您当前的位置:检测资讯 > 科研开发
嘉峪检测网 2021-11-01 23:19
镁金属因具有理想的力学模量、良好的生物相容性、体内可降解性及促骨生成效应,有望发展成为新一代内固定器械用于ACL重建。然而,其体内降解速率过快和力学强度不足是限制其在临床应用的主要障碍。对此,本文聚焦在以下三个部分进行展术:首先,介绍了镁及其合金作为潜在的界面螺钉的优势;随后,阐述了镁离子促进腱-骨愈合的可能机制;最后,讨论了镁基界面螺钉在未来临床应用中的难题以及针对性解决方案,包括开发镁/钛组合器械和具有新型结构的镁基界面螺钉,以满足临床手术需求。总而言之,镁基界面螺钉的基础研究和临床转化的努力可能为腱骨愈合和相关疾病的治疗提供了新的思考策略。
01、研究内容简介
前交叉韧带(ACL)损伤是最为常见的运动型损伤,会引起膝关节不稳,进而导致关节软骨磨损而诱发骨性关节炎(OA)的发生。临床普遍认为ACL重建是恢复膝关节功能最有效的手段。虽然大部分患者可通过重建手术重获其功能,但每年仍有10%以上患者重建愈合不理想。肌腱-骨界面愈合不良被认为是治疗结果不理想的主要原因之一。通过与正常愈合的腱-骨界面(1A)中的结构相比较,肌腱移植物与骨隧道的骨整合失败会导致移植物滑动(1B),最终影响膝关节的稳定性。据分析,这与现有界面螺钉材质有关(1C)。钛界面螺钉由于力学模量过高,易造成应力遮挡效应,引起骨隧道扩大(1D)。聚乳酸因降解产生酸性小分子,会诱发无菌性炎症,导致产生过量纤维组织(1E),阻碍腱骨界面正常愈合。聚醚醚酮(PEEK)界面螺钉则面临无生物活性,因此开发出新型具有生物活性材料构建的前交叉韧带内固定器械极为重要。镁金属因具有良好的力学模量和生物相容性, 成为ACL重建中非常有前景的骨科植入物材料(1F)。

Figure 1. The limitations and drawbacks of the existing orthopaedic implants in ACL reconstruction. (A) Representative histological images showing the normal tendon-bone healing with bony ingrowth towards the interface structure of the fibrous tissue or fibrocartilage after reconstruction. (B) Representative histological images showing the healing failure between the tendon graft and bone after reconstruction. (C) Representative images of Ti, PLA, PEEK, and Mg based interference screws. (D) Representative radiographic images showing the bone tunnel enlargement in patients after ACL reconstruction with currently used metallic interference screws. (E) The degradation of PLA screws producing a significant amount of oligomers, resulting in aseptic inflammation around them, eventually leading to enlarged tendon-bone interface. (F) Summary of the Young's modulus and tensile yield strength of natural bone, FDA-approved polymers and metals in orthopaedics, along with Mg or its alloys.
此外,通过有限元模型(2A)比较了钛钉与镁钉周围骨组织中的应力分布。与钛组相比,镁组中螺钉周围骨组织表现出更高的最大应力和更大的应力分布(图2B),表明镁界面螺钉能够有效降低应力屏蔽效应,进而减少ACL 重建后骨隧道周围应力相关性骨质流失。

Fig. 2. Appropriate Young’s modulus of the Mg-based orthopaedic implants. (A) FEA model of the trabecular bone with insertion of an interference screw under 1000 N loading condition from the horizontal direction. The bone model is fixed by restricting all 6 degrees of freedom (DOF), while the interaction between the screw and bone is fixed using a binding constraint. (B) Compared to the Ti group in the FEA model, the Mg group exhibits higher von Mises stress distribution in the peri-screw bone tissue. Further, the maximum stress around the contacting bone along the force direction is 2227 MPa and 1670 MPa for the Mg and the Ti groups, respectively.
有文献报道镁离子可通过上调X型胶原和血管内皮生长因子(VEGF),显著增强骨髓间充质干细胞(BMSC)和成骨细胞的成骨分化能力(3A)。此外,有研究表明高纯镁界面螺钉释放的镁离子有利于转化生长因子-β1(TGF-β1)和血小板衍生生长因子 BB(PDGF-BB)的分泌,募集更多的BMSC参与腱骨界面愈合,最终促进腱骨界面处的血管生成和新骨长入(图3B)。

