thereafter in accordance with the interval requirements of Table 11 or 12.
应按照表11或12的间隔要求再使用前和定期进行SAT。
3.4.2.2 For equipment that has documented “out of use/service” periods beyond the due date and extension days in table 22, a new SAT shall be performed on all applicable systems before being returned to service.
对于表22中记载的超出到期日期和延期日期的“停止使用/服务”期间的设备,在恢复服务之前,应对所有适用系统重新进行SAT。
3.4.2.3 An SAT (comparison, alternate, or re-establishing the relationship for the waiver) shall also be performed after any maintenance that could affect the SAT difference. Examples include, but are not limited to:
进行了影响SAT精度的任何维护之后应进行SAT(比较、替代或重新建立豁免关系)。例子包括但不限于:
• Replacement of the sensor for the system being tested. (i.e., systems utilizing individually calibrated sensors require an SAT upon replacement of each sensor, but systems utilizing sensors from the same calibrated roll/spoolrequire an SAT upon replacement of the roll/spool).
为正在测试的系统更换传感器。(即使用单独校准的传感器的系统在更换每个传感器时需要SAT,但使用来自相同校准卷芯的传感器的系统在更换卷芯时需要SAT)。
• Replacement of the control or recording instrument更换控制或记录仪表。
• Calibration of the control or recording instrument when any adjustment has been made.
在进行了任何调整后,对控制或记录仪表进行校准。
• If an internal correction offset is introduced, removed or an existing internal correction offset is altered如果内部校正偏移量被引入、移除或现有的内部校正偏移量被改变。
• After implementation of corrective action due to a failed SAT 由于SAT失败而采取纠正措施后。
3.4.2.4 The quality assurance organization shall make and document a determination whether equipment maintenance requires an SAT.
质量保证组织应确定设备维护是否需要SAT,并形成文件。
3.4.3 SAT Interval间隔
3.4.3.1 The SAT interval shall be based upon the furnace class and instrumentation type (see 2.2.25). SAT间隔应根据炉类别和仪表类型确定(见2.2.25)。
3.4.3.1.1 For furnaces with multiple qualified operating temperature ranges, the SAT shall be performed in accordance with the most stringent interval for the furnace class used.
对于具有多个合格操作温度范围的炉,应按照所使用的炉类别最严格的间隔进行SAT。
3.4.3.2 The SAT interval may be extended to the maximum allowed SAT interval in Table 11 or 12, if a preventive maintenance program is in effect as described in 2.2.42, and one of the following conditions is met:
如果预防性维护计划如2.2.42所述有效,且满足下列条件之一,则SAT间隔可延长至表11或表12中允许的最大SAT间隔:
3.4.3.2.1 At least two sensors in each control zone are non-expendable Type B, N, R, or S.
每个控制区至少有两个非易耗性B、N、R或S型传感器。
3.4.3.2.2 The relationship requirements of 3.4.9.6, 3.4.9.8, and Table 14 are documented and met.
3.4.9.6、3.4.9.8和表14的关系要求已编制并满足。
3.4.3.2.2.1 If the weekly relationship exceeds 2.0 ℉ or 1.1 ℃, a comparison SAT shall be performed prior to returning the thermal processing equipment to production, and the interval shall return to the normal interval until the next TUS is performed to establish the new relationship.
如果每周关系超过1.1℃,应在热加工设备恢复生产之前进行SAT比较,并将间隔恢复到正常间隔,直到下次进行TUS以建立新的关系。
3.4.4 SAT Difference差异
3.4.4.1 The maximum allowable SAT difference shall be defined by the furnace class as shown in Table 11 or 12.
最大允许的SAT差值应由炉类别定义,如表11或12所示。
3.4.4.2 The difference calculated between the readings of the sensor system being tested (instrument/extension wire/sensor) and the corrected reading of the SAT sensor and SAT instrument (after the SAT sensor and SAT instrument correction factors have been applied algebraically) shall be documented as the SAT difference
被测传感器系统(仪表/延长线/传感器)的读数与SAT传感器和SAT仪表的修正读数(在代数应用SAT传感器和SAT仪表修正因子后)之间的差值应被记录为SAT差值。
3.4.4.2.1 The correction factors for the SAT sensor and SAT instrument may be determined by the SAT set temperature or the observed SAT instrument reading.
SAT传感器和SAT仪表的修正系数可以由SAT设定温度或观测到的SAT仪表读数决定。
3.4.4.2.2 Whichever method is used shall be defined and applied consistently.
无论使用哪种方法,都应一致地定义和应用。
3.4.4.3 The temperature readings from the process instrument and sensor being compared with the SAT sensor and field test instrument shall be the temperature reading, read or recorded during production heat treatment. Certain offsets, if consistently applied during production heat treatment in accordance with 3.4.4.4 and supported by documented procedures, shall be algebraically applied to the system being tested
工艺仪表和传感器的温度读数与SAT传感器和现场测试仪表的比较应是在热处理生产期间读取或记录的温度读数。如果在热处理生产过程中按照3.4.4.4的要求一致使用某些偏移量,并有文件程序支持,应代数应用于被测试系统。
3.4.4.4 Allowable instrument correction or modification offsets include允许的仪表校正或修正偏移量包括:
3.4.4.4.1 Internal modification offsets applied to the control and control recording channel instruments solely to correct a skewed TUS result.
用于控制和控制记录通道仪表的内部修正偏移量,仅用于纠正扭曲的TUS结果。
Example: Reading from control instrument is 1000.0 ℉ and there is a -3.0 ℉ modification offset applied electronically to the control instrument. Then +3.0 ℉ shall be added to the 1000.0 ℉ reading before calculating the difference in 3.4.4.2.
例如:从控制仪表上读出的读数为1000.0℉,在控制仪表上施加电子校正偏移-3.0℉。然后在1000.0℉的读数上加上+3.0℉,再计算3.4.4.2的差值。
3.4.4.4.2 A previously documented and specified manual correction offset to the control or recording instrument to correct an SAT difference.
对控制或记录仪表进行预先记录和指定的手动校正,以校正SAT差值。
Example: Reading from control instrument is 1352.0 ℉ and there is a +2.0 ℉ correction offset for SAT applied manually. Then -2.0 ℉ shall be added to the 1352.0 ℉ control reading before calculating the difference in 3.4.4.2.
例如:控制仪表的读数为1352.0℉,手动应用SAT时有+2.0℉的校正偏移。然后在1352.0℉的控制读数上加上-2.0℉,再计算3.4.4.2的差值。
3.4.5 Prohibited instrument offsets include禁止的仪表补偿包括:
3.4.5.1 External (manual) modification offset applied to the control instrument that has been specified for production solely to correct a skewed TUS result. These manual modification offsets have no effect on the performance of the SAT or calculation of the SAT difference.
仅用于纠正不对称的TUS结果,对控制仪表人工施加的补偿,该控制仪表已指定用于生产。这种人工补偿对SAT的结果或SAT误差的计算没有影响。
Example: Reading from control instrument is 1905.0 ℉ and there is a +5.0 ℉ modification offset for TUS applied manually. Then the 1905.0 ℉ control reading is used when calculating the difference in 3.4.4.2.
示例:控制仪表读数为1905.0℉,手动施加TUS时有+5.0℉修正偏移量。然后在3.4.4.2计算差值时使用1905.0℉控制读数。
3.4.6 SAT Methods方法
3.4.6.1 The SAT requirement may be fulfilled using any one of three methods interchangeably, provided the sensor system meets the requirements of the method implemented:
可以使用三种方法中的任意一种交换满足SAT要求,前提是传感器系统满足所实现方法的要求:
3.4.6.1.1 Comparison SAT (see 3.4.7) 比对SAT
3.4.6.1.2 Alternate SAT (see 3.4.8) 替代SAT
3.4.6.1.3 SAT waiver (see 3.4.9) 豁免SAT
3.4.7 Comparison SAT 比对SAT
3.4.7.1 The displayed temperature indication and recording of the sensor being tested as used in production, with appropriate offsets or correction factors, at any temperature within the qualified operating temperature range(s), shall be compared with the corrected temperature indication of the SAT sensor on a test instrument.
在合格的操作温度范围内的任何温度下,被测试的传感器显示的温度指示和记录(带有适当的偏移或校正因子)应与测试仪表上的SAT传感器校正的温度指示进行比对。
3.4.7.1.1 For furnaces with multiple qualified operating temperature ranges, a periodic SAT shall be performed in each range at least annually.
对于具有多个合格操作温度范围的炉子,应至少每年对每个温度范围进行周期性的SAT。
3.4.7.2 The tip (measuring junction) of the SAT sensor shall be as close as practical to the tip (measuring junction) of the control, or recording sensor, but the sensor tip to tip distance shall not exceed 3 inches or 76 mm.
SAT传感器的尖端(测量端)应尽可能接近控制或记录传感器的尖端(测量端),但传感器尖端到尖端的距离不得超过76毫米。
3.4.7.3 The SAT sensor may be inserted temporarily to perform the comparison SAT or may be a resident SAT sensor subject to the limitations of 3.4.7.4.1 to 3.4.7.4.3.
可以临时插入SAT传感器以执行比对SAT,也可以是受3.4.7.4.1至3.4.7.4.3限制的固定SAT传感器。
3.4.7.3.1 The resident SAT sensors shall be restricted to Type B, R, S or N at temperatures greater than 500 ℉ or 260 ℃ and shall be non-expendable at temperatures greater than 1000 ℉ or 538 ℃ (see Table 5).
固定SAT传感器在温度大于260℃时应为B、R、S或N型,在温度大于538℃时应是耐久型(见表5)。
3.4.7.3.2 The resident SAT sensor type shall be different from that of the sensor being tested as defined by Table 13 固定SAT传感器的类型应与表13所定义的被测试传感器不同。
Table 13 - Allowable combinations of resident SAT sensor and sensor being tested for temperatures greater than 500 ℉ or 260 ℃
在温度大于260℃时允许使用的SAT传感器和传感器组合
3.4.7.3.3 The resident SAT sensor shall be affixed in position to an assembly to prevent movement in relation to the sensor under test. The position shall be verified on installation and replacement. Alternatively, the resident SAT sensor may be located independently of the sensor under test and its position shall be verified before each SAT to ensure that it has not moved between sensor installation events.
固定SAT传感器应固定在一个组件的位置上,以防止与被测试传感器互相移动。安装和更换时应验证该位置。或者,固定SAT传感器可以独立于被测传感器进行定位,其位置应在每次SAT之前进行验证,以确保其在传感器安装过程中没有移动。
3.4.7.3.4 It is permitted to use the over-temperature sensor as the resident SAT sensor provided it is used only for over temperature protection and meets all of the requirements of an SAT sensor, 3.4.7.3, and Table 13.
允许使用超温传感器作为固定SAT传感器,前提是它只用于超温保护,并满足SAT传感器的所有要求(3.4.7.3和表13)。
3.4.8 Alternate SAT 替代SAT
3.4.8.1 The alternate SAT method shall only be applied to the following sensor systems:
替代SAT方法只适用于以下传感器系统:
3.4.8.1.1 Load sensor systems (expendable and non-expendable) where the sensor is used only once (single use) at temperatures >500 ℉ or >260 ℃
在温度>260℃时的载荷传感器系统(易耗型和耐久型)其传感器仅使用1次(单次使用)。
3.4.8.1.2 Load sensor systems (expendable and non-expendable) used at temperatures ≤500 ℉ or ≤260 ℃ where the sensor is replaced at the same or less than the SAT interval.
载荷传感器系统(易耗型和耐久型)使用在温度≤260℃,传感器在相同或更小SAT间隔替换。
3.4.8.1.3 Control and recording sensors (e.g., hot and/or cold recording sensors for instrumentation Types A or C and the additional recording sensor for instrumentation Type D+) where the sensor is replaced at the same or less than the SAT interval. Section 3.1.10 shall also apply to base metal recording sensors when the alternate SAT is used.
控制和记录传感器(例如,用于A或C类型仪表的热和/或冷记录传感器,以及用于D+类型仪表的附加记录传感器),传感器在相同或更小SAT间隔替换。当使用备用SAT时,第3.1.10条也适用于廉金属记录传感器。
3.4.8.2 Alternate SAT Method SAT方法
Periodic calibration of control and/or recording instruments as stated in 3.2.3.4 or 3.2.3.5 and meeting the requirements of Table 7 shall be performed from the point at which the sensor will be connected (including the instrument/extension wire/connector) and one of the following three options are met.
按照3.2.3.4或3.2.3.5的规定,对控制和/或记录仪器进行定期校准,并满足表7的要求,应从传感器连接点(包括仪器/延长线/连接器)开始,并满足以下三种选择之一。
3.4.8.2.1 The sum of the sensor calibration error plus the instrument calibration error or sensor calibration correction factor plus the instrument calibration correction factor shall meet the maximum SAT difference requirements of Table 11 or 12, as appropriate.
传感器校准误差+仪表校准误差或传感器校准修正系数+仪表校准修正系数的总和应满足表11或表12的最大SAT差值要求,视情况而定。
3.4.8.2.2 Use the appropriate sensor and instrument correction factors applied manually or via programming, as allowed by the calibration limits of Tables 1 and 7, so that data used from the control and recording instrument combined meets the maximum SAT difference requirements of Table 11 or 12, as appropriate.
在表1和表7的校准范围允许的情况下,使用适当的传感器和仪表修正因子(手动或通过编程),以便从控制和记录仪表组合使用的数据满足表11或表12的最大SAT差值要求。
3.4.8.2.3 Limit instrument calibration error or correction factor and/or sensor error or correction factor such that the sum of the errors or correction factors cannot exceed the maximum SAT difference defined by Table 11 or 12 accordingly. The sensor lot identification used in the equipment during the alternate SAT period shall be documented.
限制仪表校准误差或修正系数和/或传感器误差或修正系数,使误差或修正系数之和不能超过表11或12相应定义的最大SAT差值。应记录替代SAT期间设备中使用的传感器批次标识。
Example 1: Maximum SAT difference for a Class 5 furnace is the greater of ±5.0 ℉ or ±3.0 ℃ or ±0.5% (see Table 11). Limiting instrument calibration to ±1.0 ℉ or ±.0.6 ℃ or ±0.1% and limiting sensor calibration to (±2.0 ℉ or ±1.1 ℃ or ±0.3%) will always meet the maximum SAT difference.
例1:5类炉的最大SAT差值为±3.0℃或±0.5%(见表11)。将仪表校准限制在±0.6℃或±0.1%,将传感器校准限制在(±1.1℃或±0.3%)将始终满足最大SAT差值。
Example 2: Maximum SAT difference for a Class 2 furnace is the greater of ±3.0 ℉ or ±1.7 ℃ or ±0.3% (see Table 11). Limiting instrument calibration to ±1.0 ℉ or ±0.6 ℃ or ±0.1% and limiting sensor calibration to ±2.0 ℉ or ±1.1 ℃ or ±0.2% will always meet the maximum SAT difference.
例2:2类炉的最大SAT差值为±1.7℃或±0.3%(见表11)。将仪表校准限制在±0.6℃或±0.1%,将传感器校准限制在±1.1℃或±0.2%,将始终满足最大SAT差值。
3.4.8.3 Alternate SAT Frequency
The alternate SAT shall be performed and documented when any of the following occurs
当出现下列任何情况时,应执行并记录备用SAT
• Systems utilizing individually calibrated sensors require the alternate SAT upon replacement of each sensor.
使用单独校准传感器的系统在更换每个传感器时需要备用SAT。
• Systems utilizing sensors from the same calibrated roll/spool require an alternate SAT upon replacement of the roll/spool.
使用来自同一校准卷/轴的传感器的系统在更换卷/轴时需要备用SAT。
• Calibration of the system instrument (control or recording).
•系统仪器的校准(控制或记录)。
3.4.8.4 The alternate SAT calculation shall be performed at each temperature on the most recent instrumentation calibration report and using sensor data from the sensor calibration report applicable to the sensor used. Sections 3.1.4.8 through 3.1.4.10 shall apply for sensor temperatures.
应在最近的仪表校准报告上对每个温度进行替换SAT计算,并使用适用于所用传感器的传感器校准报告中的传感器数据。第3.1.4.8至3.1.4.10节适用于传感器温度。
3.4.9 SAT Waiver豁免
The SAT waiver requirements are as follows SAT豁免要求如下:
3.4.9.1 There shall be at least two recording load sensors in each control zone.
每个控制区至少有两个可记录的载荷传感器。
3.4.9.2 Noble metal load sensors shall be either replaced or recalibrated quarterly.
贵金属载荷传感器应每季度更换或重新校准。
3.4.9.3 Base metal load sensors shall be controlled as follows廉金属载荷传感器应按以下方式控制:3.4.9.3.1 Expendable base metal load sensors shall be single use only.
易耗型廉金属载荷传感器仅一次性使用。
3.4.9.3.2 Non-expendable base metal load sensors shall meet the replacement requirements in Table 6 and shall be recalibrated or replaced anytime that observations, made and recorded at least weekly, reveal any unexplainable difference between their readings and the readings of the two recording sensors in 3.4.9.6.
耐久型廉金属载荷传感器应满足表6的更换要求,如果至少每周观察和记录,发现其读数与两个记录传感器在3.4.9.6中的读数之间存在无法解释的差异,则应随时重新校准或更换。
3.4.9.4 Noble metal control and recording sensors shall be replaced at least every 2 years.
贵金属控制和记录传感器应至少每两年更换。
3.4.9.5 Base metal control and recording sensors shall be replaced at least quarterly.
廉金属控制和记录传感器应至少每季度更换。
3.4.9.6 Weekly readings at one production set point measured within 5 minutes of the end of a production soak period shall be compared. The relationship between the control sensor and an additional sensor in each control zone shall remain within 2.0 ℉ or 1.1 ℃ of their relationship determined at the time of the most recent TUS (at the nearest temperature tested during the most recent TUS). The additional sensor may be the over-temperature sensor. Weekly readings shall be taken from the same sensor pair between two consecutive TUS.
应比较在生产浸泡期结束后5分钟内测量的一个生产设定点的每周读数。每个控制区的控制传感器和另一个传感器之间的关系应保持在最近的TUS时间(最近的TUS期间测试的最近的温度)确定的1.1℃范围内。附加的传感器可能是超温传感器。每周读数应从两个连续的TUS之间的同一传感器对中读取。
3.4.9.6.1 The two sensors chosen shall be different types following the same restrictions as resident SAT sensors in Table 13. The additional recording sensor shall be restricted to Type B, R, S, or N at temperatures greater than 500 ℉ or 260 ℃ and shall be non-expendable at temperatures greater than 1000 ℉ or 538 ℃ (see Table 5).
选择的两种传感器应是不同类型的,与表13中固定SAT传感器的限制相同。附加的记录传感器在温度大于260℃时应限制为B、R、S或N型,在温度大于538℃时应是耐久型的(见表5)。
3.4.9.6.2 During each periodic TUS, the relationship between the control sensor system and the additional sensor system shall be determined by calculating the temperature of the control sensor minus the temperature of the additional sensor within the final 5 minutes (single reading or average of the last 5 minutes) of the TUS soak period to determine the relationship at each TUS temperature (see Table 14).
在每个周期的TUS中,控制传感器系统和附加传感器系统之间的关系应通过计算控制传感器的温度减去附加传感器在TUS浸泡周期的最后5分钟内的温度(单次读数或最后5分钟的平均值)来确定在每个TUS温度下的关系(见表14)。
3.4.9.6.3 If the weekly relationship exceeds 2.0 ℉ or 1.1 ℃, then one of the following options shall apply.
如果每周关系超过1.1℃,则下列选项之一将适用。
3.4.9.6.3.1 A successful SAT using one of the other methods (comparison or alternate) shall be performed before returning to production.
在返回生产之前,应使用其他方法(比较或替代)中的一种进行成功的SAT。
3.4.9.6.3.2 After 4.5, 4.6, 4.7, and 4.8 are completed, the SAT waiver relationship shall be reestablished by performing a TUS at all required temperatures of the initial TUS. The TUS interval shall continue at the interval in use at the time of the last periodic TUS.
在完成4.5、4.6、4.7和4.8后,通过在初始TUS的所有要求温度下进行TUS,重新建立SAT豁免关系。TUS间隔应继续在最后一个周期TUS时的使用间隔。
3.4.10 SAT Difference Pass/Fail Requirements SAT差值通过/失败要求
3.4.10.1 It is not permitted to apply modification offsets to achieve an acceptable SAT.
不允许使用修改偏移来达到可接受的SAT。
3.4.10.2 If the calculated SAT difference exceeds the allowable difference of Table 11 or 12, the failure shall be documented, the cause of the difference determined, and corrective action taken before commencing additional thermal processing. The requirements of Section 4 shall apply.
如果计算出的SAT差值超过表11或表12的允许差值,则应记录故障,确定差值的原因,并在开始额外的热处理之前采取纠正措施。应用第4章的要求。
3.4.10.3 If the cause is wholly or partially a result of movement of the sensor being tested from its documented location and depth of insertion, it shall be returned to its original documented location and depth of insertion and the SAT repeated.
如果原因完全或部分是由于传感器从文件记录的插入位置和深度进行测试时移动造成的,则应将其返回到其原始文件记录的插入位置和深度,并重复进行SAT测试。
3.4.10.4 Instrument recalibration or adjustment, including any correction offset of the control or recording instrument calibration, is permitted within the maximum limitations of Table 15 or 16. The effect of this recalibration adjustment over the entire qualified operating temperature range shall be evaluated and objective evidence that the correction offset would not cause a failure of any other calculated SAT or TUS shall be documented. The requirements of 3.4.2.3 and Section 4 shall apply.
允许在表15或16的最大限度内进行仪表重新校准或调整,包括控制或记录仪表校准的任何校正偏移量。应评估该重校调整对整个合格操作温度范围的影响,并记录修正偏差不会导致任何其他计算的SAT或TUS失效的客观证据。适用3.4.2.2和4的要求。
3.4.10.5 All corrective actions shall be documented. After corrective action has been implemented and prior to any additional thermal processing, the SAT shall be repeated and yield an acceptable SAT difference. The results of both the failed and acceptable SAT shall be documented.
所有纠正措施应形成文件。在实施纠正措施后,在进行任何额外的热处理之前,应重复进行SAT测试,并产生可接受的SAT差值。失败的和可接受的SAT都应被记录。
3.4.11 SAT Results and Records SAT结果和记录
3.4.11.1 Comparison SAT (see 3.4.7) 比对SAT
The results of the comparison SAT shall be documented. At a minimum, the documentation for each sensor system tested shall include 应记录比对SAT的结果。被测试的每个传感器系统的文件至少应包括:
a. Identification of the sensor system being tested识别正在测试的传感器系统。
b. Identification of the SAT sensor and depth of insertion when Type K or E is reused.
当K型或E型重复使用时,SAT传感器的识别和插入深度。
c. Identification of the SAT instrument 仪表的识别。
d. Date and time of the SAT 日期和时间。
e. Set point of the thermal processing equipment during the SAT, The test temperature shall be documented as the SAT set point for thermal processing equipment that dose not have a set point temperature
期间热处理设备的设定值,对于没有设定点温度的热加工设备,测试温度应作为SAT设定点记录在案。
f. Observed control or recording instrument readings and recordings观察控制或记录仪表读数和记录。
g. Observed SAT instrument readings观测到的SAT仪表读数。
h. SAT sensor correction factor 传感器校正系数。
i. SAT instrument correction factor 仪表校正系数。
j. Corrected SAT instrument reading 修正SAT仪表读数。
k. Calculated SAT difference (control and recording instrument readings minus the corrected SAT instrument reading) 计算SAT差值(控制和记录仪表读数减去校正的SAT仪表读数)。
l. As-found and as-left correction and/or modification offsets if used during production.
如在生产过程中使用,发现和左校正和/或修改偏移。
m. SAT difference pass or fail statement SAT差异通过或不通过声明。
n. Identification of the technician who performed the SAT 鉴定参加SAT考试的技术人员。
o. Identification of the agency if SAT is not performed internally 如果SAT没在内部进行,对该机构的识别。
p. Approval of an authorized agent for the calibration agency if not performed internally.