Fig. 3. Favorable osteopromotive functions of the Mg-based orthopaedic implants. (A) Higher extent of Mg ions can directly promote the osteogenic differentiation-related genes including BMP-2 and VEGF of BMSCs as well as osteoblasts via HIF-2α and PGC-1α-dependent mechanisms.(B) The released Mg ions from the Mg-based screws enhance the recruitment, adhesion and osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs, along with the secretion of PDGF-BB and TGF-β1, thereby, contributing to angiogenesis and osteogenesis in the tendon-bone interface, ultimately leading to the improved bone ingrowth towards the tendon graft.
人体组织环境复杂,无机离子(如 Ca 2+、Cl -、OH -、HPO 4 2-、H 2 PO 4 -、HCO 3-和 CO 3 2-)和有机分子(如葡萄糖、氨基酸和蛋白质)等均可参与镁界面螺钉降解产物的形成(5A)。因镁界面螺钉降解会导致其力学完整性受损,同时会伴随气体释放到周围组织并形成富集,故如何调控镁界面螺钉的降解行为也是影响其临床应用的主要因素(图 5B和5C)。因此,临床上可安全使用的镁界面螺钉必须具有合适的降解行为,匹配组织愈合,但不会在完全愈合之前完全失去其机械完整性(图5D)。
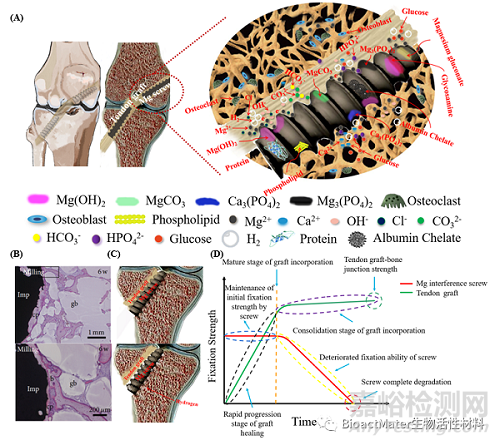
Figure 5. Challenges of Mg-based interference screws in clinical application. (A) The degradation behavior of the Mg-based interference screws in physiological condition involves the release of Mg ions, H2 evolution, and production of OH-, contributing to the formation of inorganic substances containing Mg(OH)2, MgCO3, Ca3 (PO4)2, and Mg3 (PO4)2 as well as organic products composed of magnesium gluconate, glycosamine, and albumin chelate. Importantly, the presence of amino acids, proteins, and lipids may alter the degradation rate of the Mg-based screws due to the deposition of the organic layers. (B) Representative histological images demonstrating the fast degradation of the Mg-based implants containing gas voids (b: bone, gb: gas voids, cp: corrosion product, square: area shown under high magnification in the below image). (C) Fast degradation of the Mg-based interference screws in vivo leading to poor fixation. (D) Illustration of desirable Mg-based interference screws with favorable degradation behavior to maintain their mechanical integrity for sufficient fixation during the graft healing process in ACL reconstruction.
除降解速率外,镁界面螺钉的抗扭矩性能不足也是影响临床应用的重要原因之一。通过有限元模拟证实:与钛界面螺钉相比,镁界面螺钉的最大扭矩降低了近7倍(6A)。图6B表明因接触部位的变形,致使螺丝刀和螺钉头之间滑丝,极易造成手术操作失败。因此,如何解决螺钉的实际扭矩与完全植入骨隧道所需克服的扭矩之间的差距问题(图6C),极其关键和重要(图6D)。