对校准机构的授权代理的批准(如果不是内部执行)。
q. User quality organization approval 用户质量组织批准。
3.4.11.2 Alternate SAT (see 3.4.8) 替代SAT
The results of the alternate SAT shall be documented. At a minimum, the documentation for each sensor system tested shall include应记录替代SAT的结果。被测试的每个传感器系统的文件至少应包括:
a. Identification of the sensor system being tested识别正在测试的传感器系统。
b. Identification of the sensor or roll识别传感器或辊。
c. Date and time of the alternate SAT 替代SAT的日期和时间
d. Method used使用的方法
1. Sum of calibration errors or correction factors (see 3.4.8.2.1)校正误差或校正因子之和(见3.4.8.2.1
2. Correction factors applied manually or via programming (see 3.4.8.2.2)手动或通过编程应用的校正因子(见3.4.8.2.2)。
3. Limit instrument/thermocouple calibration errors or correction factors such that SAT is always met (see 3.4.8.2.3) 限制仪表/热电偶校准误差或校正系数,使其始终满足SAT(见3.4.8.2.3)。
e. Final SAT results calculated for the method used with supporting documentation
最终SAT结果计算方法使用的支持文件。
f. Identification of the technician who performed the alternate SAT, as applicable
适用时,对执行替代SAT的技术人员的识别。
g. Identification of the agency if the alternate SAT is not performed internally
如果SAT没在内部进行,识别机构。
h. Approval of an authorized agent for the agency performing the alternate SAT if not performed internally
如果没在内部进行,则授权代理人对执行替代SAT的机构的批准。
i. User quality organization approval用户质量组织批准。
3.4.11.3 SAT Waiver (see 3.4.9) SAT豁免
The results of the SAT waiver shall be documented. At a minimum, the documentation for each piece of thermal processing equipment shall include应记录SAT豁免的结果。每件热加工设备的文件至少应包括:
a. Identification of the thermal processing equipment using the SAT waiver.
识别使用SAT豁免的热加工设备。
b. Identification of the control and additional sensor system used for the relationship test.
识别用于关系测试的控制和附加传感器系统。
c. Date of installation of the control and additional sensor used for the relationship test.
用于关系测试的控制装置和附加传感器的安装日期。
d. Date and temperature(s) of the most recent TUS.
最近一次TUS的日期和温度。
e. Documentation of the relationship at each TUS temperature (see Table 14).
各温度下的关系文档(见表14)。
f. Documentation of the weekly readings and relationship (see Table 14).
每周读数的记录及其关系(见表14)。
g. Identification of the agency if the SAT waiver is not performed internally如果SAT豁免没在内部执行,识别机构。
h. Approval of an authorized agent for the agency performing the SAT waiver if not performed internally如果没在内部执行SAT豁免,授权代理机构的批准。
i. User quality organization approval用户质量组织批准。
Table 14 - SAT waiver relationship SAT豁免关系
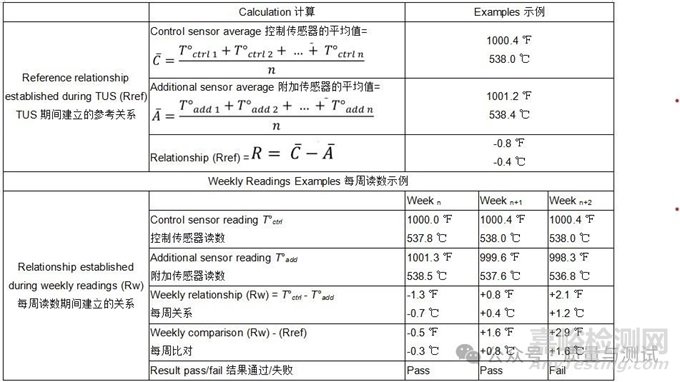
3.5 Temperature Uniformity Surveys (TUS)温度均匀性测量
3.5.1 General TUS Requirements一般要求
3.5.1.1 The TUS shall be performed using calibrated and independent TUS sensors meeting the requirements of Table 1 and calibrated and independent TUS instruments meeting the requirements of Table 7.
使用符合表1要求校准的、单独的TUS传感器和符合表7要求校准的、单独的TUS仪表进行TUS。
3.5.1.2 Recording instruments used on thermal processing equipment shall not be used to record TUS sensor temperatures unless it can be demonstrated that the TUS sensor recording channels of an integrated system are separated from the thermal processing equipment recording system and also meet field test instrument requirements.
热加工设备上使用的记录仪表不得用于记录TUS传感器的温度,除非能证明集成系统的TUS传感器记录通道与热处理设备记录系统是分离的,并且满足现场测试仪表的要求。
3.5.1.3 An initial TUS shall be performed to determine the temperature uniformity and establish the qualified work zone(s) and qualified operating temperature range(s).
初始温度均匀性测量应确定温度均匀性并建立合格的工作区和合格的操作温度范围。
3.5.1.4 During initial and periodic TUS, the dimensions of the measuring junction locations of the corner sensors for a square or rectangle work zone or the periphery sensors of a cylindrical work zone shall define the extremities of the work zone such that no material heat treated extends beyond these boundaries.
在初始和周期性温度均匀性测量过程中,方形或矩形工作区的拐角传感器或圆柱形工作区的外边界传感器测量端位置的尺寸定义为工作区的边界,这样就不会有经过热处理的材料延伸出这些边界。
Table 15 - Parts furnace class, instrument type, and TUS interval工件炉类别、仪表类型和TUS周期
(1) The maximum permitted offset shall be the same for manual and electronic methods.
对于手工和电子方法最大允许补偿相同。
(2) ℉ or ℃ or % of reading, whichever is greater ℃或读数的%,取较大者。
(3) The maximum is permitted for TUS modification offsets and SAT correction offsets separately.
系统精度校验和温度均匀性测量的补偿是独立的,对两者都是最大允许调整量。
Table 16 - Raw material furnace class, instrument type, and TUS interval
原材料炉类别、仪表类型和温度均匀性测量周期
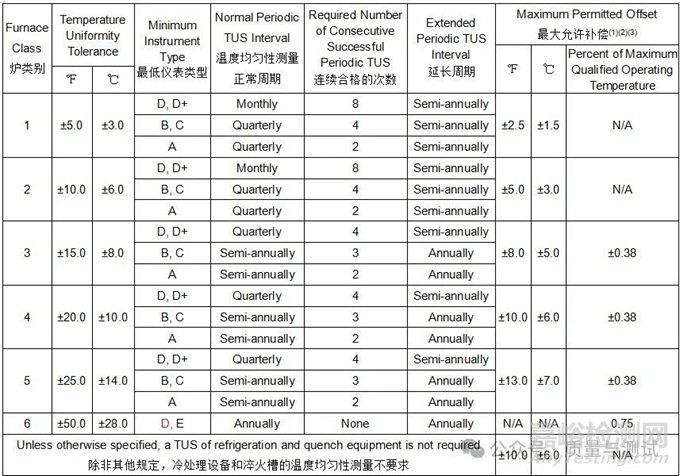
(1) The maximum permitted offset shall be the same for manual and electronic methods.
对于手工和电子方法最大允许补偿相同。
(2) ℉ or ℃ or % of reading, whichever is greater ℃或读数的%,取较大者。
(3) The maximum is permitted for TUS modification offsets and SAT correction offsets separately.
系统精度校验和温度均匀性测试的补偿是独立的,对两者都是最大允许调整量。
3.5.2 Initial TUS Temperatures初始温度均匀性测量温度
3.5.2.1 The initial TUS shall be performed at the minimum and maximum temperatures of each qualified operating temperature range(s).
初始温度均匀性测量应在每个合格工作作温度范围的最低温度和最高温度下进行。
3.5.2.2 Additional TUS temperatures shall be added to ensure that there are no more than 600 ℉ or 335 ℃ increments between adjacent TUS temperatures.
附加温度均匀性测量温度应确保相邻的温度均匀性测量温度之间的增量不超过335℃。
Example: If a furnace is used from 800 to 1800 ℉ or 425 to 980 ℃, the furnace shall be surveyed at 800 ℉ or 425 ℃, 1800 ℉ or 980 ℃, and one intermediate temperature to meet the maximum permitted 600 ℉ or 335 ℃ range requirement. Performing a TUS at any temperature from 1200 to 1400 ℉ or 645 to 760 ℃ would satisfy the 600 ℉ or 335 ℃ range requirement.
示例:如果炉子在425℃ ~ 980℃范围内使用,炉应在425℃、980℃和一个中间温度测量,以满足最大允许的335℃范围要求。在645(980-335)℃ ~ 760(425+335)℃的任何温度下进行温度均匀性测量将满足335℃的范围要求。
3.5.2.3 It is not required to include hottest and coldest recording sensors for instrument Type A and C equipment during the initial TUS. The initial TUS defines the location of these sensors.
在初始温度均匀性测量期间,不要求包括A型和C型仪表设备的最高温度和最低温度的记录传感器。初始温度均匀性测量定义了这些传感器的位置。
3.5.2.4 For thermal processing equipment used only at a single set point temperature, the TUS shall be performed at that single temperature.
对于仅在单一设定点温度下使用的热加工设备,应在该单一温度下进行TUS。
3.5.3 Periodic TUS Temperatures周期性温度均匀性测量温度
3.5.3.1 Periodic TUS shall be performed at any temperature within each qualified operating temperature range(s)温度均匀性周期测量应在每个合格工作温度范围内的任一温度下进行。
3.5.3.2 A periodic TUS shall be performed at the minimum of each qualified temperature range and at the maximum temperature of each qualified operating temperature range at least annually.
温度均匀性周期测量每年至少在每个合格温度范围的最低温度和最高温度下进行一次。
3.5.3.3 TUS Temperatures for Equipment with Single Qualified Operating Temperature Range.
具有单一合格工作温度范围设备的温度均匀性测量温度。
3.5.3.3.1 For single operating temperature ranges greater than 600 ℉ or 335 ℃, during each periodic TUS, temperatures shall be selected so that one temperature is within 300 ℉ or 170 ℃ of the maximum and another temperature is within 300 ℉ or 170 ℃ of the minimum of qualified operating temperature range(s) and there are no more than 600 ℉ or 335 ℃ increments in between adjacent TUS temperatures.
对于单一工作温度范围超过335℃的,在每个周期性的温度均匀性测量时,测量温度应选择合格工作温度上下限170℃范围内,并且相邻的温度均匀性测量温度之间的增量不超过335℃。
Example: If the qualified operating temperature range is 200 to 1200 ℉ ±10 ℉ or 90 to 650 ℃ ± 6 ℃, a TUS temperature shall be selected between 200 ℉ and 500 ℉ or 90 ℃ and 260 ℃ and between 900 ℉ and 1200 ℉ or 480 ℃ and 650 ℃. No two adjacent TUS temperatures shall be greater than 600 ℉ or 335 ℃ apart.
示例:如果合格的工作温度范围为90℃ ~ 650℃±6℃,则温度均匀性测量温度应在90℃ ~ 260(90+170)℃和480(650-170)℃ ~ 650℃之间选择。两个相邻的温度均匀性测量温度间隔不超过335℃。
A TUS at 350 ℉ or 177 ℃ and at 950 ℉ or 510 ℃ would be acceptable. However, a TUS at 250 ℉ or 121 ℃ and 1000 ℉ or 538 ℃ would not be acceptable since these temperatures exceed the 600 ℉ or 335 ℃ separation increment.
温度均匀性测量在177℃和510℃是可以接受的。然而,温度均匀性测量在121℃和538℃是不可接受的,因为这些温度超过335℃的间隔增量。
3.5.3.4 TUS Temperatures for Equipment with Multiple Qualified Operating Temperature Ranges.
设备具有多个合格工作温度范围的温度均匀性测量温度。
3.5.3.4.1 For equipment with multiple operating temperature ranges, each sub-range shall be treated as a single operating temperature range and the requirements of 3.5.3.1, 3.5.3.2, and 3.5.3.3 apply to each sub-range.
对于具有多个工作温度范围的设备,每个子范围应视为一个工作温度范围,每个子范围适用于3.5.3.1、3.5.3.2、3.5.3.3的要求。
Example 1: A furnace may be qualified to operate within from 600 to 1000 ℉ ± 10.0 ℉ or 315 to 540 ℃ ± 6.0 ℃ and from 1000 to 1800 ℉ ± 25.0 ℉ or 540 to 980 ℃ ± 14.0 ℃. The furnace contains two separate qualified operating temperature ranges.
A furnace meeting ±10.0 ℉ at 1000 ℉ or ±6.0 ℃ at 540 ℃ automatically meets ±25.0 ℉ at 1000 ℉ or ±14.0 ℃ at 540 ℃; therefore, a duplicate TUS at 1000 ℉ or 540 ℃ is not required.
示例1:一个炉子可在315~540℃±6.0℃和540~980℃±14.0℃的合格工作范围。该炉包含两个独立的合格工作温度范围。
炉子在540℃满足±6.0℃,自然在540℃满足±14.0℃;因此,不需要在540℃重复温度均匀性测量。
Example 2: If the qualified operating temperature ranges are 800 to 1025 ℉ ± 10.0 ℉ or 425 to 550 ℃ ± 6.0 ℃, 1025 to 1400 ℉ ± 15.0 ℉ or 550 to 760 ℃ ± 8.0 ℃ and 1400 to 1600 ℉ ± 25.0 ℉ or 760 to 870 ℃ ± 14.0 ℃.
Annually, the TUS would be performed at: 800 ℉ and 1025 ℉ or 425 ℃ and 550 ℃ and meet ±10.0 ℉ or ±6.0 ℃, 1400 ℉ or 760 ℃ and meet ±15.0 ℉ or ±8.0 ℃ and 1600 ℉ or 870 ℃ and meet ±25.0 ℉ or ±14.0 ℃.
示例2:如果工作温度范围是425 ~ 550℃±6.0℃, 550 ~ 760℃±8.0℃和760 ~ 870℃±14.0℃。
每年,温度均匀性将在425℃和550℃测量满足±6.0℃,760℃测量满足±8.0℃和870℃测量满足±14.0℃。
3.5.4 Equipment Modifications and Repairs设备改造及维修
When maintenance is performed on thermal processing equipment, the maintenance task shall be documented, and a determination shall be made and documented by the user quality assurance organization whether any testing is required before returning the equipment into service. This determination may require a new initial TUS, performing an additional TUS, or no testing at all.
当对热加工设备进行维护时,维护活动应形成文件。在设备恢复使用前是否需要进行任何测量,应由用户质量保证组织确定并形成文件。这个确定可能需要一个新的初始温度均匀性测量,执行附加的温度均匀性测量,或者根本不需要测量。
3.5.4.1 Major Modifications and Repairs重要改造及维修
3.5.4.1.1 A new initial TUS and SAT shall be performed after any of the following equipment modifications, repairs, or adjustments that could have altered the thermal characteristics of the equipment. Examples where an initial TUS and SAT is required include, but are not limited to, the following:
在下列任一项可能改变设备加热特性的设备改造、维修或调整后,应执行新的初始温度均匀性测量和系统精度校验。初始温度均匀性测量和系统精度校验要求包括但不限于以下内容:
a. Relocation of thermal processing equipment. The initial TUS may be waived if the thermal processing equipment is designed to be portable—i.e., the thermal processing equipment has permanent wheels or other means of portability —but in some cases, a new periodic TUS can be necessary.
热加工设备搬迁。初始温度均匀性测量可能豁免,如果热加工设备是便携式的,即,热加工设备有永久性的轮子或其他便携工具,但在某些情况下,一个新的温度均匀性测量周期是必要的。
b. Increase in the maximum qualified operating temperature or decrease in the minimum qualified operating temperature. 提高最高合格工作温度或降低最低合格工作温度。
c. Burner size, number, type, or location change. 炉膛尺寸、数量、类型或位置发生改变。
d. Heating element number, type, or location change. 加热元件数量、类型或位置发生改变。
e. Changes to airflow pattern/velocity such as baffle positions, fan speed, fan quantity, etc.
气流模式/速度的改变,如挡板位置、风扇速度、风扇数量等。
f. Change of refractory thickness. 耐火材料厚度的改变。
g. New refractory with different thermal properties. 具有不同热性能的新型耐火材料。
h. Change of vacuum furnace hot zone design or materials. 真空炉加热区布局或材料的改变。
i. Change of control sensor (e.g., type, thickness of sensor assembly, gauge of the sensor elements, or hot junction construction). 控制传感器的改变(例如,传感器组件的类型、厚度,传感器元件的规格或热接端)。
j. Change of the control sensor location. 控制传感器位置的改变。
k. Change of combustion pressure settings from their original settings. 燃烧压力设置从原来设置的改变。
l. Change of furnace operating atmosphere damper system settings from their original settings.
炉膛工作气氛阻尼器系统设置从原来的设置的改变。
m. Control instrument or program change 控制仪表或程序的改变:
1. Proportional versus high-low/off-on 成比例高低/断开。
2. Change of the control instrument model or type 控制仪表的模式或类型的改变。
3. PLC logic program change to the furnace heat control scheme PLC逻辑程序改为炉膛热控制方案。
4. Adjustment of control instrument tuning constants, parameters, or rheostats.
控制仪表调谐常数、参数或可变电阻的改变。
n. Qualified work zone volume increase covering a volume not previously surveyed.
合格工作区容积增加,包括先前未测量的容积。
o. Qualified work zone location change covering a volume not previously surveyed.
合格的工作区位置的改变,包括以前未测量的体积。
3.5.5 Periodic TUS Intervals温度均匀性测量周期
3.5.5.1 A periodic TUS shall be performed at the normal periodic TUS interval in accordance with Table 15 or 16 based on furnace class and instrumentation type.
周期性温度均匀性测量应按照表15或表16炉子类别和仪表类型的温度均匀性测量的正常周期进行。
3.5.5.2 Extended periodic TUS intervals may be used based on furnace class, instrument type, and history of the required number of consecutive successful periodic TUS shown in Tables 15 and 16 after an initial TUS. In addition, a documented equipment preventive maintenance program, in accordance with 2.2.42, shall be in effect.
基于炉子类别、仪表类型、初始TUS后表15和表16所示的连续合格的TUS次数,可以使用延长周期的TUS间隔。此外,应根据2.2.42制定文件化的设备预防性维护程序。
3.5.5.3 If equipment modifications, repairs, or adjustments as described in 3.5.4.1.1 are made the TUS interval shall revert to the normal periodic TUS interval until the required number of consecutive successful periodic TUS are completed.
如果进行了3.5.4.1.1所述的设备改造、维修或调整,则温度均匀性测量间隔应恢复到正常的周期性温度均匀性测量间隔,直到完成连续合格的周期性温度均匀性测量次数。
3.5.6 Equipment Parameters During the TUS温度均匀性测量期间的设备参数
3.5.6.1 During each TUS, except as outlined in 3.5.8 and 3.5.9, all parameters shall reflect the normal operation of the equipment during production. Examples of normal equipment operation include, but are not limited to, the following:
在每次温度均匀性测量期间,除3.5.8和3.5.9所述外,所有参数均应反映设备在生产过程中正常运行的情况。设备正常运行的例子包括但不限于:
a. If the doors of a continuous furnace are normally open during production, they shall also be open during the TUS.
如果连续炉的炉门在生产过程中正常开着的,则在温度均匀性测量期间也应开着。
b. If slow heat up rates and stabilization temperatures are not used during production, they shall not be used during the TUS.
如果在生产过程中没有使用慢速加热和稳定温度,则在温度均匀性测量期间不得使用。
c. Any documented ramp rate used during production shall be acceptable when performing the TUS. 在进行温度均匀性测量时,任何在生产过程中使用的升温速率文件都是可以接受的。
d. If excess combustion air is used during production, it shall also be used during the TUS.
如果在生产过程中使用了多余的助燃空气,则在温度均匀性测量期间也应使用。
e. If circulating fans are operated during production, they shall also be operated during the TUS.
如果循环风机在生产过程中运行,则在温度均匀性测量期间也应运行。
3.5.7 Equipment Temperature When TUS Sensors Are Inserted温度均匀性测量传感器插入时设备温度
3.5.7.1 If the normal operation of the equipment when used during production is to load parts or raw material into a hot furnace, it is acceptable to insert the TUS sensors into the furnace with the furnace cold or with the furnace stabilized at or below the TUS temperature.
如果设备在生产使用时正常操作是将工件或原材料装入热炉,则可在冷炉或炉温稳定在或低于温度均匀性测量温度的情况下将温度均匀性测量传感器插入炉中。
3.5.7.2 If the normal operation of the equipment when used during production is to load parts or raw material into a cold furnace, pre-heating the furnace prior to the coldest TUS temperature to perform the TUS is not permitted. Ramping from the coldest TUS temperature to a higher test temperature is permitted.
如果设备在生产使用时正常操作是将工件或原材料装入冷炉,则不允许在低于温度均匀性测量温度对炉子进行预热。允许从低于温度均匀性测量温度升到更高的测试温度。
3.5.8 Load Condition and Atmospheres During the TUS温度均匀性测量期间载荷情况和气氛
3.5.8.1 A TUS may be performed with a production load, simulated production load, a rack, or empty. Once a method of surveying the equipment is established during the initial TUS, subsequent periodic TUS shall be conducted using the same method. If changes are made to the established method, an initial TUS shall be performed to validate the revised method and the TUS interval shall revert to the normal periodic TUS interval until the required number of consecutive successful periodic TUS are completed.
温度均匀性测量可在生产载荷、模拟生产载荷、支架或空载下进行。一旦在初始温度均匀性测量时确定了该设备的测量方法,随后的周期温度均匀性测量应采用相同的方法。如对已建立的方法进行了更改,应进行初始温度均匀性测量以验证更改后的方法,并将温度均匀性测量周期恢复到正常周期,直到完成连续合格的周期性温度均匀性测量次数。
3.5.8.2 If the TUS is performed empty or with a rack, and if TUS sensors are attached to or inserted into heat sinks, the side-to-side thickness or diameter of the heat sink shall not exceed 0.5 inch or 13 mm and shall not exceed the thickness of the thinnest material being processed in that equipment. Heat sink material shall be the material with the highest room temperature thermal conductivity consistent with the predominant part or raw material processed in the equipment.
如温度均匀性测量是空载或有支架进行的,温度均匀性测量传感器紧贴在或插入到测温试块中,测温试块的厚度或直径应不超过13mm,且不应超过该设备加工的最薄材料的厚度。测温试块材料的室温热传导率应与设备所处理工件或原材料室温热传导率相一致或更高的材料。
3.5.8.3 When the TUS is performed with a load and the TUS sensors are attached to simulated parts or raw material, the load shall represent the thickness of the material normally used during production.
当温度均匀性测量在装载下进行,且温度均匀性测量传感器紧贴在模拟工件或原材料上时,装料应代表生产中通常使用的材料厚度。
3.5.8.4 The atmosphere used during a TUS shall be the normal atmosphere used during production. Equipment used for processes whose required atmospheres could contaminate the TUS sensors (i.e., carburizing, nitriding, endothermic, and exothermic gases) or atmospheres that could pose a safety hazard (i.e., hydrogen or ammonia containing gases) may be surveyed with an atmosphere of air or inert gas.
在温度均匀性测量中使用的气氛应是正常生产时的气氛。对于可能污染温度均匀性测量传感器的工艺过程(如渗碳、氮化、吸热和放热气体)或可能造成安全危害的环境(如含氢或含氨气体),可以采用空气或惰性气体来代替。
3.5.8.5 The furnace vacuum level used during the TUS shall be the lowest vacuum level used during production but need not be less than 1.0 x 10-3 mm Hg (1 x 10-3 Torr or 1.3 x 10-3 millibar).
温度均匀性测量时使用的炉膛真空度应是生产时的最低真空度,但应不低于1.0×10-3 mm Hg (0.133Pa)。
3.5.8.6 For vacuum furnaces operated in partial pressure (with backfill gas) during production, at least one of the periodic TUSs shall be performed annually at a minimum of one operating temperature and within the partial pressure range used in production. The gas used shall be one of the gases used during production.
对生产中分压(带回填气体)操作的真空炉,每年至少要进行一次周期温度均匀性测量,至少要在生产中使用分压范围内的每个操作温度下进行一次。使用的气体应是生产使用的气体之一。
3.5.9 TUS Requirements for Batch Furnaces, Salt Baths, Controlled Temperature Liquid Baths, and Fluidized Bed Furnaces (Excluding Controlled Temperature Quench Baths)
周期炉、盐浴炉、控温液浴炉和流态床炉(不包括控温淬火浴)的温度均匀性测量要求
3.5.9.1 The number of TUS sensors required during the TUS shall be in accordance with Figure 1 and Tables 17 and 18. An initial TUS of multiple control zone furnaces with Type A or C instrumentation shall be performed with sufficient additional TUS sensors to adequately evaluate the temperature extremes of each control zone to identify hot and cold recording sensor locations.