Figure 6. Challenges of Mg-based interference screws in clinical application. (A) In the model, a linear hexahedral type was used for the screwdriver with 340 elements, and the screw used the quadratic tetrahedral type to create 41002 elements. The tip of the screw (highlighted area) was clamped, whereas the screwdriver was rotated at a controlled rate of 0.2 rad/s, simulating the same boundary conditions as the experiment. The numerical torque over rotation angle curve for the pure Ti- and pure Mg-based interference screws. (B) The Mg interference screw is implanted into the bone tunnel due to insufficient torque, which causes the screw head to wear. (C) Schematic diagram of comparison between the torque required for the implantation of the Mg interference screw into the bone tunnel and the actual torque. (D) Unsatisfactory torque of the Mg-based interference screws results in surgical failure due to the damage in the screw head.
在过去的几十年里,人们做出了巨大的努力来克服与镁或其合金在骨科应用中的不当降解行为和机械性能不足相关的临床问题如合金化、表面改性及复合材料等策略。在本文中着重关注于开发出新型含镁界面螺钉的新策略,通过增加螺丝刀导通深度来提高螺钉头承受的最大扭矩(7A),以及将涂层镁棒插入在空心钛界面螺钉的组合系统调节镁离子释放速率以匹配骨愈合过程(7B)。为加速腱骨界面愈合,可考虑多孔界面螺钉(8B),以完成含祖细胞或生长因子的水凝胶微球的原位释放(8A),进而促进腱骨界面新生血管或骨的形成(8C和8D)。
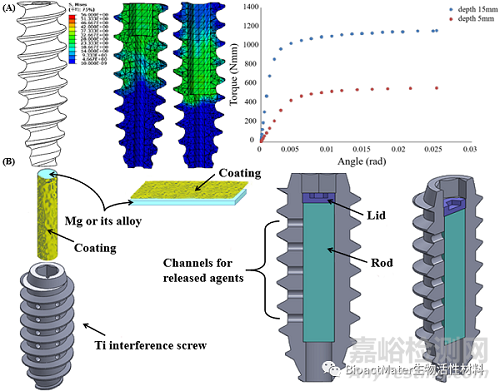
Figure 7. R&D strategies for the novel Mg-containing interference screws feasible for clinical applications. (A) Optimization of the structural design of the Mg-based interference screw by altering the drill insertion depth and pitch distance for improved maximal torque. (B) Mg/Ti hybrid fixators composed of Mg rod and Ti-based interference screw with holes in the screw body to allow the release of the Mg ions in the surrounding bone tissue, exerting favorable biological effects while overcoming the concerns associated with insufficient mechanical strength.
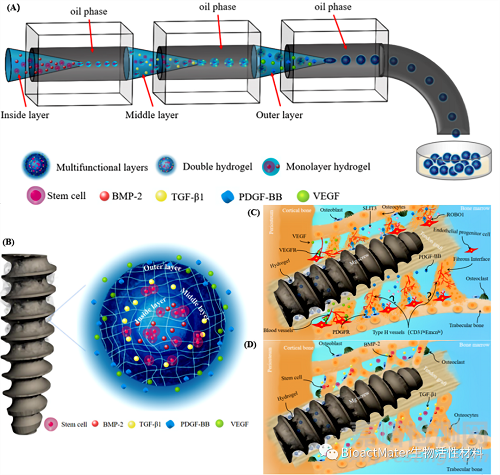
Figure 8. R&D of the Mg-based interference screws with holes to release hydrogel microparticles with multifunctional layers for enhancing tendon-bone healing. (A) Schematic diagram of multifluidic technology for preparation of multi-layered hydrogel microparticles (W/O/W/O/W). (B) The structure diagram of multifunctional hydrogel particles showing PDGF-BB and VEGF in the outer layer, TGF-β1 in the middle layer and stem cells and BMP-2 in the inner layer. (C) The injected hydrogels in the Mg-based interference screws further improve angiogenesis including type H vessels in the presence of PDGF-BB and VEGF released from the outer layer during the early healing stages. (D) TGF-β1, stem cells and BMP-2 released from the middle and inner layers of the hydrogel increase the number of stem cells involved in tendon-bone healing, along with promoting their osteogenic differentiation capability for bony ingrowth towards the tendon-bone interface during the later healing stage (VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor, PDGF-BB: platelet-derived growth factor-BB, TGF-β1: transforming growth factor-β1, and BMP-2: bone morphogenetic protein-2).
综上,新型可生物降解镁界面螺钉有望成为新一代 ACL 重建内固定器械。虽然扭矩性能和合适的降解行为是镁界面螺钉走向规模化临床试验的主要障碍,但合金化、表面改性、新型结构设计优化、组合器械的采用可有效部分解决上述担忧。此外,可注射含活性因子水凝胶的多孔镁界面螺钉将可能展示出更为出色的促血管/新骨形成的潜能,从而为临床改善腱-骨愈合提供新的治疗策略。

来源:BioactMater生物活性材料