温度均匀性测量中所需的测量传感器数量按照图1、表17和表18。采用A型或C型仪表的多区控制炉的初始温度均匀性测量应使用足够的附加测量传感器来充分评估每个控制区的极端温度,以识别最高和最低温度记录传感器的位置。
Table 17 - Minimum number of TUS sensors and required locations最少测量传感器数量和所需位置
(1)The location of TUS sensors for ≥3 ft3 to <6.4 m3 may be used for volumes <3 ft3.
≥ 0.085 m3 to < 6.4 m3的温度均匀性测量传感器位置可使用体积< 0.085 m3的。
Table 18 - Number of TUS sensors required for batch furnaces, salt baths,controlled temperature
liquid baths, fluidized bed furnaces, or continuous furnaces surveyed using the volumetric method
使用容积法测量的周期炉、盐浴炉、控温液浴炉、流态床炉或连续炉所需的测量传感器数量
Notes:
(1) For qualified work zone volumes greater than 4000 ft3 or 113 m3, the applicable furnace class formula as illustrated in the table below shall be used to determine the number of TUS sensors.
(1)对于超过4000立方英尺或113立方米的合格工作区,适用的炉级公式如下表应使用所示,以确定TUS传感器的数量。
(2) For qualified work zone volumes less than 4000 ft3 or 113 m3, it is acceptable to use the appropriate furnace class formula, as illustrated in the table below or interpolation, to determine the number of TUS sensors
对于合格的工作区域体积小于4000立方英尺或113立方米的,可以使用适当的炉级公式,如下表所示或插补,来确定TUS传感器的数量


For square/rectangular volumes < 3 ft3 or 0.085 m3 users shall choose locations 1, 4, 5, 7, & 8
or, locations 2, 3, 5, 6, & 9. Location 5 being in the center.
对于小于3平方英尺或0.085立方米的方形/矩形体量,用户应选择位置1、4、5、7和8或位置2、3、5、6和9。位置5位于中心。
For cylindrical volumes < 3 ft3 or 0.085 m3, locations 1 & 2 and 3 & 4, the pairs being 180 degrees apart at the opposite ends and location 5 in the center shall be used. Locations 1/2 and 3/4 shall be offset 90 degrees rotationally from each other.
对于< 3立方英尺或0.085立方米的圆柱体,位置1和2和3和4,对在相反的两端相距180度,位置5在中心应使用。位置1/2和3/4应该互相旋转偏移90度。
For square/rectangular volumes and cylindrical volumes ≥ 3 ft3 or 0.085 m3 but less than 225 ft3 or 6.4 m3, all 9 locations shall be used as shown. Cylindrical location 5 being in the center. 4 & 6 are examples only.
正方形/矩形体量和圆柱形体量≥3平方英尺或0.085立方米但小于225平方英尺或6.4立方米,9个位置均为应使用,如图所示。圆柱形位置5在中心。4和6只是例子
Once locations are established during initial TUS, the same locations shall be used during periodic TUSs (see 3.5.9.2).
一旦在初始TUS期间建立了位置,在周期性TUSs期间相同的位置应使用(参见3.5.9.2)。
Numbering of sensor locations in diagrams is provided as an example only图中传感器位置的编号仅作为示例。
Figure 1 - TUS sensor locations for square/rectangle cubic and cylindrical volumes
方形/矩形立方和圆柱形体积的测量传感器位置
3.5.9.2 For qualified work zone volumes ≥225 ft3 or 6.4 m3, the additional TUS sensors required by Table 18 shall be uniformly distributed to best represent the qualified work zone. One TUS sensor shall be located at the approximate center of the qualified work zone volume. When radiant heat from the periphery of the qualified work zone is used to heat the parts or raw material, the additional TUS sensors shall be uniformly distributed at the periphery of the qualified work zone. Once locations are established during the initial TUS, the same locations shall be used during periodic TUSs.
对于合格工作区体积≥225立方英尺或6.4立方米的,表18要求的额外TUS传感器应均匀分布,以最好地代表合格工作区。一个TUS传感器应位于合格工作区体积的近似中心。当使用合格工作区外围的辐射热来加热零件或原材料时,额外的TUS传感器应均匀分布在合格工作区外围。一旦位置在初始的TUS建立,相同的位置应使用在周期性TUSs
3.5.9.3 When a retort is used, the following shall apply使用蒸馏器时,应适用下列规定:
3.5.9.3.1 The temperature of the furnace in which the retort is inserted shall be controlled so that the specified temperature is maintained within the retort. TUS sensors shall be located within the retort.
应控制插入蒸馏器的熔炉的温度,使蒸馏器内保持规定的温度。TUS传感器应位于蒸馏器内。
3.5.9.3.2 The tip (measuring junction) of at least one TUS sensor shall be as close as practical to the tip (measuring junction) of the sensor used to record temperature within the retort during production but the sensor tip to tip distance shall not exceed 2 inches or 50 mm.
至少一个TUS传感器的尖端(测量结)应尽可能接近生产过程中用于记录蒸馏釜内温度的传感器的尖端(测量结),但传感器尖端与尖端的距离不得超过2英寸或50毫米。
3.5.10 TUS Data Collection TUS数据收集
3.5.10.1 Data collection shall begin when the temperature of all TUS and furnace sensors are at least ≤100 ℉ or 55 ℃ below each TUS temperature so that any TUS or furnace sensor failing to reach the lower TUS tolerance or exceed the upper TUS tolerance can be detected. This is not applicable to salt bath or other thermal processing equipment that is maintained at a single set point. For TUS temperatures of 200 ℉ or 93 ℃ and below, data collection shall begin at the ambient temperature of the furnace or refrigeration equipment prior to the start of heating (or cooling for refrigeration equipment). If the furnace or refrigeration equipment is pre-stabilized, data collection shall begin prior to the TUS sensors being inserted.
当所有TUS和熔炉传感器的温度低于每个TUS的温度≤100℉或55℃时,应开始收集数据,以便能够检测到任何TUS或熔炉传感器未能达到TUS的下公差或超过TUS的上公差。这不适用于保持在单一设定点的盐浴或其他热加工设备。对于200℉或93℃及以下的TUS温度,在开始加热(或制冷设备的冷却)之前,应从熔炉或制冷设备的环境温度开始收集数据。如果熔炉或制冷设备是预先稳定的,数据收集应在插入TUS传感器之前开始
3.5.10.2 Once data collection begins, temperature data shall be recorded simultaneously from all TUS sensors at a frequency of at least one set of readings every 2 minutes for the duration of the TUS.
一旦数据收集开始,在TUS运行期间,应以每2分钟至少一组读数的频率同时记录从所有TUS传感器温度数据。
3.5.10.3 Temperature data from control, and recording sensors required by the applicable instrumentation type, Table 9, shall also be recorded by the process recorder during the TUS. Load sensors used in addition to the identified instrumentation type during production are not required to be recorded during the TUS (e.g., if a Type D instrumentation furnace occasionally uses a load sensor, a load sensor is not required during the TUS), but those recording systems shall require instrument calibration and an SAT.
控制和适用仪表类型(表9)要求的记录传感器的温度数据也应在测试过程中由过程记录仪记录。在生产过程中,除了已识别的仪表类型外,不要求在测试期间记录负载传感器(例如,如果D型仪表炉偶尔使用负载传感器,则在测试期间不要求记录负载传感器),但这些记录系统应要求仪表校准和SAT。
3.5.10.4 Regardless of the frequency of temperature data collection of control, and recording sensors used during production the temperature data shall be documented in the normal format used during production throughout the TUS.
无论在生产过程中使用的控制温度数据和记录传感器的采集频率如何,温度数据应在整个TUS中以生产过程中使用的正常格式进行记录。
3.5.10.5 If the normal frequency of control and recording sensor temperature data collection used during production is greater than 5 minutes, the recording frequency of these same sensors shall not exceed 5 minutes during the TUS.
如果生产过程中使用的控制和记录传感器温度数据采集的正常频率大于5分钟,则在TUS过程中这些传感器的记录频率不得超过5分钟。
3.5.10.6 At no time shall any TUS, control, or recording sensor exceed the upper TUS tolerance. The equipment shall be held at the TUS temperature until all TUS sensors have stabilized (see 2.2.71). After stabilization, data collection shall continue for a minimum of 30 additional minutes.
任何时候,任何TUS、控制或记录传感器都不得超过TUS上限公差。设备应保持在TUS温度,直到所有TUS传感器稳定(见2.2.71)。稳定后,数据收集应继续至少30分钟。
3.5.10.6.1 For Unloaded/Empty Equipment 卸载/空的设备
If the temperature readings of any TUS sensor exhibit an upward or downward trend that is not converging toward the set temperature, the data collection shall be extended as necessary until the trend is no longer evident.
如果任何TUS传感器的温度读数出现上升或下降趋势,但不向设定温度收敛,则应根据需要延长数据收集时间,直到趋势不再明显为止。
3.5.10.6.2 For Equipment Tested with a Load用于带负载测试的设备
If a load is used during the TUS, some TUS sensors may continue to rise in temperature and slowly approach the set temperature. This rise in temperature of TUS sensors towards the set temperature meets the requirement for stabilization.
接近设定的温度。TUS传感器的温度向设定温度的升高满足了稳定的要求。
3.5.11 TUS Requirements for Continuous and Semi-Continuous Furnaces
连续式和半连续式熔炉的通用技术要求
3.5.11.1 Continuous and semi-continuous furnaces may be surveyed with TUS sensors arranged volumetrically or in a plane.
连续炉和半连续炉可以用体积布置或平面布置的TUS传感器进行测量。
3.5.11.2 Both the volumetric and plane methods shall measure the entire qualified work zone volume. The difference between the two methods is the arrangement and number of TUS sensors.
容积法和平面法都应测量整个合格工作区的容积。两种方法的区别在于传感器的布置和数量。
3.5.11.3 Regardless of which method is used, the entire qualified work zone volume shall be surveyed. Multiple surveys may be required to accomplish measurement of the entire qualified work zone volume. For tubular furnaces equipped with several passages (e.g., ceramic tubes), each individual passage/tube used shall be surveyed.
无论采用哪种方法,都应对整个合格工作区体积进行测量。可能需要多次测量以完成整个合格工作区体积的测量。对于配置了多个通道(如陶瓷管)的管状炉,应对所使用的每个通道/管进行检查。
3.5.11.4 All parameters used during the TUS shall reflect the normal operation of the equipment used during production.
测试期间使用的所有参数应反映生产期间使用的设备的正常运行。
3.5.11.5 An initial TUS shall be performed at the minimum and maximum temperatures of the qualified operating temperature range(s) at the highest and lowest traverse speeds used during production. The additional temperatures of 3.5.2.2 apply to the initial TUS. The periodic TUS may be performed at any traverse speed used during production. A TUS shall be performed at the highest and lowest traverse speeds used during production at least annually.
初始TUS应在合格工作温度范围的最低和最高温度下,以生产过程中使用的最高和最低横穿速度进行。3.5.2.2的附加温度适用于初始TUS。周期TUS可以在生产过程中使用的任何横穿速度下执行。至少每年应以生产过程中使用的最高和最低的贯穿速度进行操作。
3.5.11.6 Volumetric Method 体积法
3.5.11.6.1 TUS sensors shall be located in three dimensions to represent a portion, e.g., basket, tray, or the entire qualified work zone volume.
TUS传感器应位于三维空间,代表一个部分,例如,篮子,托盘,或整个合格工作区体积
3.5.11.6.2 The number and location of TUS sensors shall be in accordance with Figure 1 and Tables 17 and 18 based on the volume of the TUS basket or tray(s) used.
根据使用的TUS篮或托盘的体积,TUS传感器的数量和位置应按照图1和表17和表18。
3.5.11.6.3 When surveying a portion of the qualified work zone incrementally, the entire volume of that portion shall be surveyed as the TUS sensors traverse through the furnace.
当增量测量合格工作区的一部分时,当TUS传感器穿过熔炉时,应测量该部分的整个体积。
Table 19 - Number and location of TUS sensors for continuous and semi-continuous furnaces
when using the plane method使用平面法时连续和半连续炉的TUS传感器数量和位置
3.5.11.7 Plane Method平面方法
3.5.11.7.1 TUS sensors shall be located in a single plane perpendicular to the furnace conveyance direction such that passing the plane through the furnace measures the entire qualified work zone volume of all zones required to be surveyed.
TUS传感器应位于垂直于炉膛输送方向的单一平面上,使该平面通过炉膛测量所有需要测量的区域的整个合格工作区体积。
3.5.11.7.2 The number and location of TUS sensors shall be in accordance with Table 19 based on the height and cross section of the qualified work zone.
根据合格工作区域的高度和横截面,TUS传感器的数量和位置按照表19规定。
3.5.11.7.3 A TUS sensor for each location shall be secured to a rack or in a load and traversed through the qualified work zone.
每个位置的TUS传感器应固定在机架上或在负载中,并穿过合格的工作区域。
3.5.11.7.4 All required locations need not be traversed simultaneously; multiple TUSs may be required to accomplish measurement of the entire qualified work zone volume.
所有需要的位置不需要同时贯穿;可能需要多个TUSs来完成整个合格工作区域体积的测量。
3.5.11.8 TUS Data Collection TUS数据收集
3.5.11.8.1 Temperature readings from all TUS sensors shall be recorded at least every 2 minutes with a minimum of ten sets of readings recorded for each qualified work zone. The traverse may be repeated as many times as necessary to ensure that any recurrent temperature pattern is identified at all locations through each qualified work zone. If the normal frequency of control and recording sensor temperature data collection used during production is greater than 5 minutes, the recording frequency of these same sensors shall not exceed 5 minutes during the TUS.
所有TUS传感器的温度读数应至少每2分钟记录一次,每个合格的工作区域至少记录10组读数。导线可以根据需要重复多次,以确保通过每个合格工作区域的所有位置都能确定任何反复出现的温度模式。如果生产过程中使用的控制和记录传感器温度数据采集的正常频率大于5分钟,则在TUS期间这些相同传感器的记录频率不得超过5分钟。
3.5.11.8.2 Starting the TUS with the furnace temperature higher than the TUS temperature is not permitted unless:
不允许在炉子温度高于TUS温度的情况下启动TUS,除非:
It is performed in only the initial or preheating zones of multi-zone furnaces.
它只在多区加热炉的初始区或预热区进行。
OR
It is specifically permitted by the applicable material or process specification.
或适用的材料或工艺规范明确允许。
3.5.11.9 The qualified work zone length is a unique value for each traverse speed and shall be calculated and documented after the TUS. Each qualified work zone length is the sum of the elapsed time during which the TUS sensors were within the required TUS tolerance at the traverse speed used.
合格的工作区域长度是每个横移速度的唯一值,并应在TUS后进行计算和记录。每个合格的工作区域长度是在所使用的贯穿速度下,TUS传感器在所需的TUS公差范围内所经过的时间的总和。
3.5.11.10 There shall be objective evidence that the soak time and temperature conform to the process or material specification requirements using the stated traverse speed. The qualified work zone length is the traversed distance through which all TUS sensor readings meet the required TUS tolerance.
应有客观证据证明浸泡时间和温度符合工艺或材料规格要求使用规定的贯穿速度。合格的工作区长度是所有TUS传感器读数满足要求的TUS公差所经过的距离。
3.5.12 Alternative TUS Methods for Continuous, Semi-Continuous Furnaces, or Furnaces with Retorts or Muffles
连续炉,半连续炉,或带蒸馏炉或消声器的TUS替代方法
3.5.12.1 Where it is impractical to traverse the TUS sensors through a continuous or semi-continuous furnace, or to install TUS sensors into the retort, batch, or muffle of a furnace, it is acceptable to use either the probe method (see 3.5.12.2) or a property survey (see 3.5.12.3).
如果将TUS传感器穿过连续或半连续的加热炉,或将TUS传感器安装到加热炉的蒸馏器、间歇器或马弗中不可行,则可以采用探头法(参见3.5.12.2)或性能测量法(参见3.5.12.3)。
3.5.12.2 Probe Method探针测
3.5.12.2.1 In lieu of locating TUS sensors in accordance with Figures 1 and Table 19, it is acceptable to insert TUS sensors through the side walls, hearth, or roof within 3 inches or 76 mm of the locations identified in Figure 1 and Tables 17 and 18. If this method is used, the number of TUS sensors shall be in accordance with Figure 1 and Tables 17 and 18 based on the volume of the qualified work zones surveyed.
如果不按照图1和表19定位TUS传感器,则可以通过图1和表17和表18中标识的位置3英寸或76毫米范围内的侧壁、灶台或屋顶插入TUS传感器。若采用此方法,则根据调查的合格工作区域的数量,TUS传感器的数量按照图1和表17、18。
3.5.12.2.2 Temperature readings from all TUS sensors shall be taken at least every 2 minutes for a minimum of 30 minutes once all sensor temperatures have stabilized. If the normal frequency of control and recording sensor temperature data collection used during production is greater than 5 minutes, the recording frequency of these same sensors shall not exceed 5 minutes during the TUS.
在所有传感器温度稳定后,应至少每2分钟读取所有TUS传感器的温度读数,持续至少30分钟。如果生产过程中使用的控制和记录传感器温度数据采集的正常频率大于5分钟,则在TUS期间这些相同传感器的记录频率不得超过5分钟。
3.5.12.2.3 If a continuous or semi-continuous furnace is being probed, it is not required that a load be traversed through the furnace during the TUS.
如果探测的是连续或半连续炉,则不要求在TUS期间在炉内贯穿负载。
3.5.12.3 Property Survey 材料测试
3.5.12.3.1 A property survey shall require 需要进行的材料测试
Testing material initially and annually thereafter 开始测试材料,之后每年测试一次。
AND
Monthly analysis of property survey trends. The material selected shall be one whose properties are known to be sensitive to variations in thermal processing soak times and temperatures and whenever possible, one that is processed frequently.
每月物业调查趋势分析。所选择的材料应具有对热加工浸泡时间和温度变化敏感的性能,并且尽可能频繁加工
3.5.12.3.2 Material thickness shall be within the normal size range used during production. If a two-step treatment is required (e.g., harden and temper), it is permitted to perform the second step on the test specimens separately from the remainder of the lot, e.g., in a laboratory furnace.
材料厚度应在生产过程中使用的正常尺寸范围内。如果需要两步处理(例如,硬化和回火),允许对试样进行第二步处理,与该批的其余部分分开,例如,在实验室熔炉中
3.5.12.3.3 Initial and annual property surveys shall be performed at the highest and lowest operating temperatures used during production. Additional temperatures shall be added to ensure that no two adjacent temperatures are greater than 300 ℉ or 165 ℃ apart. Continuous and semi-continuous furnace traverse speeds shall be those normally used during production. At least ten test specimens shall be processed at each operating temperature.
初始和年度性能调查应在生产过程中使用的最高和最低操作温度下进行。应增加额外的温度,以确保两个相邻的温度不大于300℉或165℃的间隔。连续和半连续的炉膛横向速度应为生产中通常使用的速度。在每个操作温度下,至少要处理十个试样。
3.5.12.3.4 Test specimens shall be taken from parts or raw material located at the extremes and center of the load except for coils where test specimens shall be taken at both ends of the coil. Coil test samples shall be tested at both edges and at the center of each specimen.
除线圈应在线圈的两端取试样外,试样应从位于荷载的极端和中心的部分或原材料取试样。线圈测试样品应在每个样品的边缘和中心进行测试。
3.5.12.4 Monthly Analysis of Property Survey Trends每月物业调查趋势分析
3.5.12.4.1 Properties of thermally processed specimens shall be analyzed by a statistical technique described in ASTM MNL7 or other recognized statistical process control reference work.
热处理试样的性能应通过ASTM MNL7或其他公认的统计过程控制参考著作中描述的统计技术进行分析。
3.5.12.4.2 If the trend of properties exhibits a shift outside of the known upper or lower control limits, no further processing shall occur until the cause of the shift is determined and corrected. The requirements of Section 4 shall apply.
如果性能趋势出现在已知的控制上限或下限之外的偏移,在确定并纠正偏移原因之前,不进行进一步处理。应适用第4节的要求。
3.5.13 TUS Sensor Failure Requirements TUS传感器故障要求
3.5.13.1 TUS sensor or recording channel failure at the corner locations of a rectangle/square work zone or periphery (top/bottom or front/back) locations of a cylindrical work zone is not permitted. A temporary condition such as a short or loose connection where normal temperature indication is restored shall not be considered as a failed TUS sensor.
不允许矩形/方形工作区或外围(顶部/底部或前/后)矩形工作区角落位置的TUS传感器或记录通道故障。在恢复正常温度指示的情况下,如连接短路或松动等临时情况不应被视为失效的TUS传感器。
3.5.13.2 The failure of one or more TUS sensors at corner locations, any two adjacent TUS sensors, or a number exceeding the requirements in Table 20 or 21 shall require corrective action to be taken and the TUS repeated.
角落位置的一个或多个TUS传感器失效,任意两个相邻的TUS传感器,或超过表20或21要求的数量应要求采取纠正措施并重复使用TUS
Table 20 - Allowable number of TUS sensor failures for TUSs performed <2000 ℉ or <1093 ℃
在<2000℉或<1093℃时,允许的TUS传感器故障次数
Table 21 - Allowable number of TUS sensor failures for TUSs performed ≥2000 ℉ or ≥1093 ℃
温度≥2000℉或≥1093℃时,TUS传感器允许故障次数
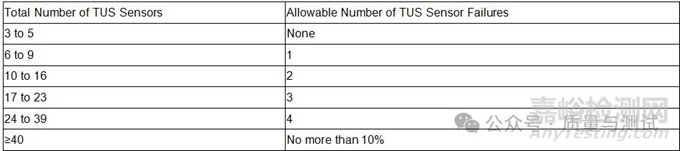
3.5.14 TUS Pass/Fail Requirements TUS通过/失败的需求
3.5.14.1 A TUS shall be considered acceptable if all previously described requirements are met including the following如果所有之前描述的要求都满足,包括以下要求,则TUS应被认为是可接受的:3.5.14.1.1 When compiling and analyzing TUS temperature data, compensation for known correction factors for the TUS sensors and TUS instrumentation shall have been applied algebraically.
在编译和分析TUS温度数据时,对TUS传感器和TUS仪表的已知修正因子进行代数补偿。
3.5.14.1.2 Control, and recording sensor readings and corrected TUS sensor readings shall not have exceeded the upper TUS tolerance at any time.
控制,并记录传感器读数和修正的TUS传感器读数在任何时候都不应超过上TUS公差。
3.5.14.1.3 The time required to achieve TUS sensor temperature recovery, stabilization or a recurrent temperature pattern shall not have exceeded the time limit specified in the applicable material or process specification.
实现TUS传感器温度恢复、稳定或循环温度模式所需的时间不得超过适用材料或工艺规范中规定的时间限制。
3.5.14.1.4 The TUS soak period shall not have been less than the minimum required time.
浸泡时间不应低于最低要求时间。
3.5.14.1.5 The readings of all TUS sensors, control, or recording sensors shall have been within the temperature tolerance requirements shown in Table 15 or 16 during the minimum TUS soak period except as allowed by 3.5.13.
除3.5.13允许的温度外,所有仪表传感器、控制传感器或记录传感器的读数应在表15或16所示的温度公差要求范围内
3.5.14.1.6 If any temperature overshoot occurred where the upper TUS tolerance was exceeded during the approach period or the minimum TUS soak period, the temperature overshoot shall have been noted on the TUS report and the TUS shall have been documented as a failed TUS.
如果任何温度超调发生在接近期或浸渍期内超过了最高温度单位公差,则温度超调应在TUS报告中注明,并将TUS记录为失效的TUS。
3.5.14.1.7 If the TUS was not within the allowable tolerances of Table 15 or 16, the cause of the deviation shall be determined and documented. The requirements of Section 4 apply.
如果模具不在表15或表16的允许公差范围内,应确定偏差的原因并形成文件。适用第4节的要求。
3.5.14.1.8 For equipment surveyed at an extended periodic TUS interval, a TUS failure shall be cause for the interval to revert to the normal periodic TUS interval specified in Table 15 or 16 until the required number of consecutive successful periodic TUSs are completed.
对于在较长的周期TUS时间间隔内进行测量的设备,如果出现TUS故障,则周期TUS时间间隔将恢复到表15或表16中规定的正常周期TUS时间间隔,直到完成所需的连续成功周期TUS次数。
3.5.14.1.9 If the corrective action for a failed TUS takes the form of implementing a modification offset, and if the qualified operating temperature range exceeds 300 ℉ or 165 ℃, a re-survey is required where uniformity is verified at the temperature extremes of the TUS range where the offset is applied. TUS temperatures for each range where offsets are applied shall not be more than 600 ℉ or 335 ℃ apart.
如果不合格的TUS的纠正措施是实施修正偏移量,如果合格的工作温度范围超过165℃,则需要重新测量,以验证施加偏移量的TUS范围的极端温度的均匀性。每个偏移量范围的温度间隔不得超过335℃。
3.5.15 Relocation of Hot or Cold Recording Sensors for Type A and C Instrumentation
A型和C型仪表的热或冷端记录传感器的移位
3.5.15.1 When the hot and cold temperature locations change within the furnace based on the readings from the most recent TUS, the hot and cold recording sensors may need to be relocated to reflect the new hot and cold locations within each qualified work zone.
当炉内的冷热端温度位置根据最新的温度读数发生变化时,可能需要重新配置冷热端记录传感器,以反映每个合格工作区域内新的冷热端位置。
3.5.15.2 The hot and/or cold recording sensors do not require relocation if either of the following conditions is met 如满足以下任一条件时,冷和/或热端记录传感器不需要移位:
3.5.15.2.1 The temperature uniformity results do not exceed one half of the maximum temperature uniformity tolerance for the applicable furnace class at all temperatures surveyed. The intent of this requirement condition is that the TUS results do not exceed 1/2 of the uniformity tolerance in either the cold direction from the set point temperature to evaluate the cold recording location and that the TUS results do not exceed 1/2 of the uniformity tolerance in the hot direction from the set point temperature to evaluate the hot recording location. The hot and cold locations are to be assessed individually.
在所有测量温度下,温度均匀性结果不超过适用炉级最高温度均匀性公差的一半。此条件的目的是,TUS结果在冷端上不超过从设定点温度评估冷端记录位置的均匀性公差的1/2,并且TUS结果在热方向上不超过从设定点温度评估热端记录位置的均匀性公差的1/2。热区和冷区将分别进行评估。
Example: Furnace Class 2 ±10 °F and the TUS results showed that both the hot and cold locations changed. The TUS results were -4.0 °F to +5.5 °F. This means that the cold location does not need to be relocated, but because the TUS results exceeded the half tolerance in the positive direction, the hot location does not pass this test.
例:2级炉±10°F, TUS结果显示冷热端位置都发生了变化。TUS结果为-4.0°F至+5.5°F。这意味着冷端位置不需要重新定位,但由于TUS结果超过了正方向的一半公差,因此热端位置不通过此测试。
NOTE: A TUS modification offset may be used to center the TUS results to meet the above requirement for both locations (see Figure 2).
注意:可以使用TUS修改偏移量来居中TUS结果,以满足上述两个位置的要求(参见图2)。
Set temperature设定温度
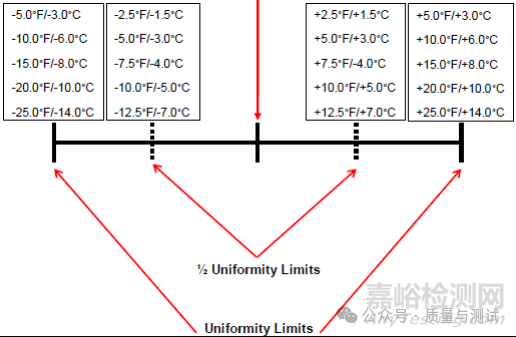
Figure 2 - Hot/cold sensor relocation condition #1冷热端传感器移位条件#1
3.5.15.2.2 The difference between the measured temperature at the current hot and cold recording sensor locations and the actual respective hottest and coldest measured locations does not exceed the maximum SAT difference for the applicable furnace class (see Tables 11 and 12). The intent of this requirement is that the maximum and minimum TUS sensor readings during the 30-minute TUS soak, recorded and corrected by the TUS recorder, are compared to the furnace recording of the current hot and cold recording sensors at the same time, and shall not exceed the applicable SAT difference. See Figure 3.
当前冷热记录传感器位置的测量温度与各自实际最热和最冷测量位置的测量温度之间的差值不超过适用炉级的最大SAT差值(见表11和表12)。这一要求的目的是,由TUS记录仪记录并修正的TUS传感器浸泡30分钟期间的最大和最小读数,与当前热记录和冷记录传感器同时的炉子记录相比较,不应超过适用的SAT差值。见图3.
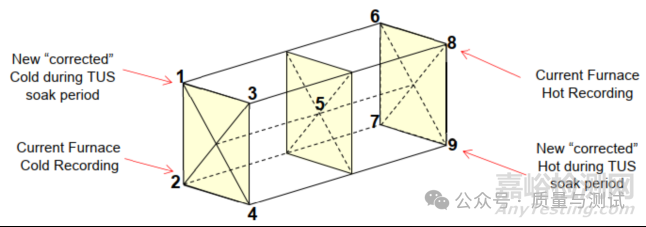
New “corrected” Cold During TUS soak period新的”修正“在TUS浸泡期间的
Current Furnace Cold Recording电炉冷端记录
Current Furnace Hot Recording电炉热端记录
New “corrected” Hot During TUS soak period新的”修正“在TUS热端期间的
Current Furnace Cold Recording - New “corrected” Cold During TUS ≤ Maximum SAT difference
当前炉冷端记录 - TUS期间冷端新修正 ≤ 最大SAT差
Current Furnace Hot Recording - New “corrected” Hot During TUS ≤ Maximum SAT difference
当前炉热端记录 - TUS期间热端新修正 ≤ 最大SAT差
Compared at the point in time when the hot and cold corrected TUS temperature occurred
比较热校正和冷校正TUS温度发生时的时间点
Figure 3 - Hot/cold sensor relocation condition #2热/冷传感器移位条件
3.5.15.3 If the qualified operating temperature range exceeds 300 ℉ or 165 ℃ and the hot and/or cold recording sensors are permanently positioned/fixed and need to be relocated, additional TUS temperatures shall be performed to verify that the new locations are correct throughout the qualified operating temperature range of the furnace.
如果合格的操作温度范围超过165℃,并且热和/或冷记录传感器是永久定位/固定的,需要重新定位,则应执行额外的TUS温度,以验证在整个炉子的合格操作温度范围内,新位置是正确的。
3.5.15.4 If the hot and/or cold recording sensors are not permanently positioned/fixed, they can be relocated without the above testing if there is a diagram of the required location where the hot and cold recording sensors will be placed at each process temperature.
如果热和/或冷记录传感器不是永久放置/固定的,如果有一个所需位置的示意图,在每个工艺温度下,热和冷记录传感器将被放置在所需位置,它们可以在不进行上述测试的情况下重新放置。
3.5.16 TUS Results and Records TUS结果和记录
3.5.16.1 The results of the TUS shall be documented. At a minimum, the TUS documentation shall include TUS的结果应被记录。至少,TUS文件应包括:
a. Furnace identification name or number炉子标识名称或编号。
b. Identification of TUS as initial or periodic确定TUS为初始或周期性的
c. TUS instrument unique identification number仪表唯一识别码。
d. TUS sensor(s) batch or lot number TUS传感器批号或批号
e. TUS set point temperatures TUS设定温度。
f. Control instrument tuning constants 控制仪表调谐常数。
g. TUS sensor calibration report TUS传感器校准报告。
h. TUS instrument calibration report 仪表校准报告。
i. TUS, control, and recording sensor location identification required by the applicable instrumentation type including a detailed diagram, description, or photograph(s) of any load, rack, or fixture used.
控制,并记录传感器位置识别所需的适用仪表类型,包括详细的图表,描述,或照片的任何负载,机架,或夹具使用。
j. The atmosphere used 大气中使用。
k. Time and temperature data from all recorded sensors required for the instrument type for all qualified work zones surveyed.
所有被调查的合格工作区域的仪表类型所需的所有记录传感器的时间和温度数据。
l. Correction factors for the TUS sensors and TUS instrument at each TUS temperature. The TUS instrument correction factors shall be stated even when the correction factors have been electronically applied to the TUS instrument to correct the TUS instrument temperature readings.
各温度下TUS传感器和TUS仪表的校正因子。即使修正系数已通过电子方式应用于TUS仪表以修正TUS仪表的温度读数,也应说明TUS仪表修正系数
m. As-found and as-left correction and/or modification offsets if used during production.
如在生产过程中使用,发现和左校正和/或修改偏移。
n. Corrected or uncorrected (if documented) readings of all TUS sensors at each TUS temperature. TUS readings shall be identified as corrected or uncorrected.
在每个TUS温度下,所有TUS传感器的校正或未校正读数(如果有记录)。TUS读数应标识为已修正或未修正。
o. Load condition, i.e., empty, with a rack, or with a load 负载状态,即空的,带机架的,或带负载的。
p. TUS start date and time (when temperature data collection began).
TUS开始日期和时间(开始采集温度数据的时间)。
q. TUS end date and time (when temperature data collection ended).
TUS结束日期和时间(温度数据采集结束的时间)。
r. The results of hottest and coldest TUS and furnace recording sensor relocation analysis for Type A and C instrumentation, as applicable.
A型和C型仪表的最热和最冷的TUS和炉记录传感器移位分析的结果,如适用。
s. Traverse speed (s) or shaker frequency, and qualified work zone length for the TUS performed on continuous and semi-continuous furnaces, as applicable.
导线速度或激振器频率,以及在连续和半连续炉上进行的TUS合格的工作区域长度(视情况而定)。
t. TUS pass or fail statement TUS通过/不通过的声明
u. When applicable, documentation of any control, recording, or TUS sensor failures.
适用时,任何控制、记录或TUS传感器故障的文档。
v. Summary of the hottest and coldest corrected TUS readings at each test temperature during the minimum soak period compared to the TUS requirement. For example, a TUS performed at 920 ℉ ±10.0 ℉ or 493 ℃ ± 6.0 ℃. During the 30-minute soak period, the hottest corrected temperature is 923.4 ℉ or 495.2 ℃ and the lowest corrected temperature is 918.8 ℉ or 492.7 ℃. The Summary would be -1.2 to +3.4 ℉ or -0.3 to +2.2 ℃.
与TUS要求相比,在最低浸泡时间内每个测试温度下最热和最冷的修正TUS读数的汇总。例如,在493℃±6.0℃时进行超声检查。在30分钟的浸泡期间,最高修正温度为495.2℃,最低修正温度为492.7℃。摘要将为-0.3至+2.2℃。
w. Identification of the technician performing the TUS.
鉴定执行TUS的技术人员。
x. Identification of the agency if TUS is not performed internally.
如果TUS没有在内部执行,说明该机构的身份。
y. Approval of an authorized agent for the calibration agency if not performed internally.
对校准机构的授权代理的批准(如果不是内部执行)。
z. User quality organization approval 用户质量组织批准。
3.5.17 Radiation Survey辐射测量
When required by the applicable material or process specification, a radiation survey shall be performed as follows当适用材料或工艺规范有要求时,应按下列方式进行辐射测量:
3.5.17.1 Where the heat source (e.g., electrical elements or gas radiant tubes) is located in the furnace walls, ceiling, or floor, and the heat source has either a direct line of sight to the work zone or is only separated from the work zone by a single sheet of metal, a radiation survey shall be performed at the maximum operating temperature used for aluminum during production. The radiation survey shall be performed initially and after any equipment repair or modifications, including furnace relocation, that could affect the radiation characteristics of the heat source.
热源(例如,电气元件或燃气辐射管)位于炉壁、炉顶或炉底板上,热源要么直接对准工作区域,要么与工作区域隔着一块金属片,辐射测量应在铝生产过程中使用的最高工作温度下进行。辐射测量应在设备修理或修改后进行,包括炉子搬迁,可能会影响热源的辐射特性。
3.5.17.2 The radiation survey sensor(s) shall be in addition to the required number of TUS sensors. The radiation survey and the initial or periodic TUS may be performed simultaneously or separately.
辐射测量传感器应在必需数量的TUS传感器之外。辐射测量和初始或周期的TUS测量可以同时或单独进行。
3.5.17.3 The radiation survey sensors shall be peened into or welded onto the center of 6061 aluminum alloy panels. The panels shall measure approximately 12 x 12 inches or 30 x 30 cm not more than 0.125 inch or 3.1 mm in nominal thickness. The panels shall have been heated in air to a temperature in the range of 970 to 1010 ℉ ± 10.0 ℉ or 520 to 545 ℃ ± 6.0 ℃ and air cooled prior to the first radiation survey. Soak time shall be in accordance with the thickness requirements for the solution treatment as defined by the material or process specification.
辐射测量传感器应喷入或焊接到6061铝合金板的中心。面板应测量约12 × 12英寸或30 × 30厘米,不超过0.125英寸或3.1毫米公称厚度。在第一次辐射测量前,面板应在空气中加热至520-545 ℃ ± 6.0 ℃的温度范围内,并在空气中冷却。浸泡时间应与材料或工艺规范中规定的溶液处理厚度要求一致。
3.5.17.4 The panels, one for each 10 ft2 or 0.93 m2 of furnace side wall, ceiling, and/or floor area where the heat source is located, shall be distributed symmetrically, with the faces parallel to the furnace wall, ceiling, and/or floor where the heat source is located, at the outer limits of the qualified work zone. Either side of the panel(s) may face the heat source.
热源所在的炉膛侧墙、炉顶和/或地板每10平方英尺或0.93平方米的面板应对称分布,其面与热源所在的炉壁、炉顶和/或地板平行,位于合格工作区域的外边界。面板的任意一侧都可以面对热源。
3.5.17.5 For aluminum vacuum brazing equipment utilizing clamping fixtures, the panels shall be inserted into the fixturing to replicate production.
使用夹具的铝真空钎焊设备,板材要插入夹具中复制生产。
3.5.17.5.1 The number, aluminum alloy, and size of panels may be adjusted to replicate production.
面板的数量,铝合金和尺寸可以调整,以复制生产。
3.5.17.6 All radiation survey sensor readings shall meet the data collection requirements of 3.5.10.2, sensor failure requirements of 3.5.13, and the TUS requirements of 3.5.14.
所有辐射测量传感器读数应满足3.5.10.2的数据采集要求,满足3.5.13的传感器故障要求,满足3.5.14的TUS要求。
3.5.18 TUS Interval Deviations温度均匀性测量间隔偏差
3.5.18.1 The user is allowed to have thermal processing equipment exceed the allowable TUS interval, including any extension days in Table 22, with the approval from each applicable cognizant engineering or quality organization. When the TUS is next performed, it shall include all required temperatures of the initial TUS and at the highest and lowest traverse speed for continuous and semi-continuous furnaces. The TUS interval shall continue at the interval in use at the time of the last periodic TUS.
用户允许热加工设备超过允许的TUS间隔,包括表22中的任何延长天数,并得到每个适用的审理工程或质量组织的批准。下一次进行TUS时,应包括初始TUS所需的所有温度,以及连续炉和半连续炉的最高和最低切换速率。TUS间隔应继续在最后一个周期TUS时的使用间隔。
3.5.18.2 For thermal processing equipment that has been documented as being “out of use/service” beyond the next TUS due date and any extension days in Table 22, a periodic TUS shall be performed before being returned to service. The TUS interval shall continue at the interval in use at the time the equipment was taken “out of use/service”.
对于在表22中的下一个TUS到期日期和任何延期日期之后被记录为“停止使用/服务”的热加工设备,应在重新投入使用之前进行定期TUS。TUS间隔应延续在设备“停止使用/服务”时的使用间隔。
3.6 Laboratory Furnaces实验炉
3.6.1 General Laboratory Furnace Requirements通用实验炉要求
3.6.1.1 Laboratory furnaces shall be used for preparation of laboratory testing samples such as, but not limited to, response to heat treatment testing in accordance with the material or process specification.
用于制备实验室测试样品的实验炉,如,但不限于,根据材料或工艺规范对热处理测试的响应。
3.6.1.2 A laboratory furnace shall not be used for thermal processing of any parts or raw material unless the furnace meets all applicable requirements of this specification.
除非实验炉满足本规范的所有适用要求,否则不得用于任何工件或原材料的热加工。
3.6.2 Laboratory furnace requirements when a load sensor is used使用载荷传感器的实验炉要求:
a. Load sensors shall comply with 3.1.10 载荷传感器应符合3.1.10。
b. Calibration of control and recording instruments shall be performed quarterly. Calibration shall meet the requirements of Table 7 控制和记录仪表的校准应每季度进行一次。校准应满足表7的要求。
c. The SAT shall be performed quarterly. The SAT difference shall meet the requirements of Table 11 or 12 for the lowest furnace class required by the material or process specification specified.
SAT每季度校验一次。SAT差值应满足表11或表12对指定的材料或工艺规范规定的最低炉类别的要求。
d. After completion of a successful initial TUS plus two consecutive successful periodic quarterly TUS, the TUS interval may be extended to semi-annually. The TUS results shall meet the requirements of Table 15 or 16. 在初次TUS合格后再连续两次季度TUS合格后,TUS的间隔时间可以延长到半年一次。TUS结果应满足表15或表16的要求。
3.6.3 Laboratory furnace requirements when a load sensor is not used 不使用负载传感器时的实验室炉要求:
a. Control and recording instrument calibration, SAT, and TUS shall be performed in accordance with the instrument type and furnace class applicable for production equipment.
按照生产设备适用的仪表类型和炉级进行仪表校准、SAT和TUS的控制和记录。
3.7 Records记录
3.7.1 All records of sensor calibration, and instruments calibration, SAT, and TUS in addition to any calibration, SAT, and TUS failures shall be available for inspection and shall be maintained for not less than 5 years.
除所有校准、SAT和TUS失败外,所有传感器校准、仪表校准、SAT和TUS的记录应可供检查,并应保存不少于5年。
3.8 Rounding修约
3.8.1 If used, rounding shall be applied in accordance with a documented procedure and used in a consistent manner.
如使用,修约应按照文件规定的程序进行,并以一致的方式使用。
3.8.2 Rounding to 0.1℉ or 0.1 ℃ in accordance with ASTM E29, other equivalent international standards or commercial software programs is acceptable.
根据ASTM E29的修约至0.1℃,其他等效的国际标准或商业软件是可以接受的。
3.8.3 The rounding method built into commercial spreadsheet programs is also acceptable.
商业电子表格程序中内置的修约方法也是可以接受的
3.8.4 All specified limits in this specification are absolute and out of tolerance test data cannot be rounded into tolerance.
本规范中的所有规定限都是绝对的,超出公差的测试数据不能修约到公差中。
3.8.5 Rounding shall only be applied to the final calibration or test result.
修正仅适用于最终校准或测试结果。
4、 QUALITY ASSURANCE PROVISIONS质量保证条款
4.1 The user shall be responsible for the performance of all required calibration and tests and for conformance to all applicable requirements specified herein. The purchaser reserves the right to witness calibration or tests specified herein to ensure that processing conforms to applicable requirements, but such witnessing shall not hinder any process within the facility.
加工方应负责进行全部要求的校准和测试并使其符合本标准规定的全部要求。委托方保留查验本标准规定的任何校准或测试的权利,以保证工艺过程符合规定的要求,但这种查验不得妨碍设施内的任何过程。
4.2 Third party (external) pyrometry service provider companies shall have a quality system accredited to ISO/IEC 17025 from an ILAC (International Laboratory Accreditation Cooperation) recognized regional cooperation body. The scope of accreditation shall include the laboratory standards and/or field service (for testing and calibration activities), as applicable. This applies to third-party providers performing calibrations or tests at the user’s site or in their own laboratory.
第三方(外部)高温测量服务提供商公司应具有ISO/IEC 17025认可的质量体系,从ILAC(国际实验室认可合作)认可的区域合作机构。认可范围应包括适用的实验室标准和/或现场服务(用于检测和校准活动)。这适用于在用户现场或在其自己的实验室进行校准或测试的第三方供应商。
4.3 When calibrations and/or tests defined herein are performed by the user’s personnel, the user shall have procedures for calibration and testing, as applicable, detailing the methods and practices for the determination of the accuracy and measurements to minimize random errors. The user shall ensure the competence of personnel who perform calibrations and/or tests, evaluate results, and approve test results and documentation. Personnel who are undergoing training, shall be appropriately supervised. Personnel performing specific tasks shall be qualified based on documented education, training, experience and/or demonstrated skills, as applicable.
当由用户人员进行校准和/或测试时,用户应该有校准和测试的程序,如适用,详细说明确定精度和测量的方法和操作,以最大限度地减少随机误差。用户应确保执行校准和/或测试、评估结果以及批准测试结果和文件的人员的能力。接受培训的人员应得到适当的监督。适用时,执行特定任务的人员应能胜任,经过文件化的教育、培训、经历或技能展示。
4.4 Equipment that is affected by any calibration or test failing to meet applicable requirements, or that has exceeded the allowable interval including any extension period defined in Table 22, shall be removed from service (i.e., production shall not begin once the extension days expire).
由于校准或测试不符合适用要求而受到影响的设备,或超过了表22中规定的允许间隔(包括任何延长周期)的设备,应从服务中移除(即,一旦延期日届满,生产不得开始)。
Table 22 - Permitted calibration/test interval extension允许的校准/测试间隔延长
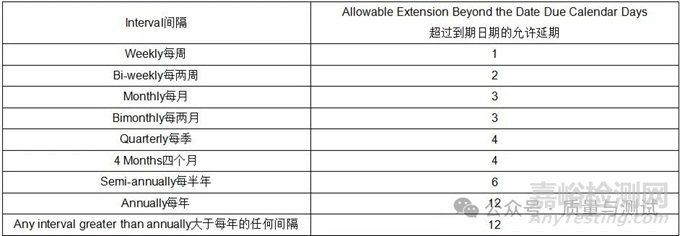
4.5 As a result of any calibration or test failure, an evaluation of the possible effects of the failure on parts and raw material processed since the last successful corresponding calibration or test shall be performed.
任何校准或测试失败,应对从最后一次合格校准或测试之后处理的工件和原材料不符合的可能影响进行评估。
4.6 Appropriate corrective action shall be in accordance with established material review procedures including the action taken to return the calibration or test to the required level of compliance and actions taken to prevent recurrence of the failure. The corrective action shall be documented and maintained on file.
采取的纠正措施应符合建立的材料评审程序,包括为使校准或测试恢复到要求的符合水平而采取的措施,以及为防止故障再次发生而采取的措施。纠正措施应形成文件并存档。
4.7 A conforming corresponding calibration or test shall be required and documented before returning the equipment into service.
在设备返回使用之前,应进行符合相应要求的校准或测试,并记录和存档。
4.8 When parts or raw material processing conditions deviate from material or process specification requirements affected purchaser(s) shall be notified.
当工件或原材料处理状态偏离材料或工艺规范要求时,应通知受影响的买方。
5、 Preparation For Delivery交货准备
Not applicable不适用
6、 Acknowledgement确认
Not applicable不适用
7、 Rejections拒绝
Not applicable不适用
8、 Notes注释
8.1 Revision Indicator
A change bar (l) located in the left margin is for the convenience of the user in locating areas where technical revisions, not editorial changes, have been made to the previous issue of this document. An (R) symbol to the left of the document title indicates a complete revision of the document, including technical revisions. Change bars and (R) are not used in original publications, nor in documents that contain editorial changes only.
位于左侧空白处的变更条(l)是为了方便用户定位对以前的文档做了技术修改而不是编辑修改的地方。文档标题左侧的(R)符号表示文档的完整修订,包括技术修订。更改条和(R)不在原始出版物中使用,也不在仅包含编辑更改的文档中使用。
8.2 Both imperial units and SI units are primary. Both Fahrenheit and Celsius temperatures are primary. Either the imperial/Fahrenheit system may be used, or the SI/Celsius system may be used.
英制单位和国际单位制单位都是主要的。华氏温度和摄氏温度都是主要的。既可以使用英制/华氏温度系统,也可以使用SI/摄氏度系统
Prepared by SAE AMS B finishes processes and fluids committee
由SAE AMS B完成工艺和流体委员会准备